|
Independent Comic Publishing Boom
Alternative comics cover a range of American comics that have appeared since the 1980s, following the underground comix movement of the late 1960s and early 1970s. Alternative comics present an alternative to mainstream superhero comics which in the past have dominated the American comic book industry. Alternative comic books span a wide range of genres, artistic styles, and subjects. Alternative comics are often published in small numbers as the author(s) deem fit. They are often published with less regard for regular distribution schedules. Many alternative comics have variously been labelled post-underground comics, independent comics, indie comics, auteur comics, small press comics, new wave comics, creator-owned comics, art comics, or literary comics. Many self-published "minicomics" also fall under the "alternative" umbrella. From underground to alternative By the mid-1970s, artists within the underground comix scene felt that it had become less creative than it had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fantagraphics Books
Fantagraphics (previously Fantagraphics Books) is an American publisher of alternative comics, classic comic strip anthologies, manga, magazines, graphic novels, and the erotic Eros Comix imprint. History Founding Fantagraphics was founded in 1976 by Gary Groth and Michael Catron in College Park, Maryland. The company took over an adzine named ''The Nostalgia Journal'', which it renamed ''The Comics Journal''. As comics journalist (and former Fantagraphics employee) Michael Dean writes, "the publisher has alternated between flourishing and nearly perishing over the years." Kim Thompson joined the company in 1977, using his inheritance to keep the company afloat.Dean, Michael"Comics Community Comes to Fantagraphics' Rescue," ''The Comics Journal'', Posted July 11, 2003. (He soon became a co-owner.) The company moved from Washington, D.C. to Stamford, Connecticut, to Los Angeles over its early years, before settling in Seattle in 1989.Matos, Michelangelo"Saved by the Beag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
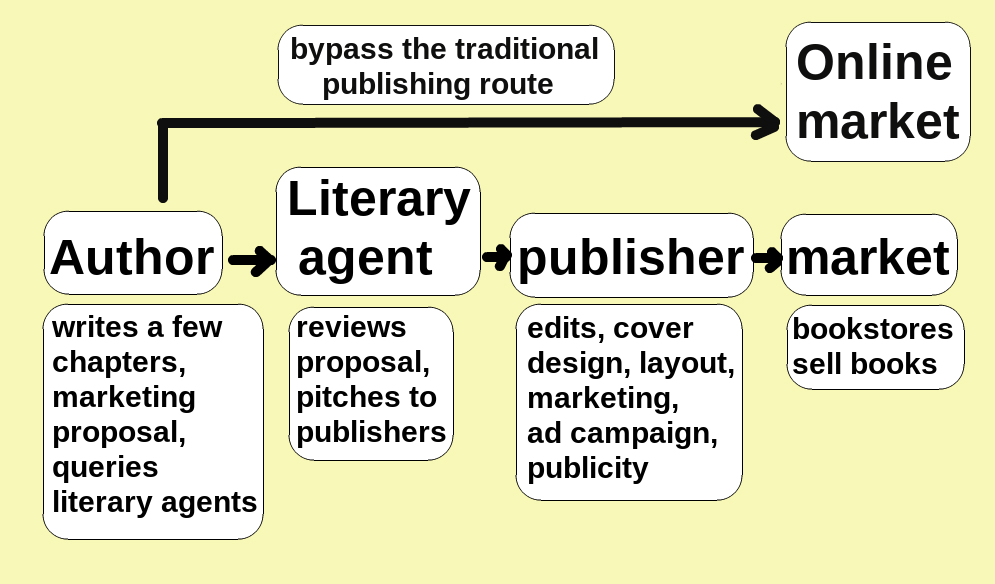
Self-published
Self-publishing is the publication of media by its author at their own cost, without the involvement of a publisher. The term usually refers to written media, such as books and magazines, either as an ebook or as a physical copy using POD (print on demand) technology. It may also apply to albums, pamphlets, brochures, games, video content, artwork, and zines. Web fiction is also a major medium for self-publishing. Definitions Although self-publishing is not a new phenomenon, dating back to the 18th century, it has transformed during the internet age with new technologies and services providing increasing alternatives to traditional publishing, becoming a $1 billion market.Jennifer Alsever, Fortune magazine, 30 December 2016The Kindle Effect Retrieved 9 November 2017, "...has become a $1 billion industry..." However, with the increased ease of publishing and the range of services available, confusion has arisen as to what constitutes self-publishing. In 2022, the Society o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebus The Aardvark
''Cerebus'' (; also ''Cerebus the Aardvark'') is a comic book series created by Canadian cartoonist Dave Sim, which ran from December 1977 until March 2004. The title character of the 300-issue series is an anthropomorphic aardvark who takes on a number of roles throughout the series—barbarian, prime minister, and Pope among them. The series stands out for its experimentation in form and content, and for the dexterity of its artwork, especially after background artist Gerhard joined with the 65th issue. As the series progressed, it increasingly became a platform for Sim's controversial beliefs. The comic began as a parody of sword and sorcery comics, primarily Marvel's version of Conan the Barbarian. However, it evolved to explore a variety of other topics, including politics, religion, and gender issues. At a total of 6,000 pages, it progressively became more serious and ambitious than its parodic roots. Sim announced early on that the series would end with the death of the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dave Sim
Dave Sim (born 17 May 1956) is a Canadian cartoonist and publisher, best known for his comic book ''Cerebus'', his artistic experimentation, his advocacy of self-publishing and creators' rights, and his controversial political and philosophical beliefs. Sim rose to prominence with ''Cerebus'', which began in December 1977. Sim initially conceived it as a parody of ''Conan the Barbarian'' and other sword and sorcery comics, but after two years he began to consider the series a self-contained work that would run for 300 issues and be subdivided into " novels". By the time the 6000-page work was completed in March 2004, Sim had delved into politics and a controversial examination of feminism and gender, while becoming progressively more sophisticated and experimental in his storytelling and artwork. Sim worked on ''Cerebus Archives'' afterward, and produced the comic books '' Glamourpuss'', which examines the history of photorealistic comics, and '' Judenhass'', about the Holocaust. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maus
''Maus'' is a graphic novel by American cartoonist Art Spiegelman, serialized from 1980 to 1991. It depicts Spiegelman interviewing his father about his experiences as a Polish Jew and Holocaust survivor. The work employs postmodern techniques, and represents Jews as mice and other Germans and Poles as cats and pigs. Critics have classified ''Maus'' as memoir, biography, history, fiction, autobiography, or a mix of genres. In 1992 it became the first graphic novel to win a Pulitzer Prize. In the frame-tale timeline in the narrative present that begins in 1978 in New York City, Spiegelman talks with his father Vladek about his Holocaust experiences, gathering material and information for the ''Maus'' project he is preparing. In the narrative past, Spiegelman depicts these experiences, from the years leading up to World War II to his parents' liberation from the Nazi concentration camps. Much of the story revolves around Spiegelman's troubled relationship with his father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manga
Manga (Japanese: 漫画 ) are comics or graphic novels originating from Japan. Most manga conform to a style developed in Japan in the late 19th century, and the form has a long prehistory in earlier Japanese art. The term ''manga'' is used in Japan to refer to both comics and cartooning. Outside of Japan, the word is typically used to refer to comics originally published in the country. In Japan, people of all ages and walks of life read manga. The medium includes works in a broad range of genres: action, adventure, business and commerce, comedy, detective, drama, historical, horror, mystery, romance, science fiction and fantasy, erotica ('' hentai'' and ''ecchi''), sports and games, and suspense, among others. Many manga are translated into other languages. Since the 1950s, manga has become an increasingly major part of the Japanese publishing industry. By 1995, the manga market in Japan was valued at (), with annual sales of 1.9billion manga books and manga magazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outsider Art
Outsider art is art made by self-taught or supposedly naïve artists with typically little or no contact with the conventions of the art worlds. In many cases, their work is discovered only after their deaths. Often, outsider art illustrates extreme mental states, unconventional ideas, or elaborate fantasy worlds. The term ''outsider art'' was coined in 1972 as the title of a book by art critic Roger Cardinal. It is an English equivalent for ''art brut'' (, "raw art" or "rough art"), a label created in the 1940s by French artist Jean Dubuffet to describe art created outside the boundaries of official culture. Dubuffet focused particularly on art by those on the outside of the established art scene, using as examples psychiatric hospital patients, hermits, and spiritualists.Cardinal, Roger (1972). ''Outsider Art''. New York: Praeger. pp. 24–30.Bibliography The 20th Century Art Book. New York, NY: Phaidon Press, 1996. Outsider art has emerged as a successful art marketing ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Crumb
Robert Dennis Crumb (; born August 30, 1943) is an American cartoonist and musician who often signs his work R. Crumb. His work displays a nostalgia for American folk culture of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and satire of contemporary American culture. Crumb is a prolific artist and contributed to many of the seminal works of the underground comix movement in the 1960s, including being a founder of the first successful underground comix publication, ''Zap Comix'', contributing to all 16 issues. He was additionally contributing to the ''East Village Other'' and many other publications, including a variety of one-off and anthology comics. During this time, inspired by psychedelics and cartoons from the 1920s and 1930s, he introduced a wide variety of characters that became extremely popular, including countercultural icons Fritz the Cat and Mr. Natural, and the images from his '' Keep On Truckin''' strip. Sexual themes abounded in all these projects, often shading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weirdo (magazine)
''Weirdo'' was a magazine-sized comics anthology created by Robert Crumb and published by Last Gasp from 1981 to 1993. Featuring cartoonists both new and old, ''Weirdo'' served as a "low art" counterpoint to its contemporary highbrow ''Raw'', co-edited by Art Spiegelman. Crumb contributed cover art and comics to every issue of ''Weirdo''; his wife, cartoonist Aline Kominsky-Crumb, also had work in almost every issue. Crumb focused increasingly on autobiography in his stories in ''Weirdo''. Many other autobiographical shorts would appear in ''Weirdo'' by other artists, including Kominsky-Crumb, Carol Tyler, Phoebe Gloeckner, and Dori Seda. David Collier, a Canadian ex-soldier, published autobiographical and historical comics in ''Weirdo''. The anthology introduced artists such as Peter Bagge, Dori Seda, Dennis Worden, and Carol Tyler. With issue #10, Crumb handed over the editing reins to Bagge; with issue #18, the reins went to Kominsky-Crumb (except for issue #25, which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Françoise Mouly
Françoise Mouly (; born 24 October 1955) is a Paris-born New York-based designer, editor, and publisher. She is best known as co-founder, co-editor, and publisher of the comics and graphics magazine ''Raw'' (1980–1991), as the publisher of Raw Books and Toon Books, and since 1993 as the art editor of ''The New Yorker''. Mouly is married to cartoonist Art Spiegelman, and is the mother of writer Nadja Spiegelman. As editor and publisher, Mouly has had considerable influence on the rise in production values in the English-language comics world since the early 1980s. She has played a role in providing outlets to new and foreign cartoonists, and in promoting comics as a serious artform and as an educational tool. The French government decorated Mouly as a Knight of the Order of Arts and Letters in 2001, and as Knight of the Legion of Honour in 2011. Biography Early life Mouly was born in 1955 in Paris, France, the second of three daughters to Josée and Roger Mouly. She grew u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Judenhass_00A_(Front_Cover).jpg)


