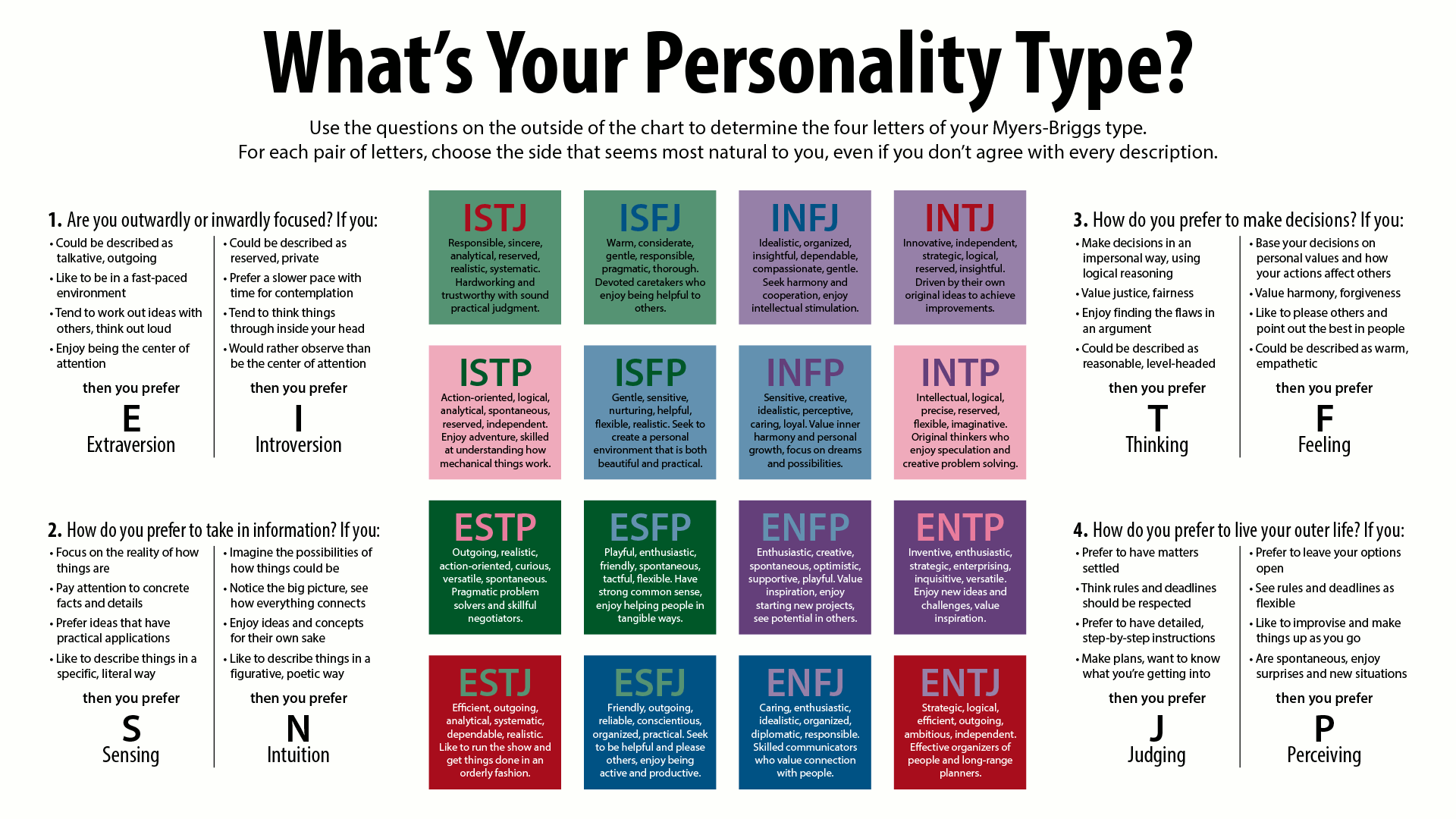
|
Introversion
The traits of extraversion (also spelled extroversion Retrieved 2018-02-21.) and introversion are a central dimension in some human personality theories. The terms ''introversion'' and ''extraversion'' were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung,Jung, C. G. (1921) ''Psychologische Typen'', Rascher Verlag, Zurich – translation H.G. Baynes, 1923. although both the popular understanding and current psychological usage vary. Extraversion tends to be manifested in outgoing, talkative, energetic behavior, whereas introversion is manifested in more reflective and reserved behavior. Jung defined introversion as an "attitude-type characterised by orientation in life through subjective psychic contents", and extraversion as "an attitude-type characterised by concentration of interest on the external object". Extraversion and introversion are typically viewed as a single continuum, so to be higher in one necessitates being lower in the other. Jung provides a different perspective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myers–Briggs Type Indicator
In Personality type, personality typology, the Myers–Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is an introspection, introspective self-report study, self-report questionnaire indicating differing Psychology, psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. The test attempts to assign a value to each of four categories: introversion or extraversion, sensing or intuition, thinking or feeling, and judging or perceiving. One letter from each category is taken to produce a four-letter test result, such as "INTP" or "ESFJ". The MBTI was constructed by two Americans: Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, who were inspired by the book ''Psychological Types'' by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung. Isabel Myers was particularly fascinated by the concept of introversion and she typed herself as an INFP. However, she felt the book was too complex for the general public, and therefore she tried to organize the Jungian cognitive functions to make it more acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyness
Shyness (also called diffidence) is the feeling of apprehension, lack of comfort, or awkwardness especially when a person is around other people. This commonly occurs in new situations or with unfamiliar people; a shy person may simply opt to avoid these situations. Although shyness can be a characteristic of people who have low self-esteem, the primary defining characteristic of shyness is a fear of what other people will think of a person's behavior. This fear of negative reactions such as being laughed at, humiliated or patronized, criticized or rejected can cause a shy person to retreat. Stronger forms of shyness can be referred to as social anxiety or social phobia. Origins The initial cause of shyness varies. Scientists believe that they have located genetic data supporting the hypothesis that shyness is, at least, partially genetic. However, there is also evidence that suggests the environment in which a person is raised can also be responsible for their shyne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philosophy, psychology, and religious studies. Jung worked as a research scientist at the Burghölzli psychiatric hospital, in Zurich, under Eugen Bleuler. During this time, he came to the attention of Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis. The two men conducted a lengthy correspondence and collaborated, for a while, on a joint vision of human psychology. Freud saw the younger Jung as the heir he had been seeking to take forward his "new science" of psychoanalysis and to this end secured his appointment as president of his newly founded International Psychoanalytical Association. Jung's research and personal vision, however, made it difficult for him to follow his older colleague's doctrine and they parted ways. This division was per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personality Psychology
Personality psychology is a branch of psychology that examines personality and its variation among individuals. It aims to show how people are individually different due to psychological forces. Its areas of focus include: * construction of a coherent picture of the individual and their major psychological processes * investigation of individual psychological differences * investigation of human nature and psychological similarities between individuals "Personality" is a dynamic and organized set of characteristics possessed by an individual that uniquely influences their environment, cognition, emotions, motivations, and behaviors in various situations. The word ''personality'' originates from the Latin ''persona'', which means "mask". Personality also pertains to the pattern of thoughts, feelings, social adjustments, and behaviors persistently exhibited over time that strongly influences one's expectations, self-perceptions, values, and attitudes. Personality also pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susan Cain
Susan Horowitz Cain Harvard Law School "Leaders for Change" (conference Program of Events), Sept. 27–29, 2013, bottom of p. 13. (born 1968) is an American writer and lecturer. She is the author of the 2012 non-fiction book '' Quiet: The Power of Introverts in a World That Can't Stop Talking'', which argues that modern misunderstands and underval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Five Personality Traits
The Big Five personality traits is a suggested taxonomy, or grouping, for personality traits, developed from the 1980s onward in psychological trait theory. Starting in the 1990s, the theory identified five factors by labels, for the US English speaking population, typically referred to as: * openness to experience (inventive/curious vs. consistent/cautious) * conscientiousness (efficient/organized vs. extravagant/careless) * extraversion (outgoing/energetic vs. solitary/reserved) * agreeableness (friendly/compassionate vs. critical/rational) * neuroticism (sensitive/nervous vs. resilient/confident) When factor analysis (a statistical technique) is applied to personality survey data, it reveals semantic associations: some words used to describe aspects of personality are often applied to the same person. For example, someone described as conscientious is more likely to be described as "always prepared" rather than "messy". These associations suggest five broad dimensions u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trait Theory
In psychology, trait theory (also called dispositional theory) is an approach to the study of human personality. Trait theorists are primarily interested in the measurement of ''traits'', which can be defined as habitual patterns of behaviour, thought, and emotion. According to this perspective, traits are aspects of personality that are relatively stable over time, differ across individuals (e.g. some people are outgoing whereas others are not), are relatively consistent over situations, and influence behaviour. Traits are in contrast to states, which are more transitory dispositions. In some theories and systems, traits are something a person either has or does not have, but in many others traits are dimensions such as extraversion vs. introversion, with each person rating somewhere along this spectrum. There are two approaches to define traits: as internal causal properties or as purely descriptive summaries. The internal causal definition states that traits influence our behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory
The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) is a standardized psychometric test of adult personality and psychopathology. Psychologists and other mental health professionals use various versions of the MMPI to help develop treatment plans, assist with differential diagnosis, help answer legal questions (forensic psychology), screen job candidates during the personnel selection process, or as part of a therapeutic assessment procedure. The original MMPI was developed by Starke R. Hathaway and J. C. McKinley, faculty of the University of Minnesota, and first published by the University of Minnesota Press in 1943. It was replaced by an updated version, the MMPI-2, in 1989 (Butcher, Dahlstrom, Graham, Tellegen, and Kaemmer). A version for adolescents, the MMPI-A, was published in 1992. An alternative version of the test, the MMPI-2 Restructured Form (MMPI-2-RF), published in 2008, retains some aspects of the traditional MMPI assessment strategy, but adopts a different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Psychology
Analytical psychology ( de , Analytische Psychologie, sometimes translated as analytic psychology and referred to as Jungian analysis) is a term coined by Carl Jung, a Swiss psychiatrist, to describe research into his new "empirical science" of the psyche. It was designed to distinguish it from Freud's psychoanalytic theories as their seven-year collaboration on psychoanalysis was drawing to an end between 1912 and 1913. (New Pathways in Psychology) The evolution of his science is contained in his monumental ''opus'', the ''The Collected Works of C. G. Jung, Collected Works'', written over sixty years of his lifetime. The history of analytical psychology is intimately linked with the biography of Jung. At the start, it was known as the "Zurich school", whose chief figures were Eugen Bleuler, Franz Riklin, Alphonse Maeder and Jung, all centred in the Burghölzli hospital in Zurich. It was initially a theory concerning psychological complexes until Jung, upon breaking with Sigmu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Eysenck
Hans Jürgen Eysenck (; 4 March 1916 – 4 September 1997) was a German-born British psychologist who spent his professional career in Great Britain. He is best remembered for his work on intelligence and personality, although he worked on other issues in psychology. At the time of his death, Eysenck was the most frequently cited living psychologist in the peer-reviewed scientific journal literature. Eysenck's research purported to show that certain personality types had an elevated risk of cancer and heart disease. Scholars have identified errors and suspected data manipulation in Eysenck's work, and large replications have failed to confirm the relationships that he purported to find. An enquiry on behalf of King's College London found the papers by Eysenck to be "incompatible with modern clinical science". In 2019, 26 of his papers (all coauthored with Ronald Grossarth-Maticek) were considered "unsafe" by an enquiry on behalf of King's College London. Fourteen of his pape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16 Personality Factors
The Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF) is a self-report personality test developed over several decades of empirical research by Raymond B. Cattell, Maurice Tatsuoka and Herbert Eber. The 16PF provides a measure of personality and can also be used by psychologists, and other mental health professionals, as a clinical instrument to help diagnose psychiatric disorders, and help with prognosis and therapy planning. The 16PF can also provide information relevant to the clinical and counseling process, such as an individual's capacity for insight, self-esteem, cognitive style, internalization of standards, openness to change, capacity for empathy, level of interpersonal trust, quality of attachments, interpersonal needs, attitude toward authority, reaction toward dynamics of power, frustration tolerance, and coping style. Thus, the 16PF instrument provides clinicians with a normal-range measurement of anxiety, adjustment, emotional stability and behavioral problems. Clinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy (psychological)
Energy is a concept in some psychological theories or models of a postulated unconscious mental functioning on a level between biology and consciousness. Philosophical accounts The idea harks back to Aristotle's conception of ''actus et potentia''. "Energy" here used in the literal meaning of "activity" or "operation". Henry More, in his 1642 ''Psychodia platonica; or a platonicall song of the soul'', defined an "energy of the soul" as including "every phantasm of the soul". Julian Sorell Huxley defines "mental energy" as "the driving forces of the psyche, emotional as well as intellectual" (''On living in a revolution'' xv.192, 1944). Psychoanalytic accounts In 1874, the concept of "psychodynamics" was proposed with the publication of ''Lectures on Physiology'' by German physiologist Ernst Wilhelm von Brücke who, in coordination with physicist Hermann von Helmholtz, one of the formulators of the first law of thermodynamics (conservation of energy), supposed that all living orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |