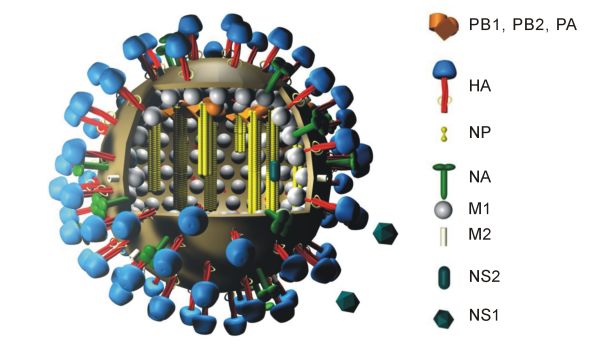
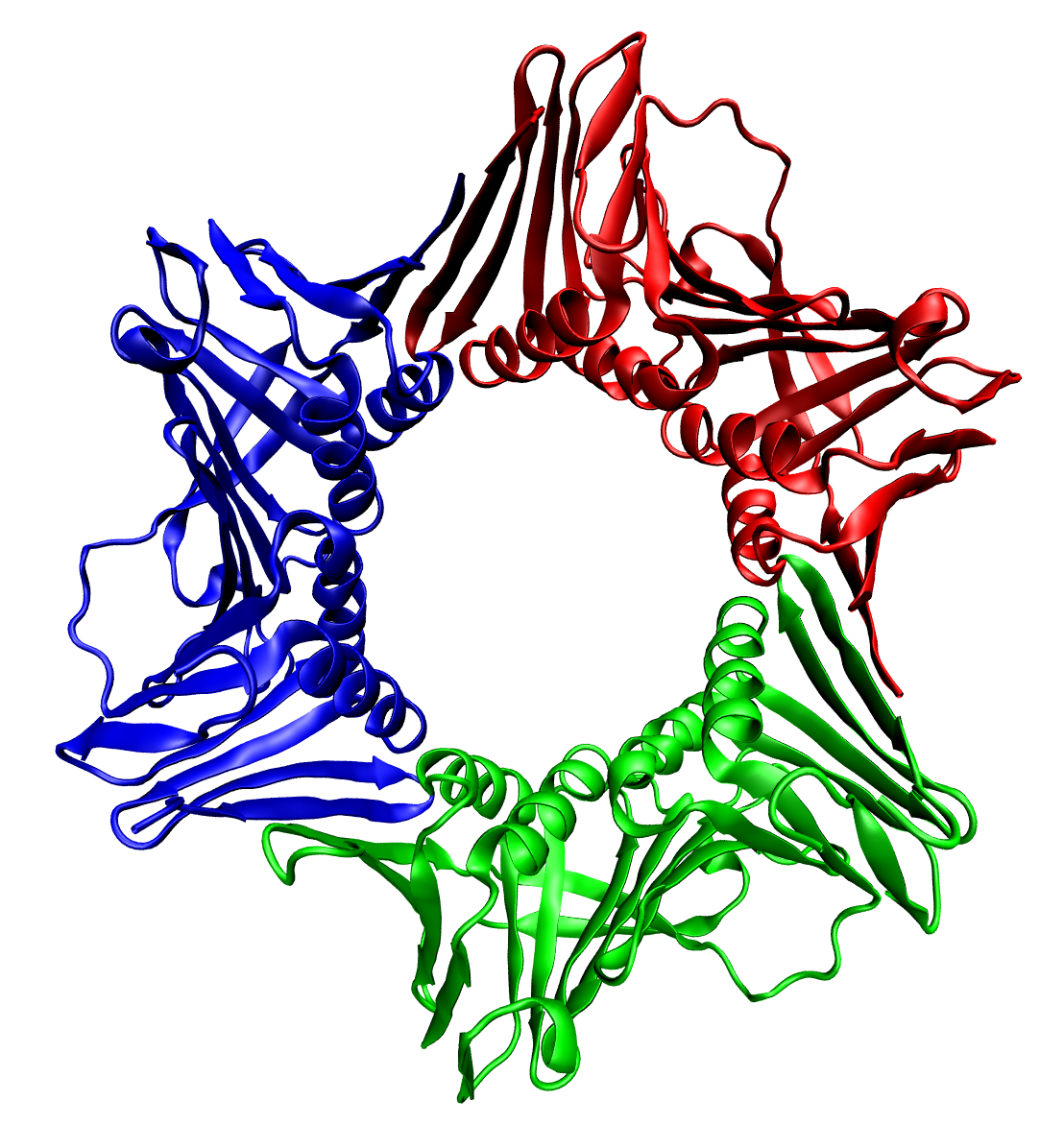
|
Homotrimer
thumbnail, 400px, Trimeric form of a TNF-α mutant A homotrimer is a protein which is composed of three identical units of polypeptide. Examples * Hemagglutinin (influenza) * Spike protein (coronavirus) See also * Protein trimer In biochemistry, a protein trimer is a macromolecular complex formed by three, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids. A homotrimer would be formed by three identical molecules. A heterotrimer would be formed ... References Peptides {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutinin (influenza)
Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) or haemagglutinin .html" ;"title="/sup>">/sup> (British English) is a homotrimeric glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and is integral to its infectivity. Hemagglutinin is a Class I Fusion Protein, having multifunctional activity as both an attachment factor and membrane fusion protein. Therefore, HA is responsible for binding Influenza virus to sialic acid on the surface of target cells, such as cells in the upper respiratory tract or erythrocytes, causing as a result the internalization of the virus. Secondarily, HA is responsible for the fusion of the viral envelope with the late endosomal membrane once exposed to low pH (5.0-5.5). The name "hemagglutinin" comes from the protein's ability to cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. Subtypes Hemagglutinin (HA) in influenza A has at least 18 different subtypes. These subtypes are named H1 through H18. H16 was discovered in 2004 on in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Spike Protein
Spike (S) glycoprotein (sometimes also called spike protein, formerly known as E2) is the largest of the four major structural proteins found in coronaviruses. The spike protein assembles into trimers that form large structures, called spikes or peplomers, that project from the surface of the virion. The distinctive appearance of these spikes when visualized using negative stain transmission electron microscopy, "recalling the solar corona", gives the virus family its name. The function of the spike glycoprotein is to mediate viral entry into the host cell by first interacting with molecules on the exterior cell surface and then fusing the viral and cellular membranes. Spike glycoprotein is a class I fusion protein that contains two regions, known as S1 and S2, responsible for these two functions. The S1 region contains the receptor-binding domain that binds to receptors on the cell surface. Coronaviruses use a very diverse range of receptors; SARS-CoV (which causes SARS) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Trimer
In biochemistry, a protein trimer is a macromolecular complex formed by three, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids. A homotrimer would be formed by three identical molecules. A heterotrimer would be formed by three different macromolecules. Type II Collagen is an example of homotrimeric protein. Porins usually arrange themselves in membranes as trimers. Bacteriophage T4 tail fiber Multiple copies of a polypeptide encoded by a gene often can form an aggregate referred to as a multimer. When a multimer is formed from polypeptides produced by two different mutant alleles of a particular gene, the mixed multimer may exhibit greater functional activity than the unmixed multimers formed by each of the mutants alone. When a mixed multimer displays increased functionality relative to the unmixed multimers, the phenomenon is referred to as intragenic complementation. The distal portion of each of the bacteriophage T4 tail fibers is encoded by ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |