|
Humanized Mice
A humanized mouse is a mouse carrying functioning human genes, cells, tissues, and/or organs. Humanized mice are commonly used as small animal models in biological and medical research for human therapeutics. A humanized mouse or a humanized mouse model is one that has been xenotransplanted with human cells and/or engineered to express human gene products, so as to be utilized for gaining relevant insights in the ''in vivo'' context for understanding of human-specific physiology and pathologies. A lot of our knowledge about several human biological processes has been obtained from studying animal models like rodents and non-human primates. In particular, small animals such as mice are advantageous in such studies owing to their small size, brief reproductive cycle, easy handling and due to the genomic and physiological similarities with humans; moreover, these animals can also be genetically modified easily. Nevertheless, there are several incongruencies of these animal systems wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenotransplantation
Xenotransplantation (''xenos-'' from the Greek meaning "foreign" or strange), or heterologous transplant, is the transplantation of living cells, tissues or organs from one species to another. Such cells, tissues or organs are called xenografts or xenotransplants. It is contrasted with allotransplantation (from other individual of same species), syngeneic transplantation or isotransplantation (grafts transplanted between two genetically identical individuals of the same species) and autotransplantation (from one part of the body to another in the same person). Xenotransplantation of human tumor cells into immunocompromised mice is a research technique frequently used in pre-clinical oncology research. Human xenotransplantation offers a potential treatment for end-stage organ failure, a significant health problem in parts of the industrialized world. It also raises many novel medical, legal and ethical issues. A continuing concern is that many animals, such as pigs, have a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocyte, as well as through monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice. History and name The name "interleukin" was chosen in 1979, to replace the various different names used by different research groups to designate interleukin 1 (lymphocyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human-animal Hybrid
Anthrozoology, also known as human–nonhuman-animal studies (HAS), is the subset of ethnobiology that deals with biological interaction, interactions between humans and other animals. It is an interdisciplinary field that overlaps with other disciplines including anthropology, ethnology, medicine, psychology, social work, veterinary medicine, and zoology. A major focus of anthrozoologic research is the quantifying of the positive effects of human–animal relationships on either party and the study of their interactions. It includes scholars from fields such as anthropology, sociology, biology, history and philosophy. Anthrozoology scholars, such as Pauleen Bennett recognize the lack of scholarly attention given to non-human animals in the past, and to the relationships between human and non-human animals, especially in the light of the magnitude of animal representations, symbols, stories and their actual physical presence in human societies. Rather than a unified approach, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
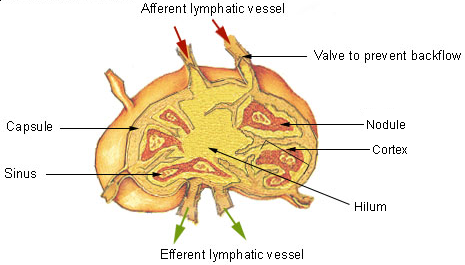
Secondary Lymphoid Organ
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Class Switching
Immunoglobulin class switching, also known as isotype switching, isotypic commutation or class-switch recombination (CSR), is a biological mechanism that changes a B cell's production of immunoglobulin from one type to another, such as from the isotype IgM to the isotype IgG. During this process, the constant-region portion of the antibody heavy chain is changed, but the variable region of the heavy chain stays the same (the terms ''variable'' and ''constant'' refer to changes or lack thereof between antibodies that target different epitopes). Since the variable region does not change, class switching does not affect antigen specificity. Instead, the antibody retains affinity for the same antigens, but can interact with different effector molecules. Mechanism Class switching occurs after activation of a mature B cell via its membrane-bound antibody molecule (or B cell receptor) to generate the different classes of antibody, all with the same variable domains as the origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen-presenting Cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). APCs process antigens and present them to T-cells. Almost all cell types can present antigens in some way. They are found in a variety of tissue types. Professional antigen-presenting cells, including macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells, present foreign antigens to helper T cells, while virus-infected cells (or cancer cells) can present antigens originating inside the cell to cytotoxic T cells. In addition to the MHC family of proteins, antigen presentation relies on other specialized signaling molecules on the surfaces of both APCs and T cells. Antigen-presenting cells are vital for effective adaptive immune response, as the functioning of both cytotoxic and helper T cells is dependent on APCs. Antigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leukocyte Antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals. Mutations in HLA genes may be linked to autoimmune disease such as type I diabetes, and celiac disease. The HLA gene complex resides on a 3 Mbp stretch within chromosome 6, p-arm at 21.3. HLA genes are highly polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles, allowing them to fine-tune the adaptive immune system. The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as ''antigens'', as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. HLAs corresponding to MHC class I ( A, B, and C), all of which are the HLA Class1 group, present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells or large granular lymphocytes (LGL), are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system that belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cell and other intracellular pathogens acting at around 3 days after infection, and respond to tumor formation. Typically, immune cells detect the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) presented on infected cell surfaces, triggering cytokine release, causing the death of the infected cell by lysis or apoptosis. NK cells are unique, however, as they have the ability to recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recombination-activating Gene
The recombination-activating genes (RAGs) encode parts of a protein complex that plays important roles in the rearrangement and recombination of the genes encoding immunoglobulin and T cell receptor molecules. There are two recombination-activating genes RAG1 and RAG2, whose cellular expression is restricted to lymphocytes during their developmental stages. The enzymes encoded by these genes, RAG-1 and RAG-2, are essential to the generation of mature B cells and T cells, two types of lymphocyte that are crucial components of the adaptive immune system. Function In the vertebrate immune system, each antibody is customized to attack one particular antigen (foreign proteins and carbohydrates) without attacking the body itself. The human genome has at most 30,000 genes, and yet it generates millions of different antibodies, which allows it to be able to respond to invasion from millions of different antigens. The immune system generates this diversity of antibodies by shuffling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |