|
Hopper Crystal
A hopper crystal is a form of crystal, the shape of which resembles that of a pyramidal hopper container. The edges of hopper crystals are fully developed, but the interior spaces are not filled in. This results in what appears to be a hollowed out step lattice formation, as if someone had removed interior sections of the individual crystals. In fact, the "removed" sections never filled in, because the crystal was growing so rapidly that there was not enough time (or material) to fill in the gaps. The interior edges of a hopper crystal still show the crystal form characteristic to the specific mineral, and so appear to be a series of smaller and smaller stepped down miniature versions of the original crystal. Hoppering occurs when electrical attraction is higher along the edges of the crystal; this causes faster growth at the edges than near the face centers. This attraction draws the mineral molecules more strongly than the interior sections of the crystal, thus the edges dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
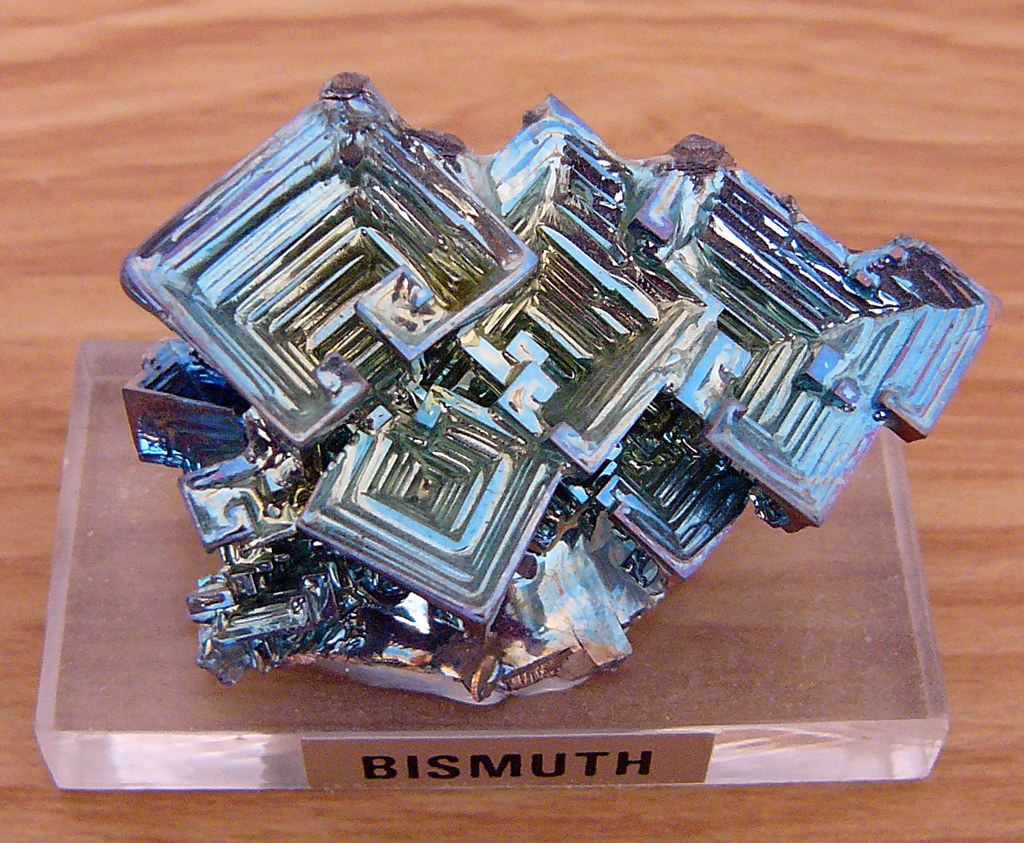
Bismuth Crystal
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The metal's only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, experiences alpha decay at such a minute rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galena
Galena, also called lead glance, is the natural mineral form of lead(II) sulfide (PbS). It is the most important ore of lead and an important source of silver. Galena is one of the most abundant and widely distributed sulfide minerals. It crystallizes in the cubic crystal system often showing octahedral forms. It is often associated with the minerals sphalerite, calcite and fluorite. Occurrence Galena is the main ore of lead, used since ancient times, since lead can be smelted from galena in an ordinary wood fire. Galena typically is found in hydrothermal veins in association with sphalerite, marcasite, chalcopyrite, cerussite, anglesite, dolomite, calcite, quartz, barite, and fluorite. It is also found in association with sphalerite in low-temperature lead-zinc deposits within limestone beds. Minor amounts are found in contact metamorphic zones, in pegmatites, and disseminated in sedimentary rock. In some deposits the galena contains up to 0.5% silver, a byprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A New Kind Of Science
''A New Kind of Science'' is a book by Stephen Wolfram, published by his company Wolfram Research under the imprint Wolfram Media in 2002. It contains an empirical and systematic study of computational systems such as cellular automata. Wolfram calls these systems ''simple programs'' and argues that the scientific philosophy and methods appropriate for the study of simple programs are relevant to other fields of science. Contents Computation and its implications The thesis of ''A New Kind of Science'' (''NKS'') is twofold: that the nature of computation must be explored experimentally, and that the results of these experiments have great relevance to understanding the physical world. Simple programs The basic subject of Wolfram's "new kind of science" is the study of simple abstract rules—essentially, elementary computer programs. In almost any class of a computational system, one very quickly finds instances of great complexity among its simplest cases (after a time serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frito-Lay
Frito-Lay is an American subsidiary of PepsiCo that manufactures, markets, and sells corn chips, potato chips, and other snack foods. The primary snack food brands produced under the Frito-Lay name include Fritos corn chips, Cheetos cheese-flavored snacks, Doritos and Tostitos tortilla chips, Lay's and Ruffles potato chips, Rold Gold pretzels, and Walkers potato crisps (in the UK and Ireland). Each brand generated annual worldwide sales over $1 billion in 2009. Frito-Lay began in the early 1930s as two separate companies, "The Frito Company" and "H.W. Lay & Company", which merged in 1961 to form "Frito-Lay, Inc". In 1965, Frito-Lay, Inc. merged with the Pepsi-Cola Company, resulting in the formation of PepsiCo. Since then, Frito-Lay has operated as a wholly owned subsidiary of PepsiCo. Through Frito-Lay, PepsiCo is the largest globally distributed snack food company, with sales of its products in 2009 comprising 40 percent of all "savory snacks" sold in the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food, energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, H2O, indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. "Water" is also the name of the liquid state of H2O at standard temperature and pressure. A number of natural states of water exist. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice may precipitate in the form of snow. The gaseous state of water is steam or water vapor. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halite
Halite (), commonly known as rock salt, is a type of salt, the mineral (natural) form of sodium chloride ( Na Cl). Halite forms isometric crystals. The mineral is typically colorless or white, but may also be light blue, dark blue, purple, pink, red, orange, yellow or gray depending on inclusion of other materials, impurities, and structural or isotopic abnormalities in the crystals. It commonly occurs with other evaporite deposit minerals such as several of the sulfates, halides, and borates. The name ''halite'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word for "salt", ἅλς (''háls''). Occurrence Halite dominantly occurs within sedimentary rocks where it has formed from the evaporation of seawater or salty lake water. Vast beds of sedimentary evaporite minerals, including halite, can result from the drying up of enclosed lakes and restricted seas. Such salt beds may be hundreds of meters thick and underlie broad areas. Halite occurs at the surface today in playas in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German ''Calcit'', a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for lime, ''calx'' (genitive calcis) with the suffix "-ite" used to name minerals. It is thus etymologically related to chalk. When applied by archaeologists and stone trade professionals, the term alabaster is used not just as in geology and mineralogy, where it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium ( gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral definin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The metal's only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, experiences alpha decay at such a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
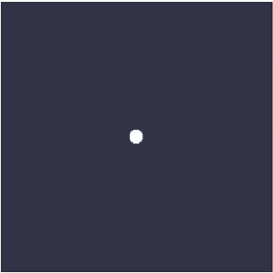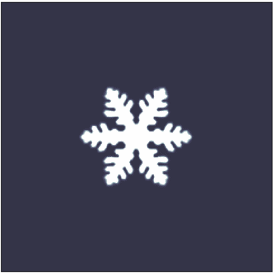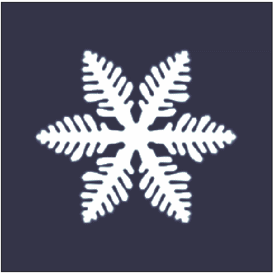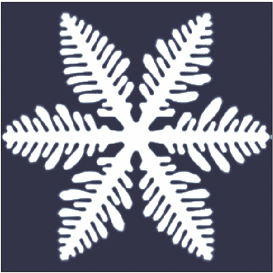
Dendrite (crystal)
A crystal dendrite is a crystal that develops with a typical multi-branching form. The name comes from the Greek word dendron (δενδρον) which means "tree", since the crystal's structure resembles that of a tree. These crystals can be synthesised by using a supercooled pure liquid, however they are also quite common in nature. The most common crystals in nature exhibit dendritic growth are snowflakes and frost on windows, but many minerals and metals can also be found in dendritic structures. History Maximum velocity principle The first dendritic patterns were discovered in palaeontology and are often mistaken for fossils because of their appearance. The first theory for the creation of these patterns was published by Nash and Glicksman in 1974, they used a very mathematical method and derived a non-linear integro-differential equation for a classical needle growth. However they only found an inaccurate numerical solution close to the tip of the needle and they f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |