|
Intraventricular Haemorrhage
Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), also known as intraventricular bleeding, is a bleeding into the brain's ventricular system, where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulates through towards the subarachnoid space. It can result from physical trauma or from hemorrhagic stroke. 30% of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) are primary, confined to the ventricular system and typically caused by intraventricular trauma, aneurysm, vascular malformations, or tumors, particularly of the choroid plexus. However 70% of IVH are secondary in nature, resulting from an expansion of an existing intraparenchymal or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Intraventricular hemorrhage has been found to occur in 35% of moderate to severe traumatic brain injuries. Thus the hemorrhage usually does not occur without extensive associated damage, and so the outcome is rarely good.Dawodu S. 2007"Traumatic Brain Injury: Definition, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology"Emedicine.com. Retrieved on June 19, 2007.Vinas FC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased intracranial pressure, pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and Parinaud's syndrome, downward pointing of the eyes. Hydrocephalus can occur due to birth defects or be acquired later in life. Associated birth defects include neural tube defects and those that result in aqueductal stenosis. Other causes include meningitis, brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. The four types of hydrocephalus are communicating, noncommunicating, ''ex vacuo'', and normal pressure hydrocephalus, normal pressure. Diagnosis is typically made by physical examination and medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
Cerebral hypoxia is a form of hypoxia (reduced supply of oxygen), specifically involving the brain; when the brain is completely deprived of oxygen, it is called ''cerebral anoxia''. There are four categories of cerebral hypoxia; they are, in order of increasing severity: diffuse cerebral hypoxia (DCH), focal cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and global cerebral ischemia. Prolonged hypoxia induces neuronal cell death via apoptosis, resulting in a hypoxic brain injury. Cases of total oxygen deprivation are termed "anoxia", which can be hypoxic in origin (reduced oxygen availability) or ischemic in origin (oxygen deprivation due to a disruption in blood flow). Brain injury as a result of oxygen deprivation either due to hypoxic or anoxic mechanisms are generally termed hypoxic/anoxic injuries (HAI). Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a condition that occurs when the entire brain is deprived of an adequate oxygen supply, but the deprivation is not total. While HIE is as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Communicating Artery
In human anatomy, the anterior communicating artery is a blood vessel of the brain that connects the left and right anterior cerebral arteries. Anatomy The anterior communicating artery connects the two anterior cerebral arteries across the commencement of the longitudinal fissure. Sometimes this vessel is wanting, the two arteries joining to form a single trunk, which afterward divides; or it may be wholly, or partially, divided into two. Its length averages about 4 mm, but varies greatly. It gives off some of the anteromedial ganglionic vessels, but these are principally derived from the anterior cerebral artery. It is part of the cerebral arterial circle, also known as the circle of Willis. Physiology Anatomical variations of the anterior communicating artery are relatively common. The artery is sometimes duplicated, multiplicated, fenestrated ("net-like") or very short, giving the impression that two anterior cerebral arteries are fused at the point where the anterior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain. Symptoms may include a severe headache of rapid onset, vomiting, decreased level of consciousness, fever, and sometimes seizures. Neck stiffness or neck pain are also relatively common. In about a quarter of people a small bleed with resolving symptoms occurs within a month of a larger bleed. SAH may occur as a result of a head injury or spontaneously, usually from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm. Risk factors for spontaneous cases include high blood pressure, smoking, family history, alcoholism, and cocaine use. Generally, the diagnosis can be determined by a CT scan of the head if done within six hours of symptom onset. Occasionally, a lumbar puncture is also required. After confirmation further tests are usually performed to determine the underlying cause. Treatment is by prompt neurosurgery or endovascular coiling. Medicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Contusion
Cerebral contusion, Latin ''contusio cerebri'', a form of traumatic brain injury, is a bruise of the brain tissue. Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head injuries. A cerebral laceration is a similar injury except that, according to their respective definitions, the pia-arachnoid membranes are torn over the site of injury in laceration and are not torn in contusion. The injury can cause a decline in mental function in the long term and in the emergency setting may result in brain herniation, a life-threatening condition in which parts of the brain are squeezed past parts of the skull. Thus treatment aims to prevent dangerous rises in intracranial pressure, the pressure within the skull. Contusions are likely to heal on their own without medical intervention. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of a cerebral contusion depend on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Herniation
Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the tentorium cerebelli, and even through the foramen magnum (the hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord connects with the brain). Herniation can be caused by a number of factors that cause a mass effect and increase intracranial pressure (ICP): these include traumatic brain injury, intracranial hemorrhage, or brain tumor. Herniation can also occur in the absence of high ICP when mass lesions such as hematomas occur at the borders of brain compartments. In such cases local pressure is increased at the place where the herniation occurs, but this pressure is not transmitted to the rest of the brain, and therefore does not register as an increase in ICP. Because herniation puts extreme pressure on parts of the brain and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high blood pressure, however, is a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to nonspecific lifestyle and genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, excess body weight, smoking, and alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary high blood pressure, defined as high blood pressure due to an identifiable cause, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into Intraparenchymal hemorrhage, the tissues of the brain, into its Intraventricular hemorrhage, ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stroke. Symptoms can include headache, Hemiparesis, one-sided weakness, vomiting, seizures, decreased level of consciousness, and neck stiffness. Often, symptoms get worse over time. Fever is also common. Causes include brain trauma, Intracranial aneurysm, aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and brain tumors. The biggest risk factors for spontaneous bleeding are high blood pressure and amyloidosis. Other risk factors include alcoholism, low cholesterol, blood thinners, and cocaine use. Diagnosis is typically by CT scan. Other conditions that may present similarly include ischemic stroke. Treatment should typically be carried out in an intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, and speaking. Often, babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl or walk as early as other children of their age. Other symptoms include seizures and problems with thinking or reasoning, which each occur in about one-third of people with CP. While symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, underlying problems do not worsen over time. Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often, the problems occur during pregnancy, but they may also occur during childbirth or shortly after birth. Often, the cause is unknown. Risk factors include preterm birth, being a twin, certain infections during pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
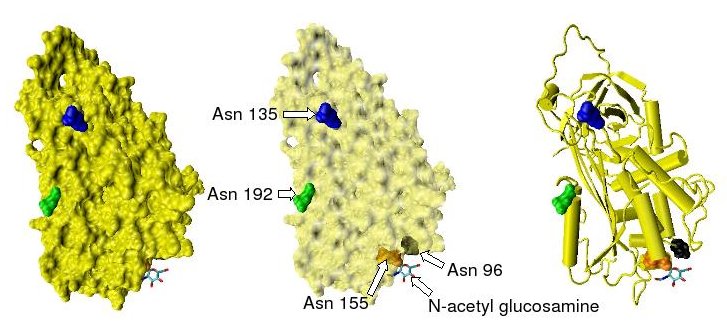
Antithrombin
Antithrombin (AT) is a small glycoprotein that inactivates several enzymes of the coagulation system. It is a 432-amino-acid protein produced by the liver. It contains three disulfide bonds and a total of four possible glycosylation sites. α-Antithrombin is the dominant form of antithrombin found in blood plasma and has an oligosaccharide occupying each of its four glycosylation sites. A single glycosylation site remains consistently un-occupied in the minor form of antithrombin, β-antithrombin. Its activity is increased manyfold by the anticoagulant drug heparin, which enhances the binding of antithrombin to factor IIa (prothrombin) and factor Xa. Nomenclature Antithrombin is also termed antithrombin III (AT III). The designations antithrombin I through to antithrombin IV originate in early studies carried out in the 1950s by Seegers, Johnson and Fell. Antithrombin I (AT I) refers to the absorption of thrombin onto fibrin after thrombin has activated fibrinogen. Antithro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraventricular Hemorrhage Grade I
Germinal matrix hemorrhage is a bleeding into the subependymal germinal matrix with or without subsequent rupture into the lateral ventricle. Such intraventricular hemorrhage can occur due to perinatal asphyxia in preterm neonates. Presentation This may lead to various neurological sequelae including presentation with cerebral palsy, mental retardation and seizures. Pathophysiology The germinal matrix is the site of proliferating neuronal and glial precursors in the developing brain, which is located above the caudate nucleus, in the floor of the lateral ventricle, and caudothalamic groove. The germinal matrix contains a rich network of fragile thin-walled blood vessels. Hence the microcirculation in this particular area is extremely sensitive to hypoxia and changes in perfusion pressure. It is most frequent before 35 weeks gestation and is typically seen in very low birth-weight (<1500g) |