|
Images
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Images
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image In Glossographia
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Created With A Mobile Phone
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera Obscura
A camera obscura (; ) is a darkened room with a aperture, small hole or lens at one side through which an image is 3D projection, projected onto a wall or table opposite the hole. ''Camera obscura'' can also refer to analogous constructions such as a box or tent in which an exterior image is projected inside. Camera obscuras with a lens in the opening have been used since the second half of the 16th century and became popular as aids for drawing and painting. The concept was developed further into the photographic camera in the first half of the 19th century, when camera obscura boxes were used to exposure (photography), expose photosensitivity, light-sensitive materials to the projected image. The camera obscura was used to study eclipses without the risk of damaging the eyes by looking directly into the sun. As a drawing aid, it allowed tracing the projected image to produce a highly accurate representation, and was especially appreciated as an easy way to achieve proper grap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very Hardness (materials science), hard surface. A mirror is a Wave (physics), wave reflector. Light consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera
A camera is an Optics, optical instrument that can capture an image. Most cameras can capture 2D images, with some more advanced models being able to capture 3D images. At a basic level, most cameras consist of sealed boxes (the camera body), with a small hole (the aperture) that allows light to pass through in order to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface (usually a Image sensor, digital sensor or photographic film). Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive surface. Lenses focus the light entering the camera, and the aperture can be narrowed or widened. A Shutter (photography), shutter mechanism determines the amount of time the photosensitive surface is exposed to the light. The still image camera is the main instrument in the art of photography. Captured images may be reproduced later as part of the process of photography, digital imaging, or photographic printing. Similar artistic fields in the moving-image camera dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of printing as applied to paper was woodblock printing, which appeared in China before 220 AD for cloth printing. However, it would not be applied to paper until the seventh century.Shelagh Vainker in Anne Farrer (ed), "Caves of the Thousand Buddhas", 1990, British Museum publications, Later developments in printing technology include the movable type invented by Bi Sheng around 1040 AD and the printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. The technology of printing played a key role in the development of the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution and laid the material basis for the modern knowledge-based economy and the spread of learning to the masses. History Woodblock printing Woodblock p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
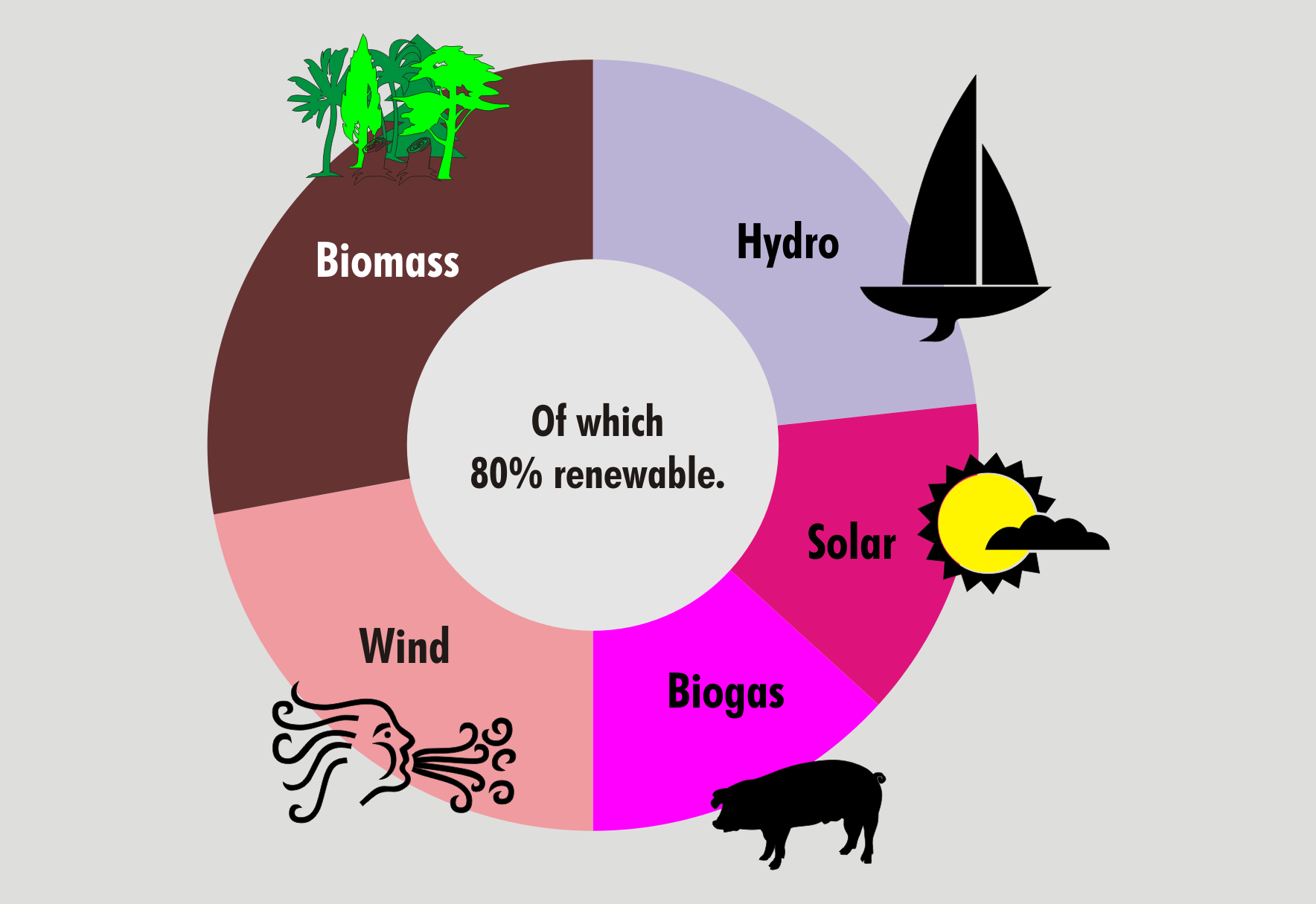
Pie Chart
A pie chart (or a circle chart) is a circular Statistical graphics, statistical graphic, which is divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each slice (and consequently its central angle and area) is Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the quantity it represents. While it is named for its resemblance to a pie which has been sliced, there are variations on the way it can be presented. The earliest known pie chart is generally credited to William Playfair's ''Statistical Breviary'' of 1801.Spence (2005)Tufte, p. 44 Pie charts are very widely used in the business world and the mass media.Cleveland, p. 262 However, they have been criticized,Wilkinson, p. 23. and many experts recommend avoiding them,Tufte, p. 178.van Belle, p. 160–162.Stephen Few"Save the Pies for Dessert" August 2007, Retrieved 2010-02-02Steve Fento"Pie Charts Are Bad"/ref> as research has shown it is difficult to compare different sections of a given pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawing
Drawing is a form of visual art in which an artist uses instruments to mark paper or other two-dimensional surface. Drawing instruments include graphite pencils, pen and ink, various kinds of paints, inked brushes, colored pencils, crayons, charcoal, chalk, pastels, erasers, markers, styluses, and metals (such as silverpoint). Digital drawing is the act of drawing on graphics software in a computer. Common methods of digital drawing include a stylus or finger on a touchscreen device, stylus- or finger-to-touchpad, or in some cases, a mouse. There are many digital art programs and devices. A drawing instrument releases a small amount of material onto a surface, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as cardboard, wood, plastic, leather, canvas, and board, have been used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard. Drawing has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)