|
Innate Releasing Mechanism
A fixed action pattern is an ethological term describing an instinctive behavioral sequence that is highly stereotyped and species-characteristic. Fixed action patterns are said to be produced by the innate releasing mechanism, a "hard-wired" neural network, in response to a sign/key stimulus or releaser. Once released, a fixed action pattern runs to completion. This term is often associated with Konrad Lorenz, who is the founder of the concept. Lorenz identified six characteristics of fixed action patterns. These characteristics state that fixed action patterns are stereotyped, complex, species-characteristic, released, triggered, and independent of experience. Fixed action patterns have been observed in many species, but most notably in fish and birds. Classic studies by Konrad Lorenz and Niko Tinbergen involve male stickleback mating behavior and greylag goose egg-retrieval behavior.Tinbergen, N. (1952). The curious behavior of sticklebacks. ''Scientific American'', 6, 22–26 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethology
Ethology is the scientific study of animal behaviour, usually with a focus on behaviour under natural conditions, and viewing behaviour as an evolutionarily adaptive trait. Behaviourism as a term also describes the scientific and objective study of animal behaviour, usually referring to measured responses to stimuli or to trained behavioural responses in a laboratory context, without a particular emphasis on evolutionary adaptivity. Throughout history, different naturalists have studied aspects of animal behaviour. Ethology has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th century, including Charles O. Whitman, Oskar Heinroth, and Wallace Craig. The modern discipline of ethology is generally considered to have begun during the 1930s with the work of Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, the three recipients of the 1973 Nobel Prize in Phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Releasing Mechanism
A fixed action pattern is an ethological term describing an instinctive behavioral sequence that is highly stereotyped and species-characteristic. Fixed action patterns are said to be produced by the innate releasing mechanism, a "hard-wired" neural network, in response to a sign/key stimulus or releaser. Once released, a fixed action pattern runs to completion. This term is often associated with Konrad Lorenz, who is the founder of the concept. Lorenz identified six characteristics of fixed action patterns. These characteristics state that fixed action patterns are stereotyped, complex, species-characteristic, released, triggered, and independent of experience. Fixed action patterns have been observed in many species, but most notably in fish and birds. Classic studies by Konrad Lorenz and Niko Tinbergen involve male stickleback mating behavior and greylag goose egg-retrieval behavior.Tinbergen, N. (1952). The curious behavior of sticklebacks. ''Scientific American'', 6, 22–26 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Alcock (behavioral Ecologist)
John Alcock (; born November 13, 1942) is an American behavioral ecologist and author. He is currently the Emeritus' Professor in the School of Life Sciences at Arizona State University. His research interests include the evolution of diversity in insect populations, studying the adaptive value of different ways in which males find mating partners. He has authored several books, including ''The Kookaburras' Song: Exploring Animal Behavior in Australia'' (1988), ''Sonoran Desert Summer'' (1990), ''The Triumph of Sociobiology'' (2003), and ''Animal Behavior: An Evolutionary Approach'' (tenth edition, 2013). He authored ''Sonoran Desert Spring'' (1994) which was illustrated by Marilyn Hoff Stewart, and also authored ''In a Desert Garden: Love and Death Among the Insects'' (1999) illustrated by Turid Forsyth. Alcock is one of the original scientists to participate in the Ask A Biologist program and continues to participate in interviews as well as answering questions from students ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Cuckoo
The common cuckoo (''Cuculus canorus'') is a member of the cuckoo order of birds, Cuculiformes, which includes the roadrunners, the anis and the coucals. This species is a widespread summer migrant to Europe and Asia, and winters in Africa. It is a brood parasite, which means it lays eggs in the nests of other bird species, particularly of dunnocks, meadow pipits, and reed warblers. Although its eggs are larger than those of its hosts, the eggs in each type of host nest resemble the host's eggs. The adult too is a mimic, in its case of the sparrowhawk; since that species is a predator, the mimicry gives the female time to lay her eggs without being attacked. Taxonomy The species' binomial name is derived from the Latin ''cuculus'' (the cuckoo) and ''canorus'' (melodious; from ''canere'', meaning to sing). The cuckoo family gets its common name and genus name by onomatopoeia for the call of the male common cuckoo. The English word "cuckoo" comes from the Old French ''cucu'', an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Parasite
Brood parasites are animals that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's. The evolutionary strategy relieves the parasitic parents from the investment of rearing young. This benefit comes at the cost of provoking an evolutionary arms race between parasite and host as they coevolve: many hosts have developed strong defenses against brood parasitism, such as recognizing and ejecting parasitic eggs, or abandoning parasitized nests and starting over. It is less obvious why most hosts do care for parasite nestlings, given that for example cuckoo chicks differ markedly from host chicks in size and appearance. One explanation, the mafia hypothesis, proposes that parasitic adults retaliate by destroying host nests where rejection has occurred; there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
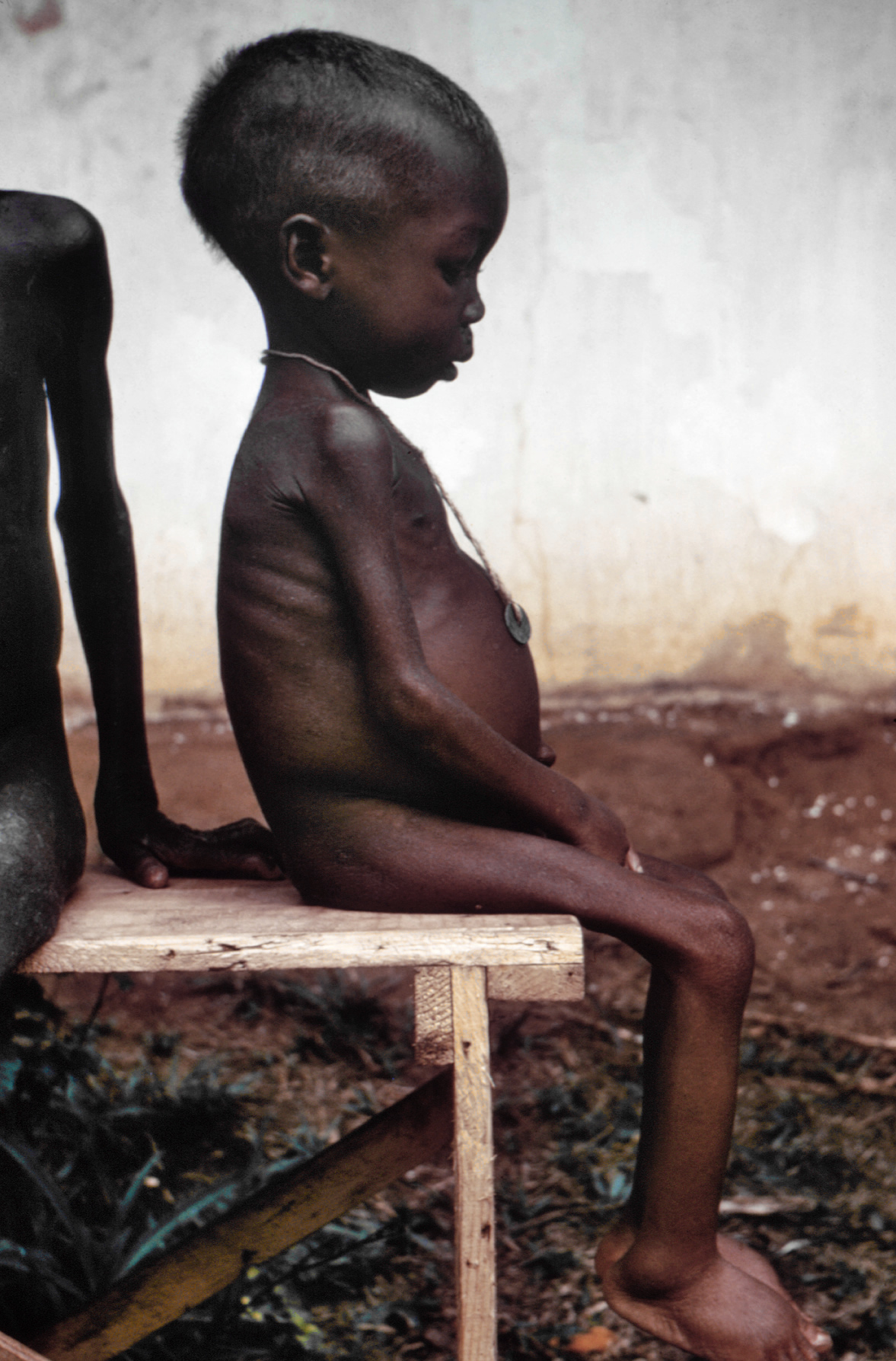
Starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, death. The term ''inanition'' refers to the symptoms and effects of starvation. Starvation may also be used as a means of torture or execution. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), hunger is the single gravest threat to the world's public health.Malnutrition The Starvelings The WHO also states that is by far the biggest contributor to [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Cowbird
Cowbirds are birds belonging to the genus ''Molothrus'' in the family Icteridae. They are of New World origin, and are obligate brood parasites, laying their eggs in the nests of other species. The genus was introduced by English naturalist William John Swainson in 1832 with the brown-headed cowbird (''Molothrus ater'') as the type species. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek , meaning "struggle" or "battle", with , meaning "to sire" or "to impregnate". Species The genus contains six species: One extinct species, the Talara cowbird (''Molothrus resinosus''), is known from fossil remains recovered from the Talara Tar Seeps of northwestern Peru, and likely went extinct during the late Quaternary. It may have been a close associate of Pleistocene megafauna communities, and may have gone extinct following their collapse in populations. The nonparasitic baywings were formerly placed in this genus; they are now classified as ''Agelaioides''. Behavior Cowbirds are insectivo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Parasitism
Brood parasites are animals that rely on others to raise their young. The strategy appears among birds, insects and fish. The brood parasite manipulates a host, either of the same or of another species, to raise its young as if it were its own, usually using egg mimicry, with eggs that resemble the host's. The evolutionary strategy relieves the parasitic parents from the investment of rearing young. This benefit comes at the cost of provoking an evolutionary arms race between parasite and host as they coevolve: many hosts have developed strong defenses against brood parasitism, such as recognizing and ejecting parasitic eggs, or abandoning parasitized nests and starting over. It is less obvious why most hosts do care for parasite nestlings, given that for example cuckoo chicks differ markedly from host chicks in size and appearance. One explanation, the mafia hypothesis, proposes that parasitic adults retaliate by destroying host nests where rejection has occurred; there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
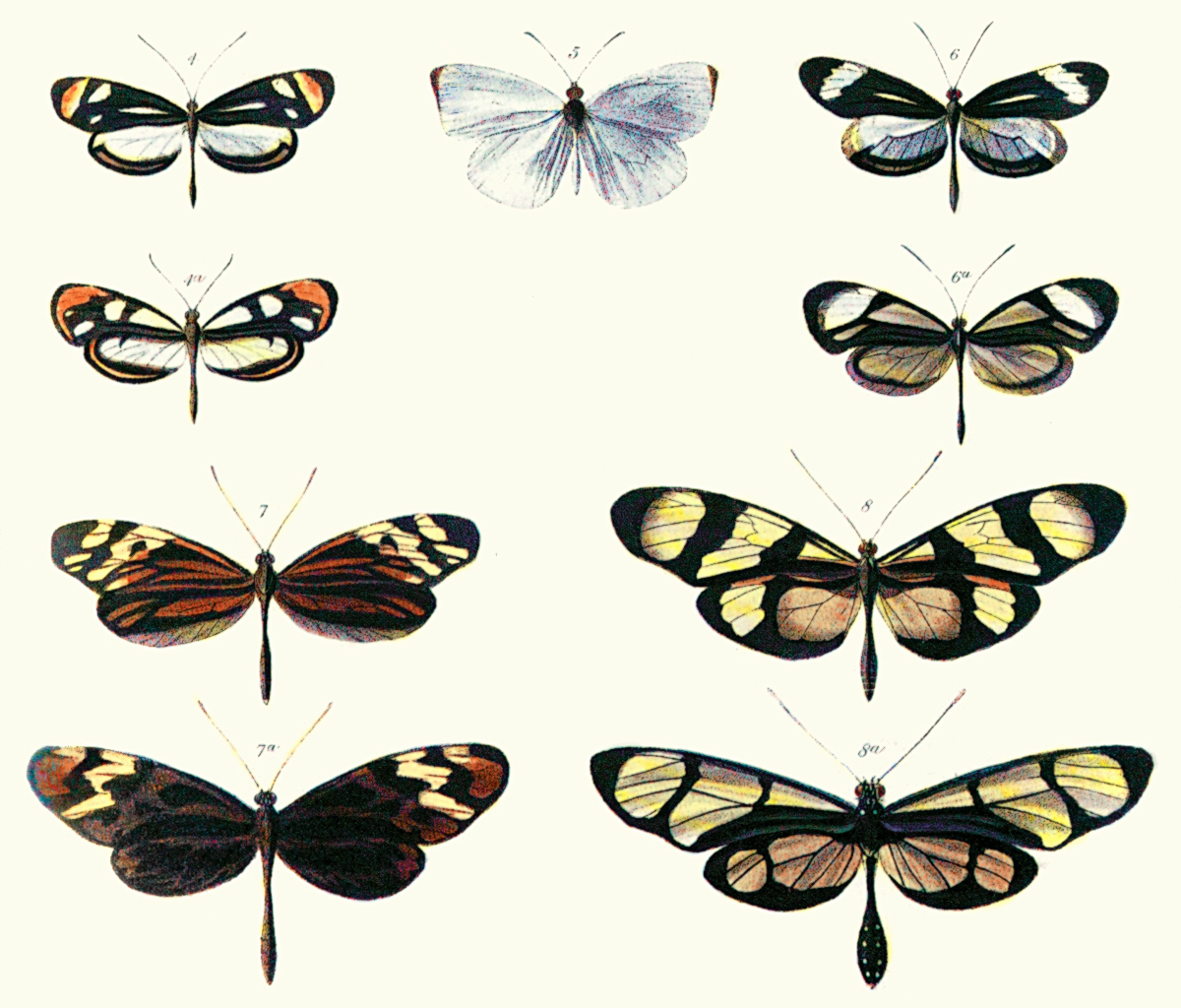
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed Warbler Cuckoo
Reed or Reeds may refer to: Science, technology, biology, and medicine * Reed bird (other) * Reed pen, writing implement in use since ancient times * Reed (plant), one of several tall, grass-like wetland plants of the order Poales * Reed reaction, in chemistry * Reed receiver, an outdated form of multi-channel signal decoding * Reed relay, one or more reed switches controlled by an electromagnet * Reed switch, an electrical switch operated by an applied magnetic field * Reed valve, restricts the flow of fluids to a single direction * Reed (weaving), a comb like tool for beating the weft when weaving * Reed's law, describes the utility of large networks, particularly social networks * Reed–Solomon error correction, a systematic way of building codes that can be used to detect and correct multiple random symbol errors * Reed–Sternberg cell, related to Hodgkin's disease Organizations * Reed (company), offering employment-related services (UK) * Reed and Stem, forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrocercus
Sage-grouse are grouse belonging to the bird genus ''Centrocercus.'' The genus includes two species: the Gunnison grouse (''Centrocercus minimus'') and the greater sage-grouse (''Centrocercus urophasianus''). These birds are distributed throughout large portions of the north-central and Western United States, as well as the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. The International Union for Conservation of Nature classified the ''C. minimus'' species as endangered in 2020 and ''C. urophasianus'' as near threatened in 2016. Names The specific epithet is from another Greek word, "oura", plus "phasianos", pheasant. The noun "pheasant" was originally applied to a bird that was native to the valley of the Phasis River (now the Rioni River), which is located in Georgia (country), Georgia. In the time of Lewis and Clark the word "pheasant" stood for "a genus of gallinaceous birds", according to lexicographer Noah Webster (1806), and the explorers often used it in that sense. "G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayfly
Mayflies (also known as shadflies or fishflies in Canada and the upper Midwestern United States, as Canadian soldiers in the American Great Lakes region, and as up-winged flies in the United Kingdom) are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families. Mayflies have ancestral traits that were probably present in the first flying insects, such as long tails and wings that do not fold flat over the abdomen. Their immature stages are aquatic fresh water forms (called "naiads" or "nymphs"), whose presence indicates a clean, unpolluted and highly oxygenated aquatic environment. They are unique among insect orders in having a fully winged terrestrial preadult stage, the subimago, which moults into a sexually mature adult, the imago. Mayflies "hatch" (emerge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_e_(_Zonotrichia_Capensis_).jpg)
.jpg)
_(cropped).jpg)
