|
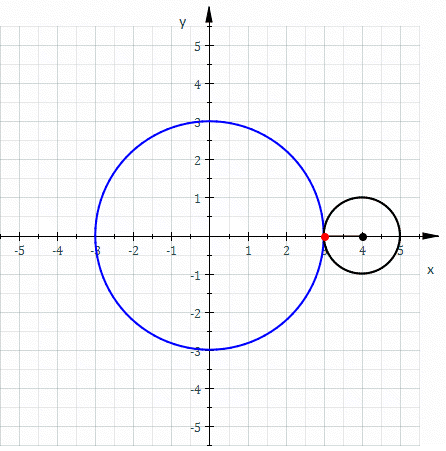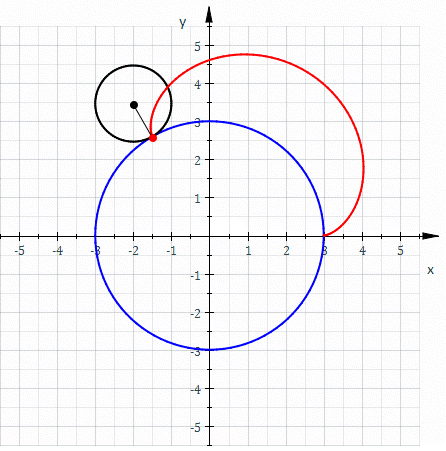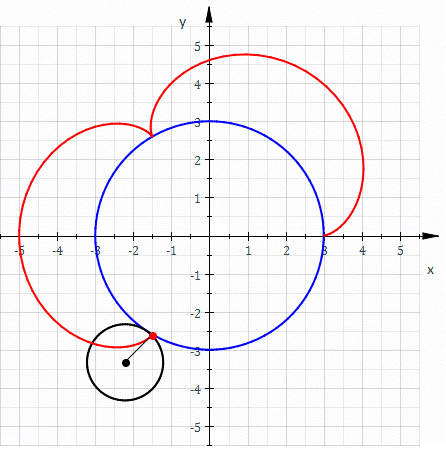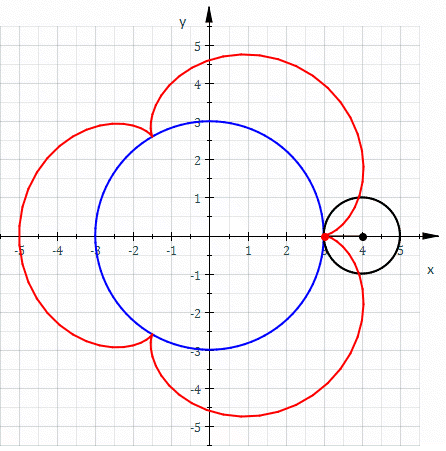
Involute
In mathematics, an involute (also known as an evolvent) is a particular type of curve that is dependent on another shape or curve. An involute of a curve is the Locus (mathematics), locus of a point on a piece of taut string as the string is either unwrapped from or wrapped around the curve. The evolute of an involute is the original curve. It is generalized by the Roulette (curve), roulette family of curves. That is, the involutes of a curve are the roulettes of the curve generated by a straight line. The notions of the involute and evolute of a curve were introduced by Christiaan Huygens in his work titled ''Horologium Oscillatorium, Horologium oscillatorium sive de motu pendulorum ad horologia aptato demonstrationes geometricae'' (1673), where he showed that the involute of a cycloid is still a cycloid, thus providing a method for constructing the cycloidal pendulum, which has the useful property that its period is independent of the amplitude of oscillation. Involute of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolute
In the differential geometry of curves, the evolute of a curve is the locus (mathematics), locus of all its Center of curvature, centers of curvature. That is to say that when the center of curvature of each point on a curve is drawn, the resultant shape will be the evolute of that curve. The evolute of a circle is therefore a single point at its center. Equivalently, an evolute is the envelope (mathematics), envelope of the perpendicular, normals to a curve. The evolute of a curve, a surface, or more generally a submanifold, is the caustic (mathematics), caustic of the normal map. Let be a smooth, regular submanifold in . For each point in and each vector , based at and normal to , we associate the point . This defines a Lagrangian map, called the normal map. The caustic of the normal map is the evolute of . Evolutes are closely connected to involutes: A curve is the evolute of any of its involutes. History Apollonius of Perga, Apollonius ( 200 BC) discussed evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cycloidal Pendulum
In geometry, a cycloid is the curve traced by a point on a circle as it rolls along a straight line without slipping. A cycloid is a specific form of trochoid and is an example of a roulette, a curve generated by a curve rolling on another curve. The cycloid, with the cusps pointing upward, is the curve of fastest descent under uniform gravity (the brachistochrone curve). It is also the form of a curve for which the period of an object in simple harmonic motion (rolling up and down repetitively) along the curve does not depend on the object's starting position (the tautochrone curve). In physics, when a charged particle at rest is put under a uniform electric and magnetic field perpendicular to one another, the particle’s trajectory draws out a cycloid. History The cycloid has been called "The Helen of Geometers" as, like Helen of Troy, it caused frequent quarrels among 17th-century mathematicians, while Sarah Hart sees it named as such "because the properties of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedean Spiral
The Archimedean spiral (also known as Archimedes' spiral, the arithmetic spiral) is a spiral named after the 3rd-century BC Ancient Greece, Greek mathematician Archimedes. The term ''Archimedean spiral'' is sometimes used to refer to the more general class of spirals of this type (see below), in contrast to ''Archimedes' spiral'' (the specific arithmetic spiral of Archimedes). It is the locus (mathematics), locus corresponding to the locations over time of a point moving away from a fixed point with a constant speed along a line that rotates with constant angular velocity. Equivalently, in Polar coordinate system, polar coordinates it can be described by the equation r = b\cdot\theta with real number . Changing the parameter controls the distance between loops. From the above equation, it can thus be stated: position of the particle from point of start is proportional to angle as time elapses. Archimedes described such a spiral in his book ''On Spirals''. Conon of Samos was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Parallel Curve
A parallel of a curve is the envelope (mathematics), envelope of a family of Congruence (geometry), congruent circles centered on the curve. It generalises the concept of ''parallel (geometry), parallel (straight) lines''. It can also be defined as a curve whose points are at a constant ''normal distance'' from a given curve. These two definitions are not entirely equivalent as the latter assumes smoothness, whereas the former does not. In computer-aided design the preferred term for a parallel curve is offset curve. (In other geometric contexts, offset (other), the term offset can also refer to Translation (geometry), translation.) Offset curves are important, for example, in numerically controlled machining, where they describe, for example, the shape of the cut made by a round cutting tool of a two-axis machine. The shape of the cut is offset from the trajectory of the cutter by a constant distance in the direction normal to the cutter trajectory at every point. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tractrix
In geometry, a tractrix (; plural: tractrices) is the curve along which an object moves, under the influence of friction, when pulled on a horizontal plane by a line segment attached to a pulling point (the ''tractor'') that moves at a right angle to the initial line between the object and the puller at an infinitesimal speed. It is therefore a curve of pursuit. It was first introduced by Claude Perrault in 1670, and later studied by Isaac Newton (1676) and Christiaan Huygens (1693). Mathematical derivation Suppose the object is placed at and the puller at the origin, so that is the length of the pulling thread. (In the example shown to the right, the value of is 4.) Suppose the puller starts to move along the axis in the positive direction. At every moment, the thread will be tangent to the curve described by the object, so that it becomes completely determined by the movement of the puller. Mathematically, if the coordinates of the object are , then by the Pythagorean the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Horologium Oscillatorium
(English language, English: ''The Pendulum Clock: or Geometrical Demonstrations Concerning the Motion of Pendula as Applied to Clocks'') is a book published by Dutch mathematician and physicist Christiaan Huygens in 1673 and his major work on pendulum, pendula and horology. It is regarded as one of the three most important works on mechanics in the 17th century, the other two being Galileo Galilei, Galileo’s ''Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences'' (1638) and Isaac Newton, Newton’s (1687). Much more than a mere description of clocks, Huygens's is the first modern treatise in which a physical problem (the Acceleration, accelerated motion of a falling body) is Mathematical model, idealized by a set of Parameter, parameters then analyzed mathematically and constitutes one of the seminal works of applied mathematics.Bruce, I. (2007). Christian Huygens: Horologium Oscillatorium'. Translated and annotated by Ian Bruce. The book is also known fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roulette (curve)
In the differential geometry of curves, a roulette is a kind of curve, generalizing cycloids, epicycloids, hypocycloids, trochoids, epitrochoids, hypotrochoids, and involutes. On a basic level, it is the path traced by a curve while rolling on another curve without slipping. Definition Informal definition Roughly speaking, a roulette is the curve described by a point (called the ''generator'' or ''pole'') attached to a given curve as that curve rolls without slipping, along a second given curve that is fixed. More precisely, given a curve attached to a plane which is moving so that the curve rolls, without slipping, along a given curve attached to a fixed plane occupying the same space, then a point attached to the moving plane describes a curve, in the fixed plane called a roulette. Special cases and related concepts In the case where the rolling curve is a line and the generator is a point on the line, the roulette is called an involute of the fixed curve. If the rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catenary
In physics and geometry, a catenary ( , ) is the curve that an idealized hanging chain or wire rope, cable assumes under its own weight when supported only at its ends in a uniform gravitational field. The catenary curve has a U-like shape, superficially similar in appearance to a parabola, which it is not. The curve appears in the design of certain types of Catenary arch, arches and as a cross section of the catenoid—the shape assumed by a soap film bounded by two parallel circular rings. The catenary is also called the alysoid, chainette,#MathWorld, MathWorld or, particularly in the materials sciences, an example of a funicular curve, funicular. Rope statics describes catenaries in a classic statics problem involving a hanging rope. Mathematically, the catenary curve is the Graph of a function, graph of the hyperbolic cosine function. The surface of revolution of the catenary curve, the catenoid, is a minimal surface, specifically a minimal surface of revolution. A ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Semicubical Parabola
In mathematics, a cuspidal cubic or semicubical parabola is an algebraic plane curve that has an implicit equation of the form : y^2 - a^2 x^3 = 0 (with ) in some Cartesian coordinate system. Solving for leads to the ''explicit form'' : y = \pm a x^, which imply that every real point satisfies . The exponent explains the term ''semicubical parabola''. (A parabola can be described by the equation .) Solving the implicit equation for yields a second ''explicit form'' :x = \left(\frac\right)^. The parametric equation : \quad x = t^2, \quad y = a t^3 can also be deduced from the implicit equation by putting t = \frac. . The semicubical parabolas have a cuspidal singularity; hence the name of ''cuspidal cubic''. The arc length of the curve was calculated by the English mathematician William Neile and published in 1657 (see section History). Properties of semicubical parabolas Similarity Any semicubical parabola (t^2,at^3) is similar to the ''semicubical unit parabola'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's ''Elements'': "The urvedline is €¦the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which €¦will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image of an interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this article, these curves are sometimes called ''topological curves'' to distinguish them from more constrained curves su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |