|
Infinite-valued Logic
In logic, an infinite-valued logic (or real-valued logic or infinitely-many-valued logic) is a many-valued logic in which truth values comprise a continuous or discrete variable, continuous range. Traditionally, in Aristotle's logic, logic other than principle of bivalence, bivalent logic was abnormal, as the law of the excluded middle precluded more than two possible values (i.e., "true" and "false") for any proposition. Modern three-valued logic (ternary logic) allows for an additional possible truth value (i.e., "undecided") and is an example of finite-valued logic in which truth values are discrete, rather than continuous. Infinite-valued logic comprises continuous fuzzy logic, though fuzzy logic in some of its forms can further encompass finite-valued logic. For example, finite-valued logic can be applied in Boolean-valued modeling, description logics, and defuzzification of fuzzy logic. History Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz used both infinity, infinities and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises in a topic-neutral way. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Formal logic contrasts with informal logic, which is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. While there is no general agreement on how formal and informal logic are to be distinguished, one prominent approach associates their difference with whether the studied arguments are expressed in formal or informal languages. Logic plays a central role in multiple fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises together with a conclusion. Premises and conclusions are usually un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinity
Infinity is that which is boundless, endless, or larger than any natural number. It is often denoted by the infinity symbol . Since the time of the ancient Greeks, the philosophical nature of infinity was the subject of many discussions among philosophers. In the 17th century, with the introduction of the infinity symbol and the infinitesimal calculus, mathematicians began to work with infinite series and what some mathematicians (including l'Hôpital and Bernoulli) regarded as infinitely small quantities, but infinity continued to be associated with endless processes. As mathematicians struggled with the foundation of calculus, it remained unclear whether infinity could be considered as a number or magnitude and, if so, how this could be done. At the end of the 19th century, Georg Cantor enlarged the mathematical study of infinity by studying infinite sets and infinite numbers, showing that they can be of various sizes. For example, if a line is viewed as the set of all o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradox
A paradox is a logically self-contradictory statement or a statement that runs contrary to one's expectation. It is a statement that, despite apparently valid reasoning from true premises, leads to a seemingly self-contradictory or a logically unacceptable conclusion. A paradox usually involves contradictory-yet-interrelated elements that exist simultaneously and persist over time. They result in "persistent contradiction between interdependent elements" leading to a lasting "unity of opposites". In logic, many paradoxes exist that are known to be invalid arguments, yet are nevertheless valuable in promoting critical thinking, while other paradoxes have revealed errors in definitions that were assumed to be rigorous, and have caused axioms of mathematics and logic to be re-examined. One example is Russell's paradox, which questions whether a "list of all lists that do not contain themselves" would include itself, and showed that attempts to found set theory on the identification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Infinite
The Absolute Infinite (''symbol'': Ω) is an extension of the idea of infinity proposed by mathematician Georg Cantor. It can be thought of as a number that is bigger than any other conceivable or inconceivable quantity, either finite or transfinite. Cantor linked the Absolute Infinite with God, Cited as ''Cantor 1883b'' by Jané; with biography by Adolf Fraenkel; reprinted Hildesheim: Georg Olms, 1962, and Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1980, . Original article. and believed that it had various mathematical properties, including the reflection principle: every property of the Absolute Infinite is also held by some smaller object.''Infinity: New Research and Frontiers'' by Michael Heller and W. Hugh Woodin (2011)p. 11 Cantor's view Cantor said: Cantor also mentioned the idea in his letters to Richard Dedekind (text in square brackets not present in original): The Burali-Forti paradox The idea that the collection of all ordinal numbers cannot logically exist seems paradoxical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Continuity
In calculus, absolute continuity is a smoothness property of functions that is stronger than continuity and uniform continuity. The notion of absolute continuity allows one to obtain generalizations of the relationship between the two central operations of calculus— differentiation and integration. This relationship is commonly characterized (by the fundamental theorem of calculus) in the framework of Riemann integration, but with absolute continuity it may be formulated in terms of Lebesgue integration. For real-valued functions on the real line, two interrelated notions appear: absolute continuity of functions and absolute continuity of measures. These two notions are generalized in different directions. The usual derivative of a function is related to the '' Radon–Nikodym derivative'', or ''density'', of a measure. We have the following chains of inclusions for functions over a compact subset of the real line: : ''absolutely continuous'' ⊆ ''uniformly continuous'' = ''con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Hausdorff
Felix Hausdorff ( , ; November 8, 1868 – January 26, 1942) was a German mathematician who is considered to be one of the founders of modern topology and who contributed significantly to set theory, descriptive set theory, measure theory, and functional analysis. Life became difficult for Hausdorff and his family after Kristallnacht in 1938. The next year he initiated efforts to emigrate to the United States, but was unable to make arrangements to receive a research fellowship. On 26 January 1942, Felix Hausdorff, along with his wife and his sister-in-law, died by suicide by taking an overdose of veronal, rather than comply with German orders to move to the Endenich camp, and there suffer the likely implications, about which he held no illusions. Life Childhood and youth Hausdorff's father, the Jewish merchant Louis Hausdorff (1843–1896), moved with his young family to Leipzig in the autumn of 1870, and over time worked at various companies, including a linen-and cotton goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Approximation
An approximation is anything that is intentionally similar but not exactly equality (mathematics), equal to something else. Etymology and usage The word ''approximation'' is derived from Latin ''approximatus'', from ''proximus'' meaning ''very near'' and the prefix ''ad-'' (''ad-'' before ''p'' becomes ap- by assimilation (phonology), assimilation) meaning ''to''. Words like ''approximate'', ''approximately'' and ''approximation'' are used especially in technical or scientific contexts. In everyday English, words such as ''roughly'' or ''around'' are used with a similar meaning. It is often found abbreviated as ''approx.'' The term can be applied to various properties (e.g., value, quantity, image, description) that are nearly, but not exactly correct; similar, but not exactly the same (e.g., the approximate time was 10 o'clock). Although approximation is most often applied to numbers, it is also frequently applied to such things as Function (mathematics), mathematical functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial And Error
Trial and error is a fundamental method of problem-solving characterized by repeated, varied attempts which are continued until success, or until the practicer stops trying. According to W.H. Thorpe, the term was devised by C. Lloyd Morgan (1852–1936) after trying out similar phrases "trial and failure" and "trial and practice". Under Morgan's Canon, animal behaviour should be explained in the simplest possible way. Where behavior seems to imply higher mental processes, it might be explained by trial-and-error learning. An example is a skillful way in which his terrier Tony opened the garden gate, easily misunderstood as an insightful act by someone seeing the final behavior. Lloyd Morgan, however, had watched and recorded the series of approximations by which the dog had gradually learned the response, and could demonstrate that no insight was required to explain it. Edward Lee Thorndike was the initiator of the theory of trial and error learning based on the findings he sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Continuity
The law of continuity is a heuristic principle introduced by Gottfried Leibniz based on earlier work by Nicholas of Cusa and Johannes Kepler. It is the principle that "whatever succeeds for the finite, also succeeds for the infinite". Kepler used the law of continuity to calculate the area of the circle by representing it as an infinite-sided polygon with infinitesimal sides, and adding the areas of infinitely many triangles with infinitesimal bases. Leibniz used the principle to extend concepts such as arithmetic operations from ordinary numbers to infinitesimals, laying the groundwork for infinitesimal calculus. The transfer principle provides a mathematical implementation of the law of continuity in the context of the hyperreal numbers. A related law of continuity concerning intersection numbers in geometry was promoted by Jean-Victor Poncelet in his "Traité des propriétés projectives des figures". Leibniz's formulation Leibniz expressed the law in the following terms in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
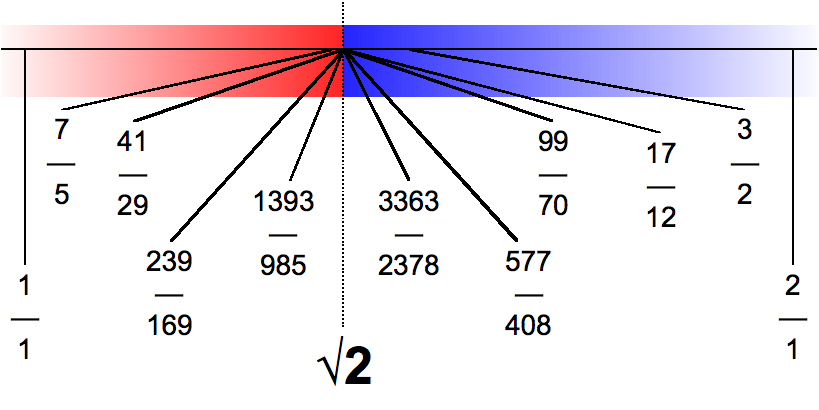
Rational Number
In mathematics, a rational number is a number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, a numerator and a non-zero denominator . For example, is a rational number, as is every integer (e.g. ). The set of all rational numbers, also referred to as "the rationals", the field of rationals or the field of rational numbers is usually denoted by boldface , or blackboard bold \mathbb. A rational number is a real number. The real numbers that are rational are those whose decimal expansion either terminates after a finite number of digits (example: ), or eventually begins to repeat the same finite sequence of digits over and over (example: ). This statement is true not only in base 10, but also in every other integer base, such as the binary and hexadecimal ones (see ). A real number that is not rational is called irrational. Irrational numbers include , , , and . Since the set of rational numbers is countable, and the set of real numbers is uncountable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Construction Of The Real Numbers
In mathematics, there are several equivalent ways of defining the real numbers. One of them is that they form a complete ordered field that does not contain any smaller complete ordered field. Such a definition does not prove that such a complete ordered field exists, and the existence proof consists of constructing a mathematical structure that satisfies the definition. The article presents several such constructions. They are equivalent in the sense that, given the result of any two such constructions, there is a unique isomorphism of ordered field between them. This results from the above definition and is independent of particular constructions. These isomorphisms allow identifying the results of the constructions, and, in practice, to forget which construction has been chosen. Axiomatic definitions An axiomatic definition of the real numbers is to define them as the elements of a complete ordered field. Precisely, this means the following. A ''model for the real number system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |