|
Isodiazene
In organic chemistry, an isodiazene, also known by the incorrectly constructed (but commonly used) name 1,1-diazene or systematic name diazanylidene, is an organic derivative of the parent isodiazene (H2N+=N–, also called 1,1-diimide) with general formula R1R2N+=N–. The functional group has two major resonance forms, a diazen-2-ium-1-ide form, and an aminonitrene form: Although isodiazenes are formally isoelectronic with ketones and aldehydes, the reactivity of this exotic functional group is very different. They are generally prepared by oxidation of the hydrazine (R2N–NH2), reduction of the 1,1-diazene oxide (R2N–N=O), 1,1-elimination of MX from R2N–NMX (M = Na, K; X = SO2Ar), or treatment of secondary amines with Angeli's salt, Na2N2O3, in the presence of acid. Isodiazenes participate in cycloaddition reactions with alkenes to generate ''N''-aminoaziridines. In the absence of other reactants, they undergo reactions in which N2 is eliminated to give an organic resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isodiazene
In organic chemistry, an isodiazene, also known by the incorrectly constructed (but commonly used) name 1,1-diazene or systematic name diazanylidene, is an organic derivative of the parent isodiazene (H2N+=N–, also called 1,1-diimide) with general formula R1R2N+=N–. The functional group has two major resonance forms, a diazen-2-ium-1-ide form, and an aminonitrene form: Although isodiazenes are formally isoelectronic with ketones and aldehydes, the reactivity of this exotic functional group is very different. They are generally prepared by oxidation of the hydrazine (R2N–NH2), reduction of the 1,1-diazene oxide (R2N–N=O), 1,1-elimination of MX from R2N–NMX (M = Na, K; X = SO2Ar), or treatment of secondary amines with Angeli's salt, Na2N2O3, in the presence of acid. Isodiazenes participate in cycloaddition reactions with alkenes to generate ''N''-aminoaziridines. In the absence of other reactants, they undergo reactions in which N2 is eliminated to give an organic resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectronicity
Isoelectronicity is a phenomenon observed when two or more molecules have the same structure (positions and connectivities among atoms) and the same electronic configurations, but differ by what specific elements are at certain locations in the structure. For example, , , and are isoelectronic, while and = are not. This definition is sometimes termed ''valence isoelectronicity''. Definitions can sometimes be not as strict, sometimes requiring identity of the ''total'' electron count and with it the entire electronic configuration. More usually, definitions are broader, and may extend to allowing different numbers of atoms in the species being compared.A. A. Aradi & T. P. Fehlner, "Isoelectronic Organometallic Molecules", in F. G. A. Stone & Robert West (eds.) ''Advances in Organometallic Chemistry Vol. 30'' (1990), Chapter 5 (at p. 190google books link/ref> The importance of the concept lies in identifying significantly related species, as pairs or series. Isoelectronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonyl Compounds
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound. The term carbonyl can also refer to carbon monoxide as a ligand in an inorganic or organometallic complex (a metal carbonyl, e.g. nickel carbonyl). The remainder of this article concerns itself with the organic chemistry definition of carbonyl, where carbon and oxygen share a double bond. Carbonyl compounds In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group characterizes the following types of compounds: Other organic carbonyls are urea and the carbamates, the derivatives of acyl chlorides chloroformates and phosgene, carbonate esters, thioesters, lactones, lactams, hydroxamates, and isocyanates. Examples of inorganic carbonyl compounds are carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulfide. A sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angeli's Salt
Angeli's salt, sodium trioxodinitrate, is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2[N2O3]. It contains nitrogen in an unusual reduced state. It is a colorless, water-soluble solid, a salt. In research, this salt is used as a source of the metastable nitroxyl (HNO), which is a signalling molecule in nature. It is also known by the name sodium trioxodinitrate(II) monohydrate. Preparation and properties As first reported by Angelo Angeli in 1896, the salt is prepared by combining hydroxylamine and an organic nitrate, as a source of nitronium (): :NH2OH + RONO2 + 2 NaOR′ → ROH + 2 R′OH + Na2N2O3 The structure of the hydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography. The anion is planar. Starting from the ONN end, the bond distances are 1.35 Å (N−O), 1.26 Å (N−N), 1.31 Å (N−O), and 1.32 Å (N−-O). The negative charge is on the oxygen atoms at opposite ends of the molecule. The angles are 112.9° (Osingle−N−N), 118.4° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericyclic Reaction
In organic chemistry, a pericyclic reaction is the type of organic reaction wherein the transition state of the molecule has a cyclic geometry, the reaction progresses in a concerted fashion, and the bond orbitals involved in the reaction overlap in a continuous cycle at the transition state. Pericyclic reactions stand in contrast to ''linear reactions'', encompassing most organic transformations and proceeding through an acyclic transition state, on the one hand and '' coarctate reactions'', which proceed through a doubly cyclic, concerted transition state on the other hand. Pericyclic reactions are usually rearrangement or addition reactions. The major classes of pericyclic reactions are given in the table below (the three most important classes are shown in bold). Ene reactions and cheletropic reactions are often classed as group transfer reactions and cycloadditions/cycloeliminations, respectively, while dyotropic reactions and group transfer reactions (if ene reactions are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereospecificity
In chemistry, stereospecificity is the property of a reaction mechanism that leads to different stereoisomeric reaction products from different stereoisomeric reactants, or which operates on only one (or a subset) of the stereoisomers."Overlap Control of Carbanionoid Reactions. I. Stereoselectivity in Alkaline Epoxidation," Zimmerman, H. E.; Singer, L.; Thyagarajan, B. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1959, 81, 108-116.Eliel, E., "Stereochemistry of Carbon Compound", McGraw-Hill, 1962 pp 434-436 In contrast, stereoselectivity is the property of a reactant mixture where a non-stereospecific mechanism allows for the formation of multiple products, but where one (or a subset) of the products is favored by factors, such as steric access, that are independent of the mechanism. A stereospecific mechanism ''specifies'' the stereochemical outcome of a given reactant, whereas a stereoselective reaction ''selects'' products from those made available by the same, non-specific mechanism acting on a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Orbital Symmetry
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws. Conservation may also refer to: Environment and natural resources * Nature conservation, the protection and management of the environment and natural resources * Conservation biology, the science of protection and management of biodiversity * Conservation movement, political, environmental, or social movement that seeks to protect natural resources, including biodiversity and habitat * Conservation organization, an organization dedicated to protection and management of the environment or natural resources * Wildlife conservation, the practice of protecting wild species and their habitats in order to prevent species from going extinct * Conservation (magazine), ''Conservation'' (magazine), published by the Society for Conservation Biology from 2000 to 2014 ** Conservation Biology (journal), ''Conservation Biology'' (journal), scientific journal of the Soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retro221
Retro style is imitative or consciously derivative of lifestyles, trends, or art forms from history, including in music, modes, fashions, or attitudes. In popular culture, the "nostalgia cycle" is typically for the two decades that begin 20–30 years ago. Definition The term ''retro'' has been in use since 1972 to describe on the one hand, new artifacts that self-consciously refer to particular modes, motifs, techniques, and materials of the past. But on the other hand, many people use the term to categorize styles that have been created in the past. Retro style refers to new things that display characteristics of the past. Unlike the historicism of the Romantic generations, it is mostly the recent past that retro seeks to recapitulate, focusing on the products, fashions, and artistic styles produced since the Industrial Revolution, the successive styles of Modernity. The English word ''retro'' derives from the Latin prefix ''retro'', meaning backwards, or in past times. In Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diazene
Diimide, also called diazene or diimine, is a compound having the formula (NH)2. It exists as two geometric isomers, ''E'' (''trans'') and ''Z'' (''cis''). The term diazene is more common for organic derivatives of diimide. Thus, azobenzene is an example of an organic diazene. Synthesis A traditional route to diimide involves oxidation of hydrazine with hydrogen peroxide or air. Alternatively the hydrolysis of diethyl azodicarboxylate or azodicarbonamide affords diimide: :(NCOOH)2 → (NH)2 + 2 CO2 Nowadays, diimide is generated by thermal decomposition of 2,4,6‐triisopropylbenzenesulfonylhydrazide. Because of its instability, diimide is generated and used ''in-situ''. A mixture of both the ''cis'' (''Z-'') and ''trans'' (''E-'') isomers is produced. Both isomers are unstable, and they undergo a slow interconversion. The ''trans'' isomer is more stable, but the ''cis'' isomer is the one that reacts with unsaturated substrates, therefore the equilibrium between them sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
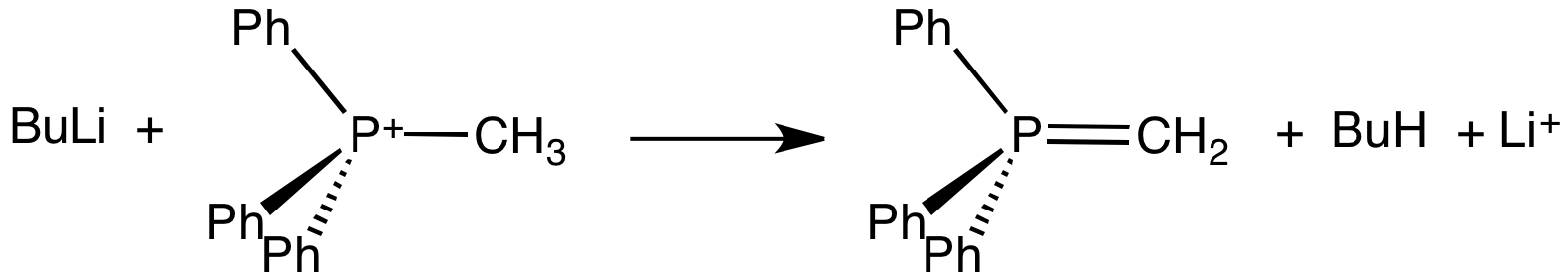
Ylide
An ylide or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2-dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates. The class name "ylide" for the compound should not be confused with the suffix "-ylide". Resonance structures Many ylides may be depicted by a multiple bond form in a resonance structure, known as the ylene form, while the actual structure lies in between both forms: : The actual bonding picture of these types of ylides is strictly zwitterionic (the structure on the right) with the strong Coulombic attraction between the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |