|
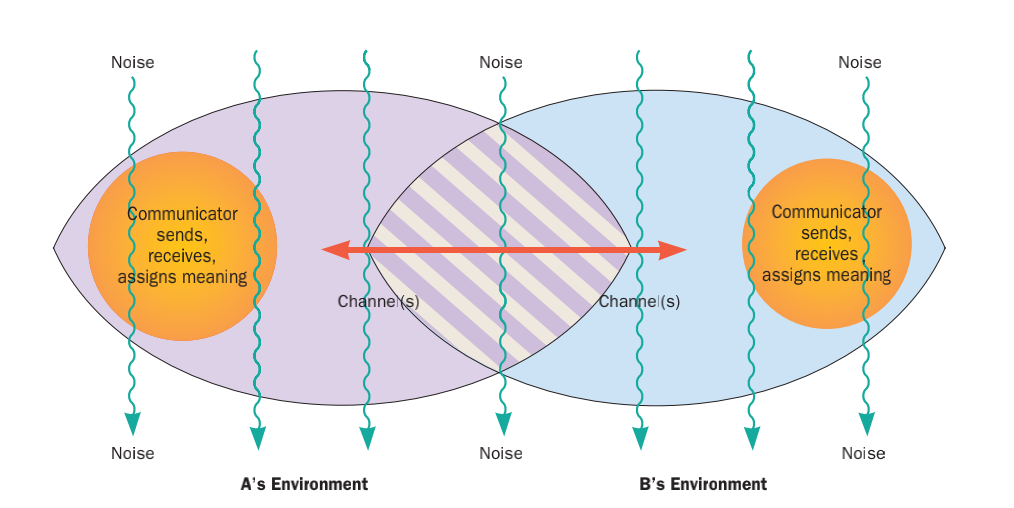
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during Face-to-face interaction, face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) Interpersonal deception theory, deceptive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More Courtesy LCCN98518549
More may refer to: Computing * MORE (application), outline software for Mac OS * more (command), a shell command * MORE protocol, a routing protocol * Missouri Research and Education Network Music Albums * More! (album), ''More!'' (album), by Booka Shade, 2010 * More (soundtrack), ''More'' (soundtrack), by Pink Floyd with music from the 1969 film * More... (Trace Adkins album), ''More...'' (Trace Adkins album), or the title song, 1999 * More (Mary Alessi album), ''More'' (Mary Alessi album), 2005 * More (Beyoncé EP), ''More'' (Beyoncé EP), 2014 * More (Michael Bublé EP), ''More'' (Michael Bublé EP), 2005 * More (Clarke-Boland Big Band album), ''More'' (Clarke-Boland Big Band album), 1968 * More (Double Dagger album), ''More'' (Double Dagger album), 2009 * More... (Montell Jordan album), ''More...'' (Montell Jordan album), 1996 * More (Crystal Lewis album), ''More'' (Crystal Lewis album), 2001 * More (Giuseppi Logan album), ''More'' (Giuseppi Logan album), 1966 * More (No Merc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-disclosure
Self-disclosure is a process of communication by which one person reveals information about themselves to another. The information can be descriptive or evaluative, and can include thoughts, feelings, aspirations, goals, failures, successes, fears, and dreams, as well as one's likes, dislikes, and favorites. Social penetration theory posits that there are two dimensions to self-disclosure: breadth and depth. Both are crucial in developing a fully intimate relationship. The range of topics discussed by two individuals is the breadth of disclosure. The degree to which the information revealed is private or personal is the depth of that disclosure. It is easier for breadth to be expanded first in a relationship because of its more accessible features; it consists of outer layers of personality and everyday lives, such as occupations and preferences. Depth is more difficult to reach, and includes painful memories and more unusual traits that we might hesitate to share with others. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward T
Edward is an English male name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortunate; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Dissonance
In the field of psychology, cognitive dissonance is described as a mental phenomenon in which people unknowingly hold fundamentally conflicting cognitions. Being confronted by situations that challenge this dissonance may ultimately result in some change in their cognitions or actions to cause greater alignment between them so as to reduce this dissonance. Relevant items of cognition include peoples' actions, feelings, ideas, beliefs, Value (ethics), values, and things in the Natural environment, environment. Cognitive dissonance exists without signs but surfaces through psychological stress when persons participate in an action that goes against one or more of conflicting things. According to this theory, when an action or idea is psychologically inconsistent with the other, people automatically try to resolve the conflict, usually by reframing a side to make the combination congruent. Discomfort is triggered by beliefs clashing with new information or by having to conceptually re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoni Kępiński
Antoni Ignacy Tadeusz Kępiński (16 November 1918 – 8 June 1972) was a Polish psychiatrist and philosopher. In his youth he was influenced by Carl Jung's approach. He is known as the originator of concepts like information metabolism (IM) and axiological psychiatry. Biography Kępiński was born in Dolina, which at that time was part of Poland (now southwestern Ukraine). During the childhood years, he resided in Nowy Sącz where his father held the position of starosta. He attended the élite Bartłomiej Nowodworski High School in Kraków. In 1936, Kępiński entered the Medical Faculty of the Jagiellonian University. In 1939, he interrupted his studies before graduation and volunteered for the Polish Army to defend his country from the impending Invasion of Poland. After the simultaneous Invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, Kępiński was captured and imprisoned in Hungary, to where he had fled. In 1940, he managed to escape imprisonment and headed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Metabolism
Information metabolism, sometimes referred to as informational metabolism or energetic-informational metabolism, is a psychological theory of interaction between biological organisms and their environment, developed by Polish psychiatrist Antoni Kępiński. Overview Kępiński described his psychological theory in several books but the most detailed description is given in his 1974 book ''Melancholy'' (in Polish: "Melancholia"). In order to explain psychological phenomena encountered in humans, he borrowed many concepts from the field of cybernetics which gained popularity in Poland at that time, thanks to the works of Marian Mazur (the father of the Polish school of cybernetics). Kępiński starts with the consideration of most basic organisms and how they are different from inanimate matter. First of all, any organism may be treated as an autonomous but open system, separated from its environment by means of a boundary (skin or cell membrane). As an open system, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Types
''Psychological Types'' () is a book by Carl Jung that was originally published in German by Rascher Verlag in 1921, and translated into English in 1923, becoming volume 6 of '' The Collected Works of C. G. Jung''. In the book, Jung proposes four main functions of consciousness: two perceiving or non-rational functions ( Sensation and Intuition), and two judging or rational functions ( Thinking and Feeling). These functions are modified by two main attitude types: extraversion and introversion. Jung proposes that the dominant function, along with the dominant attitude, characterizes consciousness, while its opposite is repressed and characterizes the unconscious. Based on this, the eight outstanding psychological types are: Extraverted sensation / Introverted sensation; Extraverted intuition / Introverted intuition; Extraverted thinking / Introverted thinking; and Extraverted feeling / Introverted feeling. Jung, as such, describes in detail the effects of tensions between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socionics
In psychology and sociology, socionics is a pseudoscientific theory of information processing and personality types. It incorporates Carl Jung's work on ''Psychological Types'' with Antoni Kępiński's theory of information metabolism. In contrast to the generally accepted views in personality psychology on age-related variability of the human psyche, socionics distinguishes 16 psychophysiological types (sociotypes) which it claims go unchanged throughout a person's life. The existence of personality types is extremely controversial in modern personality psychology. Socionics was developed in the 1970s and 1980s, primarily by the Lithuanian researcher . The name "socionics" is derived from the word "society", because believed that each sociotype has a distinct purpose in society. The central idea of socionics is that information is intuitively divisible into eight categories, called information elements, which a person's psyche processes using eight psychological functions. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palo Alto, California
Palo Alto ( ; Spanish language, Spanish for ) is a charter city in northwestern Santa Clara County, California, United States, in the San Francisco Bay Area, named after a Sequoia sempervirens, coastal redwood tree known as El Palo Alto. The city of Palo Alto was incorporated in 1894 by the American industrialist Leland Stanford and his wife, Jane Stanford, when they founded Stanford University in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr. Palo Alto later expanded and now borders East Palo Alto, California, East Palo Alto, Mountain View, California, Mountain View, Los Altos, California, Los Altos, Los Altos Hills, California, Los Altos Hills, Stanford, California, Stanford, Portola Valley, California, Portola Valley, and Menlo Park, California, Menlo Park. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 68,572. Palo Alto has one of the highest costs of living in the United States, and its residents are among the most educated in the country. However, it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Research Institute
The Palo Alto Mental Research Institute (MRI) is one of the founding institutions of brief and family therapy.Nichols, M., & Schwartz, R. (2005). ''Family Therapy: Concepts and Methods'' (7th Edition), New York City: Prentice Hall. Founded by Don D. Jackson and colleagues in 1958, MRI has been one of the leading sources of ideas in the area of interactional/systemic studies, psychotherapy Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ..., and family therapy. Overview According to an article in the ''Psychotherapy Networker'' on Jay Haley (a Research Associate at MRI in the 1960s) MRI "became the go-to place for any therapist who wanted to be on the cutting edge of psychotherapy research and practice. Fostering a climate of almost untrammeled experimentalism, MRI started the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Bateson
Gregory Bateson (9 May 1904 – 4 July 1980) was an English anthropology, anthropologist, social sciences, social scientist, linguistics, linguist, visual anthropology, visual anthropologist, semiotics, semiotician, and cybernetics, cyberneticist whose work intersected that of many other fields. His writings include ''Steps to an Ecology of Mind'' (1972) and ''Mind and Nature'' (1979). In Palo Alto, California, Bateson and in these days his non-colleagues developed the double bind, double-bind theory of schizophrenia. Bateson's interest in systems theory forms a thread running through his work. He was one of the original members of the core group of the Macy conferences in Cybernetics (1941–1960), and the later set on Group Processes (1954–1960), where he represented the social and behavioral sciences. He was interested in the relationship of these fields to epistemology. His association with the editor and author Stewart Brand helped widen his influence. Early life and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cybernetics
Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions (its outputs) return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with general principles that are relevant across multiple contexts, including in engineering, ecological, economic, biological, cognitive and social systems and also in practical activities such as designing, learning, and managing. Cybernetics' transdisciplinary character has meant that it intersects with a number of other fields, leading to it having both wide influence and diverse interpretations. The field is named after an example of circular causal feedback—that of steering a ship (the ancient Greek κυβερνήτης (''kybernḗtēs'') refers to the person who steers a ship). In steering a ship, the position of the rudder is adjusted in continual response to the effect it is observed as having, forming a feedback loop throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |