|
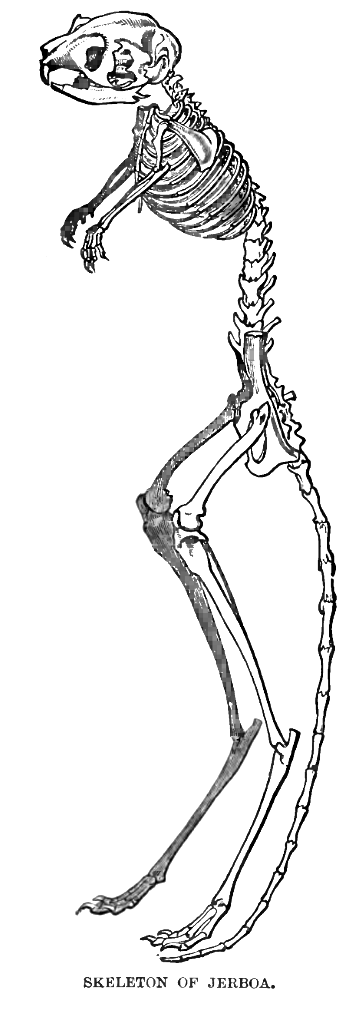
Jerboa
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allactaga Tetradactyla
The four-toed jerboa (''Allactaga tetradactyla'') is a rodent of the family Dipodidae and genus '' Allactaga'' that has four digits. It is the sole species in the subgenus ''Scarturus''. Four-toed jerboas are native to Egypt and Libya. They live in coastal salt marshes and dry deserts. Physical appearance Similar to the other jerboas in the genus '' Allactaga'', the four-toed jerboa are small hopping rodents with large ears and a long tail, with a black band near the white, feathery tip. The tail assists and serves as support when the jerboa is standing upright. They have long hind feet and short forelegs. The pelt of the four-toed jerboa is velvety in texture and the upper-parts are speckled black and orange, the rump orange, and the sides gray. The four-toed jerboa hind-limbs have an extra digit compared to other jerboas in the genus '' Allactaga''. The extra digit is smaller in size and nonfunctional compared to the other three digits. Nutrition Emerging at night, the four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zapodidae
Zapodidae, the jumping mice, is a family of mouse-like rodents in North America and China. Although mouse-like in general appearance, these rodents are distinguished by their elongated hind limbs, and, typically, by the presence of four pairs of cheek-teeth in each jaw. There are five toes to all the feet, but the first in the fore-feet is rudimentary, and furnished with a flat nail. The tail makes up about 60% of its body length and is used to gain balance while jumping. The cheeks have pouches. The Sichuan jumping "yeti" mouse (''Eozapus setchuanus'') from China can be identified by the ‘Y’ marking on its belly. Jumping mice live in wooded areas, grassy fields and alpine meadows. When disturbed, they start, in enormous bounds of eight or ten feet in length, which soon diminish to three or four, and in leaping the feet scarcely seem to touch the ground. They are nocturnal and generally live alone. The nest is placed in clefts of rocks, among timber, or in hollow trees, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sminthidae
Sminthidae is a family of mouse-like jumping rodents. They are represented by only one extant genus, ''Sicista'', represented by 19 species found throughout most of Eurasia, from central Europe east to Siberia, and south to southern China. However, they were much more diverse and had a much wider range in prehistoric times, having multiple genera and being found not only in Eurasia but also throughout North America, where they existed up to the early Pleistocene. They have a well-attested fossil record which dates as far back as the early Oligocene. They were formerly classified as the subfamily Sicistinae in the family Dipodidae alongside the jerboas and jumping mice, but phylogenetic evidence supports all three of these belonging to distinct families, thus leaving only the jerboas in Dipodidae. Extant species * Genus ''Sicista'' ** Armenian birch mouse ''Sicista armenica'' ** Northern birch mouse, ''Sicista betulina'' ** Caucasian birch mouse, ''Sicista caucasica'' ** Long-ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust Bathing
Dust bathing (also called sand bathing) is an animal behavior characterized by rolling or moving around in dust, dry earth or sand, with the likely purpose of removing parasites from fur, feathers or skin. Dust bathing is a maintenance behavior performed by a wide range of mammalian and avian species. For some animals, dust baths are necessary to maintain healthy feathers, skin, or fur, similar to bathing in water or wallowing in mud. In some mammals, dust bathing may be a way of transmitting chemical signals (or pheromones) to the ground which marks an individual's territory. Birds Birds cower close to the ground while taking a dust bath, vigorously wriggling their bodies and flapping their wings. This disperses loose substrate into the air. The birds spread one or both wings which allows the falling substrate to fall between the feathers and reach the skin. The dust bath is often followed by thorough shaking to further ruffle the feathers which may be accompanied with p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euchoreutinae
The long-eared jerboa (''Euchoreutes naso'') is a nocturnal mouse-like rodent with a long tail, long hind legs for jumping, and exceptionally large ears. It is distinct enough that authorities consider it to be the only member of both its genus, ''Euchoreutes'', and subfamily, Euchoreutinae. Long-eared jerboas are found in the Palearctic ecozone. The specific palearctic ecozone areas they are found in are southernmost Mongolia to the Takla-Makan Desert, Mengxin, Aerijin Mountain, and Qing-Zang Plateau regions of north western China. Long-eared jerboas in most cases are nocturnal, The long-eared jerboa's fur according to the book ''100 animals to see before they die'' "is reddish yellow to pale russet with white underparts." Very little is known about the species. Description The long-eared jerboa's head and body length measures to while its tail is double this size, between and . Like its disproportionately long tail, its hind feet are also large, helping it to jump high, me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipodinae
Dipodinae is a subfamily of Dipodidae. Classification Subfamily Dipodinae *Tribe Dipodini **Genus ''Dipus'' *** Northern three-toed jerboa, ''Dipus sagitta'' **Genus ''Eremodipus'' ***Lichtenstein's jerboa, ''Eremodipus lichtensteini'' **Genus '' Jaculus'' ***Blanford's jerboa, ''Jaculus blanfordi'' ***Lesser Egyptian jerboa, ''Jaculus jaculus'' ***Greater Egyptian jerboa, ''Jaculus orientalis'' *** Thaler's jerboa, ''Jaculus thaleri'' **Genus ''Stylodipus'', three-toed Jerboas ***Andrews's three-toed jerboa, ''Stylodipus andrewsi'' ***Mongolian three-toed jerboa, ''Stylodipus sungorus'' ***Thick-tailed three-toed jerboa, ''Stylodipus telum'' *Tribe Paradipodini **Genus ''Paradipus'' ***Comb-toed jerboa The comb-toed jerboa (''Paradipus ctenodactylus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Paradipus''. It is found in Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic ..., ''Paradipus ctenodactylus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygyny
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women. Incidence Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any other continent. Some scholars see the slave trade's impact on the male-to-female sex ratio as a key factor in the emergence and fortification of polygynous practices in regions of Africa. Polygyny is most common in a region known as the "polygamy belt" in West Africa and Central Africa, with the countries estimated to have the highest polygamy prevalence in the world being Burkina Faso, Mali, Gambia, Niger and Nigeria. In the region of sub-Saharan Africa, polygyny is common and deeply rooted in the culture, with 11% of the population of sub-Saharan Africa living in such marriages (25% of the Muslim population and 3% of the Christian population, as of 2019). Polygyny is especially widespread in West Africa, with the countries estimated to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptic Colouration
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the bioluminescence, ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chamel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerbillinae
Gerbillinae is one of the subfamilies of the rodent family Muridae and includes the gerbils, jirds, and sand rats. Once known as desert rats, the subfamily includes about 110 species of African, Indian, and Asian rodents, including sand rats and jirds, all of which are adapted to arid habitats. Most are primarily active during the day, making them diurnal (but some species, including the common household pet, exhibit crepuscular behavior), and almost all are omnivorous. The gerbil got its name as a diminutive form of "jerboa," an unrelated group of rodents occupying a similar ecological niche. Gerbils are typically between long, including the tail, which makes up about half of their total length. One species, the great gerbil (''Rhombomys opimus''), originally native to Turkmenistan, can grow to more than . The average adult gerbil weighs about . One species, the Mongolian gerbil ('' Meriones unguiculatus''), also known as the ''clawed jird'', is a gentle and hardy animal th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiocranius
The five-toed pygmy jerboa (''Cardiocranius paradoxus'') is a species of rodent in the family Dipodidae. It is monotypic within the genus ''Cardiocranius''. It is found in China, Kazakhstan, and Mongolia. Its natural habitat is temperate desert A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on .... This species is not well known and its population and conservation status are unresolved. References ;Notes ;Sources * Dipodidae Rodents of China Mammals of Central Asia Mammals of Mongolia Mammals described in 1903 Taxa named by Konstantin Satunin Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{rodent-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |