|
Ideal
Ideal may refer to: Philosophy * Ideal (ethics), values that one actively pursues as goals * Platonic ideal, a philosophical idea of trueness of form, associated with Plato Mathematics * Ideal (ring theory), special subsets of a ring considered in abstract algebra * Ideal, special subsets of a semigroup * Ideal (order theory), special kind of lower sets of an order * Ideal (set theory), a collection of sets regarded as "small" or "negligible" * Ideal (Lie algebra), a particular subset in a Lie algebra * Ideal point, a boundary point in hyperbolic geometry * Ideal triangle, a triangle in hyperbolic geometry whose vertices are ideal points Science * Ideal chain, in science, the simplest model describing a polymer * Ideal gas law, in physics, governing the pressure of an ideal gas * Ideal transformer, an electrical transformer having zero resistance and perfect magnetic threading * Ideal final result, in TRIZ methodology, the best possible solution * Thought experiment, someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal (ring Theory)
In ring theory, a branch of abstract algebra, an ideal of a ring is a special subset of its elements. Ideals generalize certain subsets of the integers, such as the even numbers or the multiples of 3. Addition and subtraction of even numbers preserves evenness, and multiplying an even number by any integer (even or odd) results in an even number; these closure and absorption properties are the defining properties of an ideal. An ideal can be used to construct a quotient ring in a way similar to how, in group theory, a normal subgroup can be used to construct a quotient group. Among the integers, the ideals correspond one-for-one with the non-negative integers: in this ring, every ideal is a principal ideal consisting of the multiples of a single non-negative number. However, in other rings, the ideals may not correspond directly to the ring elements, and certain properties of integers, when generalized to rings, attach more naturally to the ideals than to the elements of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal (order Theory)
In mathematical order theory, an ideal is a special subset of a partially ordered set (poset). Although this term historically was derived from the notion of a ring ideal of abstract algebra, it has subsequently been generalized to a different notion. Ideals are of great importance for many constructions in order and lattice theory. Basic definitions A subset of a partially ordered set (P, \leq) is an ideal, if the following conditions hold: # is non-empty, # for every ''x'' in and ''y'' in ''P'', implies that ''y'' is in ( is a lower set), # for every ''x'', ''y'' in , there is some element ''z'' in , such that and ( is a directed set). While this is the most general way to define an ideal for arbitrary posets, it was originally defined for lattices only. In this case, the following equivalent definition can be given: a subset of a lattice (P, \leq) is an ideal if and only if it is a lower set that is closed under finite joins ( suprema); that is, it is non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal (set Theory)
In the mathematical field of set theory, an ideal is a partially ordered collection of sets that are considered to be "small" or "negligible". Every subset of an element of the ideal must also be in the ideal (this codifies the idea that an ideal is a notion of smallness), and the union of any two elements of the ideal must also be in the ideal. More formally, given a set X, an ideal I on X is a nonempty subset of the powerset of X, such that: # \varnothing \in I, # if A \in I and B \subseteq A, then B \in I, and # if A, B \in I then A \cup B \in I. Some authors add a fourth condition that X itself is not in I; ideals with this extra property are called . Ideals in the set-theoretic sense are exactly ideals in the order-theoretic sense, where the relevant order is set inclusion. Also, they are exactly ideals in the ring-theoretic sense on the Boolean ring formed by the powerset of the underlying set. The dual notion of an ideal is a filter. Terminology An element of an ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Point
In hyperbolic geometry, an ideal point, omega point or point at infinity is a well-defined point outside the hyperbolic plane or space. Given a line ''l'' and a point ''P'' not on ''l'', right- and left-limiting parallels to ''l'' through ''P'' converge to ''l'' at ''ideal points''. Unlike the projective case, ideal points form a boundary, not a submanifold. So, these lines do not intersect at an ideal point and such points, although well-defined, do not belong to the hyperbolic space itself. The ideal points together form the Cayley absolute or boundary of a hyperbolic geometry. For instance, the unit circle forms the Cayley absolute of the Poincaré disk model and the Klein disk model. While the real line forms the Cayley absolute of the Poincaré half-plane model . Pasch's axiom and the exterior angle theorem still hold for an omega triangle, defined by two points in hyperbolic space and an omega point. Properties * The hyperbolic distance between an ideal point and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
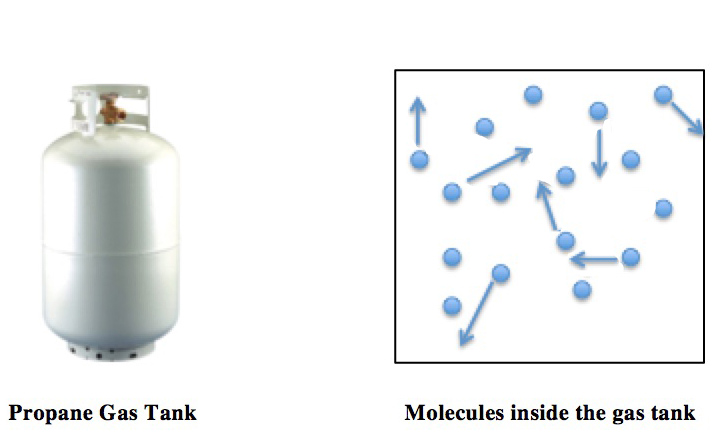
Ideal Gas Law
The ideal gas law, also called the general gas equation, is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation of the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of the empirical Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. The ideal gas law is often written in an empirical form: pV = nRT where p, V and T are the pressure, volume and temperature; n is the amount of substance; and R is the ideal gas constant. It can also be derived from the microscopic kinetic theory, as was achieved (apparently independently) by August Krönig in 1856 and Rudolf Clausius in 1857. Equation The state of an amount of gas is determined by its pressure, volume, and temperature. The modern form of the equation relates these simply in two main forms. The temperature used in the equation of state is an absolute temperature: the appropria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Solution
In chemistry, an ideal solution or ideal mixture is a solution that exhibits thermodynamic properties analogous to those of a mixture of ideal gases. The enthalpy of mixing is zero as is the volume change on mixing by definition; the closer to zero the enthalpy of mixing is, the more "ideal" the behavior of the solution becomes. The vapor pressures of the solvent and solute obey Raoult's law and Henry's law, respectively, and the activity coefficient (which measures deviation from ideality) is equal to one for each component. The concept of an ideal solution is fundamental to chemical thermodynamics and its applications, such as the explanation of colligative properties. Physical origin Ideality of solutions is analogous to ideality for gases, with the important difference that intermolecular interactions in liquids are strong and cannot simply be neglected as they can for ideal gases. Instead we assume that the mean strength of the interactions are the same between all the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Triangle
In hyperbolic geometry an ideal triangle is a hyperbolic triangle whose three vertices all are ideal points. Ideal triangles are also sometimes called ''triply asymptotic triangles'' or ''trebly asymptotic triangles''. The vertices are sometimes called ideal vertices. All ideal triangles are congruent. Properties Ideal triangles have the following properties: * All ideal triangles are congruent to each other. * The interior angles of an ideal triangle are all zero. * An ideal triangle has infinite perimeter. * An ideal triangle is the largest possible triangle in hyperbolic geometry. In the standard hyperbolic plane (a surface where the constant Gaussian curvature is −1) we also have the following properties: * Any ideal triangle has area π. Distances in an ideal triangle * The inscribed circle to an ideal triangle has radius r=\ln\sqrt = \frac \ln 3 = \operatorname\frac = 2 \operatorname(2- \sqrt) = = \operatorname\frac\sqrt = \operatorname\frac\sqrt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Type
Ideal type (german: Idealtypus), also known as pure type, is a typological term most closely associated with sociologist Max Weber (1864–1920). For Weber, the conduct of social science depends upon the construction of abstract, hypothetical concepts. The "ideal type" is therefore a subjective element in social theory and research, and one of the subjective elements distinguishing sociology from natural science. Meaning An ideal type is formed from characteristics and elements of the given phenomena, but it is not meant to correspond to all of the characteristics of any one particular case. It is not meant to refer to perfect things, moral ideals nor to statistical averages but rather to stress certain elements common to most cases of the given phenomenon. It is also important to pay attention that in using the word "ideal" Max Weber refers to the world of ideas (german: Gedankenbilder, "mental images") and not to perfection; these "ideal types" are idea-constructs that hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Toy Company
Ideal Toy Company was an American toy company founded by Morris Michtom and his wife, Rose. During the post–World War II baby boom era, Ideal became the largest doll-making company in the United States. Their most popular dolls included Betsy Wetsy,Hays, Constance L. "Judith Albert, 59, Toy Designer Whose Doll Led to Buyer Frenzy," ''New York Times'' (Aug. 1, 1998). Toni, Saucy Walker, Shirley Temple, Miss Revlon, Patti Playpal, Tammy, Thumbelina, Tiny Thumbelina, and Crissy. Their last big hit was the Rubik's Cube. History Corporate history Morris and Rose Michtom founded the Ideal Novelty and Toy Company in Brooklyn when they invented the Teddy bear in 1903. After Morris Michtom's death in 1938, the company changed its name to the Ideal Toy Company, and Michtom's nephew Abraham Katz became chief executive. During World War II, the company's value rose from $2 million all the way to $11 million. The company's dolls were so popular during the post–World War II baby boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semigroup
In mathematics, a semigroup is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an associative internal binary operation on it. The binary operation of a semigroup is most often denoted multiplicatively: ''x''·''y'', or simply ''xy'', denotes the result of applying the semigroup operation to the ordered pair . Associativity is formally expressed as that for all ''x'', ''y'' and ''z'' in the semigroup. Semigroups may be considered a special case of magmas, where the operation is associative, or as a generalization of groups, without requiring the existence of an identity element or inverses. The closure axiom is implied by the definition of a binary operation on a set. Some authors thus omit it and specify three axioms for a group and only one axiom (associativity) for a semigroup. As in the case of groups or magmas, the semigroup operation need not be commutative, so ''x''·''y'' is not necessarily equal to ''y''·''x''; a well-known example of an operation that is as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal (Lie Algebra)
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced ) is a vector space \mathfrak g together with an operation called the Lie bracket, an alternating bilinear map \mathfrak g \times \mathfrak g \rightarrow \mathfrak g, that satisfies the Jacobi identity. The Lie bracket of two vectors x and y is denoted ,y/math>. The vector space \mathfrak g together with this operation is a non-associative algebra, meaning that the Lie bracket is not necessarily associative. Lie algebras are closely related to Lie groups, which are groups that are also smooth manifolds: any Lie group gives rise to a Lie algebra, which is its tangent space at the identity. Conversely, to any finite-dimensional Lie algebra over real or complex numbers, there is a corresponding connected Lie group unique up to finite coverings ( Lie's third theorem). This correspondence allows one to study the structure and classification of Lie groups in terms of Lie algebras. In physics, Lie groups appear as symmetry groups of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signal-processing circuits. Since the invention of the first constant-potential transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |