|
Hypocycloidal
In geometry, a hypocycloid is a special plane curve generated by the trace of a fixed point on a small circle that rolls within a larger circle. As the radius of the larger circle is increased, the hypocycloid becomes more like the cycloid created by rolling a circle on a line. Properties If the smaller circle has radius , and the larger circle has radius , then the parametric equations for the curve can be given by either: :\begin & x (\theta) = (R - r) \cos \theta + r \cos \left(\frac \theta \right) \\ & y (\theta) = (R - r) \sin \theta - r \sin \left( \frac \theta \right) \end or: :\begin & x (\theta) = r (k - 1) \cos \theta + r \cos \left( (k - 1) \theta \right) \\ & y (\theta) = r (k - 1) \sin \theta - r \sin \left( (k - 1) \theta \right) \end If is an integer, then the curve is closed, and has cusps (i.e., sharp corners, where the curve is not differentiable). Specially for the curve is a straight line and the circles are called Cardano circles. Girolamo Cardano wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astroid2
In mathematics, an astroid is a particular type of roulette curve: a hypocycloid with four cusp (singularity), cusps. Specifically, it is the Locus (mathematics), locus of a point on a circle as it Rolling, rolls inside a fixed circle with four times the radius. By double generation, it is also the locus of a point on a circle as it rolls inside a fixed circle with 4/3 times the radius. It can also be defined as the Envelope (mathematics), envelope of a line segment of fixed length that moves while keeping an end point on each of the axes. It is therefore the Envelope (mathematics), envelope of the moving bar in the Trammel of Archimedes. Its modern name comes from the Greek word for "star". It was proposed, originally in the form of "Astrois", by Joseph Johann von Littrow in 1838. The curve had a variety of names, including tetracuspid (still used), cubocycloid, and paracycle. It is nearly identical in form to the evolute of an ellipse. Equations If the radius of the fixed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roulette (curve)
In the differential geometry of curves, a roulette is a kind of curve, generalizing cycloids, epicycloids, hypocycloids, trochoids, epitrochoids, hypotrochoids, and involutes. Definition Informal definition Roughly speaking, a roulette is the curve described by a point (called the ''generator'' or ''pole'') attached to a given curve as that curve rolls without slipping, along a second given curve that is fixed. More precisely, given a curve attached to a plane which is moving so that the curve rolls, without slipping, along a given curve attached to a fixed plane occupying the same space, then a point attached to the moving plane describes a curve, in the fixed plane called a roulette. Special cases and related concepts In the case where the rolling curve is a line and the generator is a point on the line, the roulette is called an involute of the fixed curve. If the rolling curve is a circle and the fixed curve is a line then the roulette is a trochoid. If, in this cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pittsburgh Steelers
The Pittsburgh Steelers are a professional American football team based in Pittsburgh. The Steelers compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the American Football Conference (AFC) North division. Founded in , the Steelers are the seventh-oldest franchise in the NFL, and the oldest franchise in the AFC. In contrast with their status as perennial also-rans in the pre-merger NFL, where they were the oldest team never to have won a league championship, the Steelers of the post-merger (modern) era are among the most successful NFL franchises, especially during their dynasty in the 1970s. The team is tied with the New England Patriots for the most Super Bowl titles at six, and they have both played in (sixteen times) and hosted (eleven times) more conference championship games than any other team in the NFL. The Steelers have also won eight AFC championships, tied with the Denver Broncos, but behind the Patriots' record eleven AFC championships. The team is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
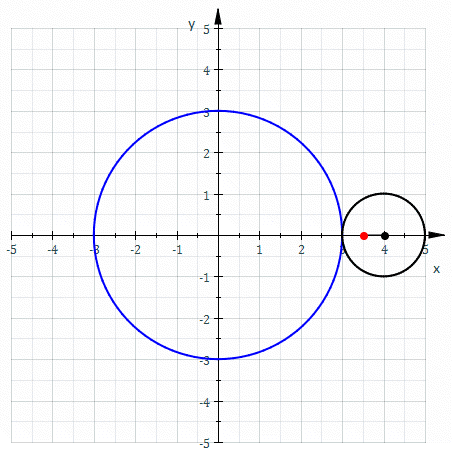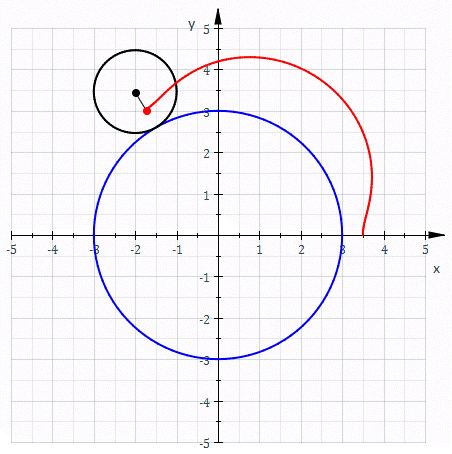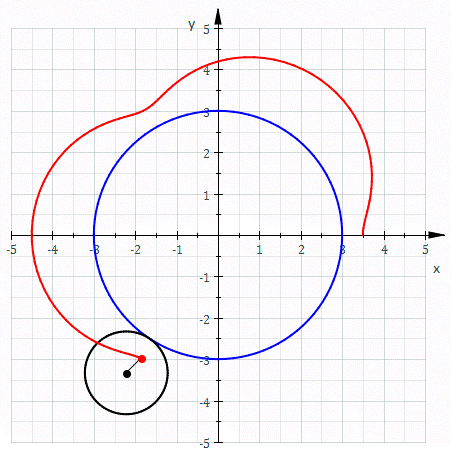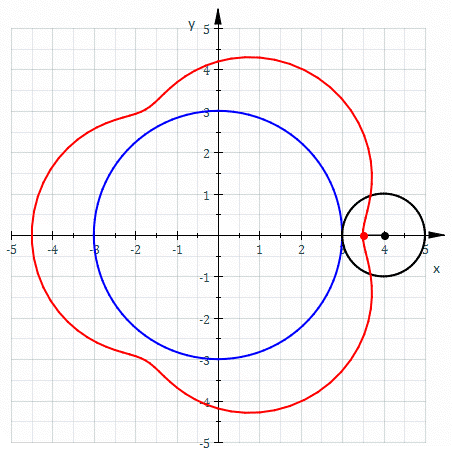
Epitrochoid
In geometry, an epitrochoid ( or ) is a roulette traced by a point attached to a circle of radius rolling around the outside of a fixed circle of radius , where the point is at a distance from the center of the exterior circle. The parametric equations for an epitrochoid are :\begin & x (\theta) = (R + r)\cos\theta - d\cos\left(\theta\right) \\ & y (\theta) = (R + r)\sin\theta - d\sin\left(\theta\right) \end The parameter is geometrically the polar angle of the center of the exterior circle. (However, is not the polar angle of the point (x(\theta),y(\theta)) on the epitrochoid.) Special cases include the limaçon with and the epicycloid with . The classic Spirograph toy traces out epitrochoid and hypotrochoid curves. The orbits of planets in the once popular geocentric Ptolemaic system are epitrochoids (see deferent and epicycle). The orbit of the moon, when centered around the sun, approximates an epitrochoid. The combustion chamber of the Wankel engine The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirograph
Spirograph is a geometric drawing device that produces mathematical roulette curves of the variety technically known as hypotrochoids and epitrochoids. The well-known toy version was developed by British engineer Denys Fisher and first sold in 1965. The name has been a registered trademark of Hasbro Inc. since 1998 following purchase of the company that had acquired the Denys Fisher company. The Spirograph brand was relaunched worldwide in 2013, with its original product configurations, by Kahootz Toys. History In 1827, Greek-born English architect and engineer Peter Hubert Desvignes developed and advertised a "Speiragraph", a device to create elaborate spiral drawings. A man named J. Jopling soon claimed to have previously invented similar methods. When working in Vienna between 1845 and 1848, Desvignes constructed a version of the machine that would help prevent banknote forgeries, as any of the nearly endless variations of roulette patterns that it could produce were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoptic
In the geometry of curves, an orthoptic is the set of points for which two tangents of a given curve meet at a right angle. Examples: # The orthoptic of a parabola is its directrix (proof: see below), # The orthoptic of an ellipse \tfrac + \tfrac = 1 is the director circle x^2 + y^2 = a^2 + b^2 (see below), # The orthoptic of a hyperbola \tfrac - \tfrac = 1,\ a > b is the director circle x^2 + y^2 = a^2 - b^2 (in case of there are no orthogonal tangents, see below), # The orthoptic of an astroid x^ + y^ = 1 is a quadrifolium with the polar equation r=\tfrac\cos(2\varphi), \ 0\le \varphi < 2\pi (see below). Generalizations: # An isoptic is the set of points for which two tangents of a given curve meet at a ''fixed angle'' (see [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rose Curve
A rose is either a woody perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred species and tens of thousands of cultivars. They form a group of plants that can be erect shrubs, climbing, or trailing, with stems that are often armed with sharp prickles. Their flowers vary in size and shape and are usually large and showy, in colours ranging from white through yellows and reds. Most species are native to Asia, with smaller numbers native to Europe, North America, and northwestern Africa. Species, cultivars and hybrids are all widely grown for their beauty and often are fragrant. Roses have acquired cultural significance in many societies. Rose plants range in size from compact, miniature roses, to climbers that can reach seven meters in height. Different species hybridize easily, and this has been used in the development of the wide range of garden roses. Etymology The name ''rose'' comes from L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedal Curve
A pedal (from the Latin '' pes'' ''pedis'', "foot") is a lever designed to be operated by foot and may refer to: Computers and other equipment * Footmouse, a foot-operated computer mouse * In medical transcription, a pedal is used to control playback of voice dictations Geometry * Pedal curve, a curve derived by construction from a given curve * Pedal triangle, a triangle obtained by projecting a point onto the sides of a triangle Music Albums * ''Pedals'' (Rival Schools album) * ''Pedals'' (Speak album) Other music * Bass drum pedal, a pedal used to play a bass drum while leaving the drummer's hands free to play other drums with drum sticks, hands, etc. * Effects pedal, a pedal used commonly for electric guitars * Pedal keyboard, a musical keyboard operated by the player's feet * Pedal harp, a modern orchestral harp with pedals used to change the tuning of its strings * Pedal point, a type of nonchord tone, usually in the bass * Pedal tone, a fundamental tone pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Involute
In mathematics, an involute (also known as an evolvent) is a particular type of curve that is dependent on another shape or curve. An involute of a curve is the locus of a point on a piece of taut string as the string is either unwrapped from or wrapped around the curve. It is a class of curves coming under the roulette family of curves. The evolute of an involute is the original curve. The notions of the involute and evolute of a curve were introduced by Christiaan Huygens in his work titled '' Horologium oscillatorium sive de motu pendulorum ad horologia aptato demonstrationes geometricae'' (1673). Involute of a parameterized curve Let \vec c(t),\; t\in _1,t_2 be a regular curve in the plane with its curvature nowhere 0 and a\in (t_1,t_2), then the curve with the parametric representation \vec C_a(t)=\vec c(t) -\frac\; \int_a^t, \vec c'(w), \; dw is an ''involute'' of the given curve. Adding an arbitrary but fixed number l_0 to the integral \Bigl(\int_a^t, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolute
In the differential geometry of curves, the evolute of a curve is the locus of all its centers of curvature. That is to say that when the center of curvature of each point on a curve is drawn, the resultant shape will be the evolute of that curve. The evolute of a circle is therefore a single point at its center. Equivalently, an evolute is the envelope of the normals to a curve. The evolute of a curve, a surface, or more generally a submanifold, is the caustic of the normal map. Let be a smooth, regular submanifold in . For each point in and each vector , based at and normal to , we associate the point . This defines a Lagrangian map, called the normal map. The caustic of the normal map is the evolute of . Evolutes are closely connected to involutes: A curve is the evolute of any of its involutes. History Apollonius ( 200 BC) discussed evolutes in Book V of his ''Conics''. However, Huygens is sometimes credited with being the first to study them (1673). Huygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicycloid
In geometry, an epicycloid is a plane curve produced by tracing the path of a chosen point on the circumference of a circle—called an ''epicycle''—which rolls without slipping around a fixed circle. It is a particular kind of roulette. Equations If the smaller circle has radius , and the larger circle has radius , then the parametric equations for the curve can be given by either: :\begin & x (\theta) = (R + r) \cos \theta \ - r \cos \left( \frac \theta \right) \\ & y (\theta) = (R + r) \sin \theta \ - r \sin \left( \frac \theta \right) \end or: :\begin & x (\theta) = r (k + 1) \cos \theta - r \cos \left( (k + 1) \theta \right) \\ & y (\theta) = r (k + 1) \sin \theta - r \sin \left( (k + 1) \theta \right) \end in a more concise and complex form :z(\theta) = r \left(e^ - (k + 1)e^ \right) where * angle is in turns: \theta \in , 2\pi * smaller circle has radius * the larger circle has radius Area (Assuming the initial point lies on the larger circle.) When is a pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgroup
In group theory, a branch of mathematics, given a group ''G'' under a binary operation ∗, a subset ''H'' of ''G'' is called a subgroup of ''G'' if ''H'' also forms a group under the operation ∗. More precisely, ''H'' is a subgroup of ''G'' if the restriction of ∗ to is a group operation on ''H''. This is often denoted , read as "''H'' is a subgroup of ''G''". The trivial subgroup of any group is the subgroup consisting of just the identity element. A proper subgroup of a group ''G'' is a subgroup ''H'' which is a proper subset of ''G'' (that is, ). This is often represented notationally by , read as "''H'' is a proper subgroup of ''G''". Some authors also exclude the trivial group from being proper (that is, ). If ''H'' is a subgroup of ''G'', then ''G'' is sometimes called an overgroup of ''H''. The same definitions apply more generally when ''G'' is an arbitrary semigroup, but this article will only deal with subgroups of groups. Subgroup tests Suppose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)