|
Incidence (graph Theory)
In mathematics, an incidence matrix is a logical matrix that shows the relationship between two classes of objects, usually called an incidence relation. If the first class is ''X'' and the second is ''Y'', the matrix has one row for each element of ''X'' and one column for each element of ''Y''. The entry in row ''x'' and column ''y'' is 1 if ''x'' and ''y'' are related (called ''incident'' in this context) and 0 if they are not. There are variations; see below. Graph theory Incidence matrix is a common graph representation in graph theory. It is different to an adjacency matrix, which encodes the relation of vertex-vertex pairs. Undirected and directed graphs In graph theory an undirected graph has two kinds of incidence matrices: unoriented and oriented. The ''unoriented incidence matrix'' (or simply ''incidence matrix'') of an undirected graph is a n\times m matrix ''B'', where ''n'' and ''m'' are the numbers of vertices and edges respectively, such that :B_=\left\{\be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Space
In mathematics, the kernel of a linear map, also known as the null space or nullspace, is the linear subspace of the domain of the map which is mapped to the zero vector. That is, given a linear map between two vector spaces and , the kernel of is the vector space of all elements of such that , where denotes the zero vector in , or more symbolically: :\ker(L) = \left\ . Properties The kernel of is a linear subspace of the domain .Linear algebra, as discussed in this article, is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. Almost all of the material in this article can be found in , , and Strang's lectures. In the linear map L : V \to W, two elements of have the same image in if and only if their difference lies in the kernel of , that is, L\left(\mathbf_1\right) = L\left(\mathbf_2\right) \quad \text \quad L\left(\mathbf_1-\mathbf_2\right) = \mathbf. From this, it follows that the image of is isomorphic to the quotient of by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levi Graph
In combinatorial mathematics, a Levi graph or incidence graph is a bipartite graph associated with an incidence structure.. See in particulap. 181 From a collection of points and lines in an incidence geometry or a projective configuration, we form a graph with one vertex per point, one vertex per line, and an edge for every incidence between a point and a line. They are named for Friedrich Wilhelm Levi, who wrote about them in 1942. The Levi graph of a system of points and lines usually has girth at least six: Any 4- cycles would correspond to two lines through the same two points. Conversely any bipartite graph with girth at least six can be viewed as the Levi graph of an abstract incidence structure. Levi graphs of configurations are biregular, and every biregular graph with girth at least six can be viewed as the Levi graph of an abstract configuration.. Levi graphs may also be defined for other types of incidence structure, such as the incidences between points and planes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biadjacency Matrix
In graph theory and computer science, an adjacency matrix is a square matrix used to represent a finite graph. The elements of the matrix indicate whether pairs of vertices are adjacent or not in the graph. In the special case of a finite simple graph, the adjacency matrix is a (0,1)-matrix with zeros on its diagonal. If the graph is undirected (i.e. all of its edges are bidirectional), the adjacency matrix is symmetric. The relationship between a graph and the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of its adjacency matrix is studied in spectral graph theory. The adjacency matrix of a graph should be distinguished from its incidence matrix, a different matrix representation whose elements indicate whether vertex–edge pairs are incident or not, and its degree matrix, which contains information about the degree of each vertex. Definition For a simple graph with vertex set , the adjacency matrix is a square matrix such that its element is one when there is an edge from vertex to ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incidence Structure
In mathematics, an incidence structure is an abstract system consisting of two types of objects and a single relationship between these types of objects. Consider the points and lines of the Euclidean plane as the two types of objects and ignore all the properties of this geometry except for the relation of which points are on which lines for all points and lines. What is left is the incidence structure of the Euclidean plane. Incidence structures are most often considered in the geometrical context where they are abstracted from, and hence generalize, planes (such as affine, projective, and Möbius planes), but the concept is very broad and not limited to geometric settings. Even in a geometric setting, incidence structures are not limited to just points and lines; higher-dimensional objects (planes, solids, -spaces, conics, etc.) can be used. The study of finite structures is sometimes called finite geometry. Formal definition and terminology An incidence structure is a triple ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergraph
In mathematics, a hypergraph is a generalization of a graph in which an edge can join any number of vertices. In contrast, in an ordinary graph, an edge connects exactly two vertices. Formally, an undirected hypergraph H is a pair H = (X,E) where X is a set of elements called ''nodes'' or ''vertices'', and E is a set of non-empty subsets of X called ''hyperedges'' or ''edges''. Therefore, E is a subset of \mathcal(X) \setminus\, where \mathcal(X) is the power set of X. The size of the vertex set is called the ''order of the hypergraph'', and the size of edges set is the ''size of the hypergraph''. A directed hypergraph differs in that its hyperedges are not sets, but ordered pairs of subsets of X, with each pair's first and second entries constituting the tail and head of the hyperedge respectively. While graph edges connect only 2 nodes, hyperedges connect an arbitrary number of nodes. However, it is often desirable to study hypergraphs where all hyperedges have the same card ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Undirected Graph
A weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. The result of this application of a weight function is a weighted sum or weighted average. Weight functions occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a measure. Weight functions can be employed in both discrete and continuous settings. They can be used to construct systems of calculus called "weighted calculus" and "meta-calculus".Jane Grossma''Meta-Calculus: Differential and Integral'' , 1981. Discrete weights General definition In the discrete setting, a weight function w \colon A \to \R^+ is a positive function defined on a discrete set A, which is typically finite or countable. The weight function w(a) := 1 corresponds to the ''unweighted'' situation in which all elements have equal weight. One can then apply this weight to various concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Edges
In graph theory, multiple edges (also called parallel edges or a multi-edge), are, in an undirected graph, two or more edges that are incident to the same two vertices, or in a directed graph, two or more edges with both the same tail vertex and the same head vertex. A simple graph has no multiple edges and no loops. Depending on the context, a graph may be defined so as to either allow or disallow the presence of multiple edges (often in concert with allowing or disallowing loops): *Where graphs are defined so as to ''allow'' multiple edges and loops, a graph without loops or multiple edges is often distinguished from other graphs by calling it a ''simple graph.'' *Where graphs are defined so as to ''disallow'' multiple edges and loops, a multigraph or a pseudograph is often defined to mean a "graph" which ''can'' have loops and multiple edges. Multiple edges are, for example, useful in the consideration of electrical networks, from a graph theoretical point of view. Additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop (graph Theory)
In graph theory, a loop (also called a self-loop or a ''buckle'') is an edge that connects a vertex to itself. A simple graph contains no loops. Depending on the context, a graph or a multigraph may be defined so as to either allow or disallow the presence of loops (often in concert with allowing or disallowing multiple edges between the same vertices): * Where graphs are defined so as to ''allow'' loops and multiple edges, a graph without loops or multiple edges is often distinguished from other graphs by calling it a ''simple graph''. * Where graphs are defined so as to ''disallow'' loops and multiple edges, a graph that does have loops or multiple edges is often distinguished from the graphs that satisfy these constraints by calling it a ''multigraph'' or ''pseudograph''. In a graph with one vertex, all edges must be loops. Such a graph is called a bouquet. Degree For an undirected graph, the degree of a vertex is equal to the number of adjacent vertices. A special case i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidirected Graph
In the mathematical domain of graph theory, a bidirected graph (introduced by ). Reprinted in ''Combinatorial Optimization — Eureka, You Shrink!'', Springer-Verlag, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2570, 2003, pp. 27–30, . is a graph in which each edge is given an independent orientation (or direction, or arrow) at each end. Thus, there are three kinds of bidirected edges: those where the arrows point outward, towards the vertices, at both ends; those where both arrows point inward, away from the vertices; and those in which one arrow points away from its vertex and towards the opposite end, while the other arrow points in the same direction as the first, away from the opposite end and towards its own vertex. Edges of these three types may be called, respectively, extraverted, introverted, and directed. The "directed" edges are the same as ordinary directed edges in a directed graph; thus, a directed graph is a special kind of bidirected graph. It is sometimes desirable to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
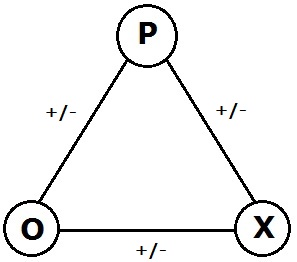
Signed Graph
In the area of graph theory in mathematics, a signed graph is a graph in which each edge has a positive or negative sign. A signed graph is balanced if the product of edge signs around every cycle is positive. The name "signed graph" and the notion of balance appeared first in a mathematical paper of Frank Harary in 1953. Dénes Kőnig had already studied equivalent notions in 1936 under a different terminology but without recognizing the relevance of the sign group. At the Center for Group Dynamics at the University of Michigan, Dorwin Cartwright and Harary generalized Fritz Heider's psychological theory of balance in triangles of sentiments to a psychological theory of balance in signed graphs. Signed graphs have been rediscovered many times because they come up naturally in many unrelated areas. For instance, they enable one to describe and analyze the geometry of subsets of the classical root systems. They appear in topological graph theory and group theory. They are a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (mathematics)
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers do. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics. The best known fields are the field of rational numbers, the field of real numbers and the field of complex numbers. Many other fields, such as fields of rational functions, algebraic function fields, algebraic number fields, and ''p''-adic fields are commonly used and studied in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebraic geometry. Most cryptographic protocols rely on finite fields, i.e., fields with finitely many elements. The relation of two fields is expressed by the notion of a field extension. Galois theory, initiated by Évariste Galois in the 1830s, is devoted to understanding the symmetries of field extensions. Among other results, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |