|
Katholikos Krites
The ''kritai katholikoi tōn Rhomaiōn'' ( el, κριταὶ καθολικοὶ τῶν Ῥωμαίων, "universal judges of the Romans") were a supreme court during the late Byzantine Empire. History The court had its antecedent in a tribunal of 12 judges, composed of both secular (senatorial) judges and of ecclesiastical members, created by Andronikos II Palaiologos () in 1296. It functioned as a supreme court, and there was no appeal from its decisions. The tribunal was reduced to four members, at least one of whom had to be a bishop, by Andronikos III Palaiologos () in 1329, and received the name "''kritai katholikoi''". According to Manuel II Palaiologos (), they had authority over all matters; received only written complaints; conducted the hearings, including expert testimony where deemed necessary; and deliberated in seclusion, with the judgement resulting from the majority of opinions. The first four judges were Joseph, Bishop of Apros, Gregory Kleidas, an archdeacon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomaioi
The Greeks ( el, Έλληνες) have been identified by many ethnonyms. The most common native ethnonym is ''Hellen'' ( grc, Ἕλλην), pl. '' Hellenes'' (); the name ''Greeks'' ( la, Graeci) was used by the ancient Romans and gradually entered the European languages through its use in Latin. The mythological patriarch '' Hellen'' is the named progenitor of the Greek peoples; his descendants the Aeolians, Dorians, Achaeans and Ionians correspond to the main Greek tribes and to the main dialects spoken in Greece and Asia Minor (Anatolia). The first Greek-speaking people, called Myceneans or Mycenean-Achaeans by historians, entered present-day Greece sometime in the Neolithic era or the Bronze Age. Homer refers to " Achaeans" as the dominant tribe during the Trojan War period usually dated to the 12th–11th centuries BC, using ''Hellenes'' to describe a relatively small tribe in Thessaly. The Dorians, an important Greek-speaking group, appeared roughly at that time. Acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
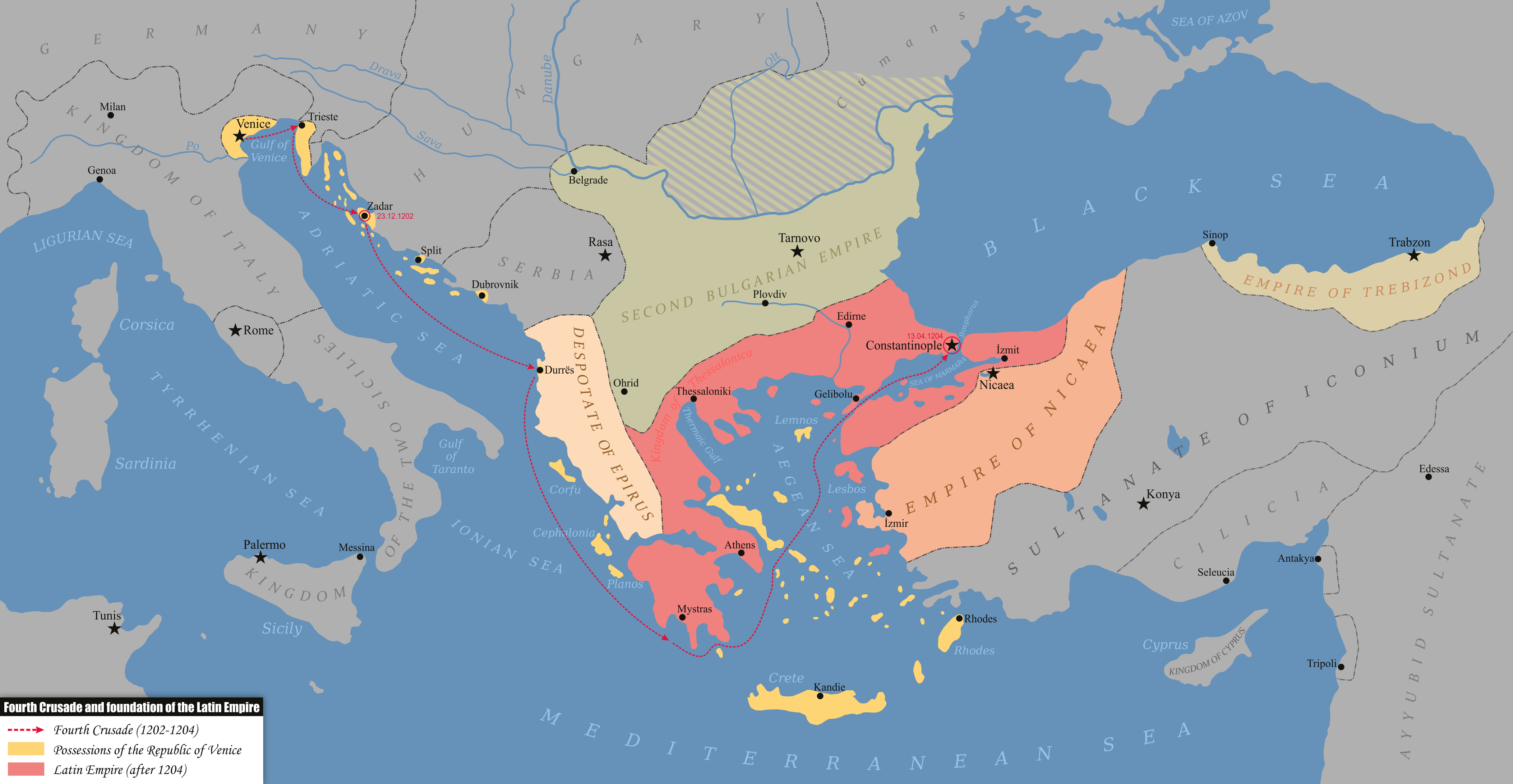
Despotate Of The Morea
The Despotate of the Morea ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μορέως) or Despotate of Mystras ( el, Δεσποτᾶτον τοῦ Μυστρᾶ) was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centuries. Its territory varied in size during its existence but eventually grew to include almost all the southern Greek peninsula now known as the Peloponnese, which was known as the Morea during the medieval and early modern periods. The territory was usually ruled by one or more sons of the current Byzantine emperor, who were given the title of ''despotes'' (in this context it should not be confused with despotism). Its capital was the fortified city of Mystras, near ancient Sparta, which became an important centre of the Palaiologan Renaissance. History The Despotate of the Morea was created out of territory seized from the Frankish Principality of Achaea. This had been organized from former Byzantine territory after the Fourth Crus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribunals
A tribunal, generally, is any person or institution with authority to judge, adjudicate on, or determine claims or disputes—whether or not it is called a tribunal in its title. For example, an advocate who appears before a court with a single judge could describe that judge as "their tribunal." Many governmental bodies that are titled as "tribunals" are described so in order to emphasize that they are not courts of normal jurisdiction. For example, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda was a body specially constituted under international law; in Great Britain, employment tribunals are bodies set up to hear specific employment disputes. In many (but not all) cases, the word ''tribunal'' implies a judicial (or quasi-judicial) body with a lesser degree of formality than a court, in which the normal rules of evidence and procedure may not apply, and whose presiding officers are frequently neither judges, nor magistrates. Private judicial bodies are also often styled " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Judicial Offices
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1329 Establishments In Europe
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number), the natural number following 12 and preceding 14 * One of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, 2013 Music * 13AD (band), an Indian classic and hard rock band Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Harmenopoulos
Constantine Harmenopoulos ( el, ; 1320 – ) was a Byzantine jurist from Greece who held the post of '' katholikos kritēs'' ("universal judge") of Thessalonica, one of the highest judicial offices in the Byzantine Empire. He is best known for his ''Hexabiblos'' (1344–1345), a law book in six volumes in which he compiles a wide range of Byzantine legal sources. First printed 1540 in Paris, the ''Hexabiblos'' was widely adopted in the Balkans under the Ottoman Empire. In 1828, it was also adopted as the interim civil code in the newly independent Greek state Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with .... References * * Foundation of the Hellenic World, History of the late Byzantine PeriodThe Hexabiblos accessed January 2007 * External links *Manuale legum sive Hexabiblos c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Law
Byzantine law was essentially a continuation of Roman law with increased Orthodox Christian and Hellenistic influence. Most sources define ''Byzantine law'' as the Roman legal traditions starting after the reign of Justinian I in the 6th century and ending with the Fall of Constantinople in the 15th century. Although future Byzantine codes and constitutions derived largely from Justinian's ''Corpus Juris Civilis'', their main objectives were idealistic and ceremonial rather than practical. Following Hellenistic and Near-Eastern political systems, legislations were tools to idealize and display the sacred role and responsibility of the emperor as the holy monarch chosen by God and the incarnation of law "'' nómos émpsychos"'', thus having philosophical and religious purposes that idealized the perfect Byzantine king. Though during and after the European Renaissance Western legal practices were heavily influenced by ''Justinian's Code'' (the ''Corpus Juris Civilis'') and Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to the 15th century, consisting of the far northeastern corner of Anatolia (the Pontus) and the southern Crimea. The empire was formed in 1204 with the help of the Georgian queen Tamar after the Georgian expedition in Chaldia and Paphlagonia, commanded by Alexios Komnenos a few weeks before the sack of Constantinople. Alexios later declared himself Emperor and established himself in Trebizond (modern day Trabzon, Turkey). Alexios and David Komnenos, grandsons and last male descendants of deposed Emperor Andronikos I Komnenos, pressed their claims as "Roman emperors" against Byzantine Emperor Alexios V Doukas. The later Byzantine emperors, as well as Byzantine authors, such as George Pachymeres, Nicephorus Gregoras and to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Empire
The Serbian Empire ( sr, / , ) was a medieval Serbian state that emerged from the Kingdom of Serbia. It was established in 1346 by Dušan the Mighty, who significantly expanded the state. Under Dušan's rule, Serbia was the major power in the Balkans and a multi-lingual empire that stretched from the Danube to the Gulf of Corinth, with its capital in Skopje. He also promoted the Serbian Archbishopric to the Serbian Patriarchate. His son and successor, Uroš the Weak, lost most of the territory conquered by Dušan, hence his epithet. The Serbian Empire effectively ended with the death of Uroš V in 1371 and the break-up of the Serbian state. Some successors of Stefan V claimed the title of Emperor in parts of Serbia until 1402, but the territory in Greece was never recovered. History Establishment Stefan Dušan was the son of the Serbian king Stefan Dečanski (r. 1322–1331). After his father's accession to the throne, Dušan was awarded with the title of "young king". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemnos
Lemnos or Limnos ( el, Λήμνος; grc, Λῆμνος) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean region. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina. At , it is the 8th-largest island of Greece. Geography Lemnos is mostly flat, but the west, and especially the northwest part, is rough and mountainous. The highest point is Mount Skopia at the altitude of 430 m. The chief towns are Myrina, on the western coast, and Moudros on the eastern shore of a large bay in the middle of the island. Myrina (also called Kastro, meaning "castle") possesses a good harbour. It is the seat of all trade carried on with the mainland. The hillsides afford pasture for sheep, and Lemnos has a strong husbandry tradition, being famous for its Kalathaki Limnou ( PDO), a cheese made from sheep and goat milk and melipasto cheese, and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of Macedonia, the administrative region of Central Macedonia and the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace. It is also known in Greek as (), literally "the co-capital", a reference to its historical status as the () or "co-reigning" city of the Byzantine Empire alongside Constantinople. Thessaloniki is located on the Thermaic Gulf, at the northwest corner of the Aegean Sea. It is bounded on the west by the delta of the Axios. The municipality of Thessaloniki, the historical center, had a population of 317,778 in 2021, while the Thessaloniki metropolitan area had 1,091,424 inhabitants in 2021. It is Greece's second major economic, industrial, commercial and political centre, and a major transportation hub for Greece and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis ( Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |