|
Kelvin Wave
A Kelvin wave is a wave in the ocean or atmosphere that balances the Earth's Coriolis force against a topographic boundary such as a coastline, or a waveguide such as the equator. A feature of a Kelvin wave is that it is non-dispersive, i.e., the phase speed of the wave crests is equal to the group speed of the wave energy for all frequencies. This means that it retains its shape as it moves in the alongshore direction over time. A Kelvin wave (fluid dynamics) is also a long scale perturbation mode of a vortex in superfluid dynamics; in terms of the meteorological or oceanographical derivation, one may assume that the meridional velocity component vanishes (i.e. there is no flow in the north–south direction, thus making the momentum and continuity equations much simpler). This wave is named after the discoverer, Lord Kelvin (1879). Coastal Kelvin wave In a stratified ocean of mean depth ''H'', perturbed by some amount ''η'', free waves propagate along coastal boundari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (resting) value at some frequency. When the entire waveform moves in one direction, it is said to be a ''traveling wave''; by contrast, a pair of superimposed periodic waves traveling in opposite directions makes a '' standing wave''. In a standing wave, the amplitude of vibration has nulls at some positions where the wave amplitude appears smaller or even zero. Waves are often described by a '' wave equation'' (standing wave field of two opposite waves) or a one-way wave equation for single wave propagation in a defined direction. Two types of waves are most commonly studied in classical physics. In a '' mechanical wave'', stress and strain fields oscillate about a mechanical equilibrium. A mechanical wave is a local deformation (str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Equations
The primitive equations are a set of nonlinear partial differential equations that are used to approximate global atmospheric flow and are used in most atmospheric models. They consist of three main sets of balance equations: # A ''continuity equation'': Representing the conservation of mass. # ''Conservation of momentum'': Consisting of a form of the Navier–Stokes equations that describe hydrodynamical flow on the surface of a sphere under the assumption that vertical motion is much smaller than horizontal motion (hydrostasis) and that the fluid layer depth is small compared to the radius of the sphere # A '' thermal energy equation'': Relating the overall temperature of the system to heat sources and sinks The primitive equations may be linearized to yield Laplace's tidal equations, an eigenvalue problem from which the analytical solution to the latitudinal structure of the flow may be determined. In general, nearly all forms of the primitive equations relate the five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which moves from east to west across the tropics, causing areas of cloudiness and thunderstorms. Tropical waves form in the easterly flow along the equatorial side of the subtropical ridge or belt of high air pressure which lies north and south of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ). Tropical waves are generally carried westward by the prevailing easterly winds along the tropics and subtropics near the equator. They can lead to the formation of tropical cyclones in the north Atlantic and northeastern Pacific basins. A tropical wave study is aided by Hovmöller diagrams, a graph of meteorological data. West-moving waves can also form from the tail end of frontal zones in the subtropics and tropics, and may be referred to as easterly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edge Wave
Edge or EDGE may refer to: Technology Computing * Edge computing, a network load-balancing system * Edge device, an entry point to a computer network * Adobe Edge, a graphical development application * Microsoft Edge, a web browser developed by Microsoft * EdgeHTML, the layout engine previously used in Microsoft Edge * ThinkPad Edge, a Lenovo laptop computer series marketed from 2010 * Silhouette edge, in computer graphics, a feature of a 3D body projected onto a 2D plane * Explicit data graph execution, a computer instruction set architecture Telecommunication(s) * Edge Wireless, an American mobile phone provider * Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution, a pre-3G digital mobile phone technology * Motorola Edge, a series of smartphones made by Motorola * Samsung Galaxy Note Edge, a phablet made by Samsung * Samsung Galaxy S7 Edge or Samsung Galaxy S6 Edge, smartphones made by Samsung * Ubuntu Edge, a prototype smartphone made by Canonical Entertainment Music * ''Edge'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin–Helmholtz Instability
The Kelvin–Helmholtz instability (after Lord Kelvin and Hermann von Helmholtz) is a fluid instability that occurs when there is velocity shear in a single continuous fluid or a velocity difference across the interface between two fluids. Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities are visible in the atmospheres of planets and moons, such as in cloud formations on Earth or the Red Spot on Jupiter, and the atmospheres of the Sun and other stars. Theory overview and mathematical concepts Fluid dynamics predicts the onset of instability and transition to turbulent flow within fluids of different densities moving at different speeds. If surface tension is ignored, two fluids in parallel motion with different velocities and densities yield an interface that is unstable to short-wavelength perturbations for all speeds. However, surface tension is able to stabilize the short wavelength instability up to a threshold velocity. If the density and velocity vary continuously in space ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Rossby Wave
Equatorial Rossby waves, often called planetary waves, are very long, low frequency water waves found near the equator and are derived using the equatorial beta plane approximation. Mathematics Using the equatorial beta plane approximation, f = \beta y, where ''β'' is the variation of the Coriolis parameter with latitude, \beta = \frac. With this approximation, the primitive equations become the following: * the continuity equation (accounting for the effects of horizontal convergence and divergence and written with geopotential height): ::\frac + c^2 \left ( \frac + \frac \right ) = 0 * the U-momentum equation (zonal component): ::\frac - v \beta y = -\frac * the V-momentum equation (meridional component): ::\frac + u \beta y = -\frac.Holton, James R., 2004: ''An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology.'' Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, MA, pp. 394–400. In order to fully linearize the primitive equations, one must assume the following solution: :: \beginu, v, \v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby-gravity Waves
Rossby-gravity waves are equatorially trapped waves (much like Kelvin waves), meaning that they rapidly decay as their distance increases away from the equator (so long as the Brunt–Vaisala frequency does not remain constant). These waves have the same trapping scale as Kelvin waves, more commonly known as the equatorial Rossby deformation radius.Gill, Adrian E., 1982: ''Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics,'' International Geophysics Series, Volume 30, Academic Press, 662 pp. They always carry energy eastward, but their 'crests' and 'troughs' may propagate westward if their periods are long enough. Derivation The eastward speed of propagation of these waves can be derived for an inviscid slowly moving layer of fluid of uniform depth H.Zhang, Dalin, 2008: Personal Communication, “Waves in Rotating, Homogeneous Fluids,” University of Maryland, College Park. Because the Coriolis parameter (''f'' = 2Ω sin(''θ'') where Ω is the angular velocity of the earth, 7.2921&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres and oceans of planets owing to the rotation of the planet. Atmospheric Rossby waves on Earth are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that have a major influence on weather. These waves are associated with pressure systems and the jet stream (especially around the polar vortices). Oceanic Rossby waves move along the thermocline: the boundary between the warm upper layer and the cold deeper part of the ocean. Rossby wave types Atmospheric waves Atmospheric Rossby waves result from the conservation of potential vorticity and are influenced by the Coriolis force and pressure gradient. The rotation causes fluids to turn to the right as they move in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. For example, a fluid that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
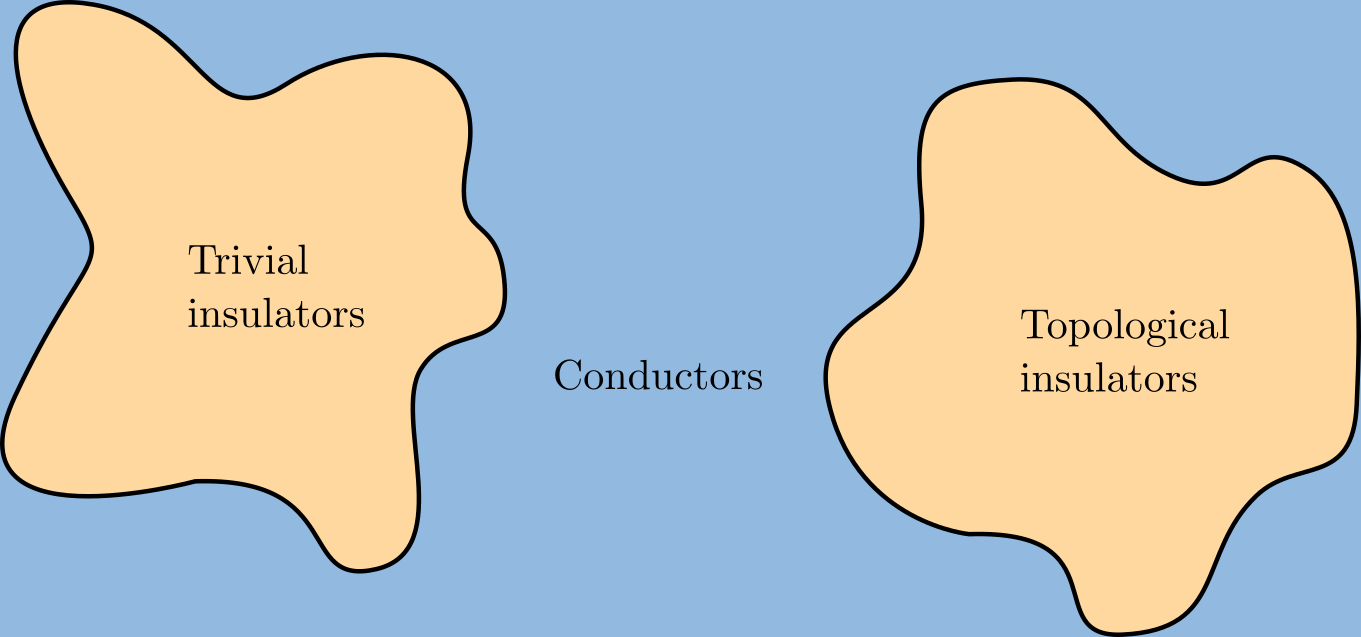
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a " trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Nino-Southern Oscillation
EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American politician * Ephrat Livni (born 1972), American street artist Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * El, short for Eleven, a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in '' Superman'' *E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film ''Road Trip'' Literature * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 2000 Japanese adult visual novel Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él'' (Lucero album), a 1982 album by Lucero * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from ''Caminando'' (album) * "Él" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroclinic
In fluid dynamics, the baroclinity (often called baroclinicity) of a stratified fluid is a measure of how misaligned the gradient of pressure is from the gradient of density in a fluid. In meteorology a baroclinic flow is one in which the density depends on both temperature and pressure (the fully general case). A simpler case, barotropic flow, allows for density dependence only on pressure, so that the curl of the pressure-gradient force vanishes. Baroclinity is proportional to: :\nabla p \times \nabla \rho which is proportional to the sine of the angle between surfaces of constant pressure and surfaces of constant density. Thus, in a ''barotropic'' fluid (which is defined by zero baroclinity), these surfaces are parallel. In Earth's atmosphere, barotropic flow is a better approximation in the tropics, where density surfaces and pressure surfaces are both nearly level, whereas in higher latitudes the flow is more baroclinic. These midlatitude belts of high atmospheric b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Plane
In geophysical fluid dynamics, an approximation whereby the Coriolis parameter, ''f'', is set to vary linearly in space is called a beta plane approximation. On a rotating sphere such as the Earth, ''f'' varies with the sine of latitude; in the so-called f-plane approximation, this variation is ignored, and a value of ''f'' appropriate for a particular latitude is used throughout the domain. This approximation can be visualized as a tangent plane touching the surface of the sphere at this latitude. A more accurate model is a linear Taylor series approximation to this variability about a given latitude \phi_0: f = f_0 + \beta y, where f_0 is the Coriolis parameter at \phi_0, \beta = (\mathrmf/\mathrmy), _ = 2\Omega\cos(\phi_0)/a is the Rossby parameter, y is the meridional distance from \phi_0, \Omega is the angular rotation rate of the Earth, and a is the Earth's radius. In analogy with the f-plane, this approximation is termed the beta plane, even though it no longer describes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |