|
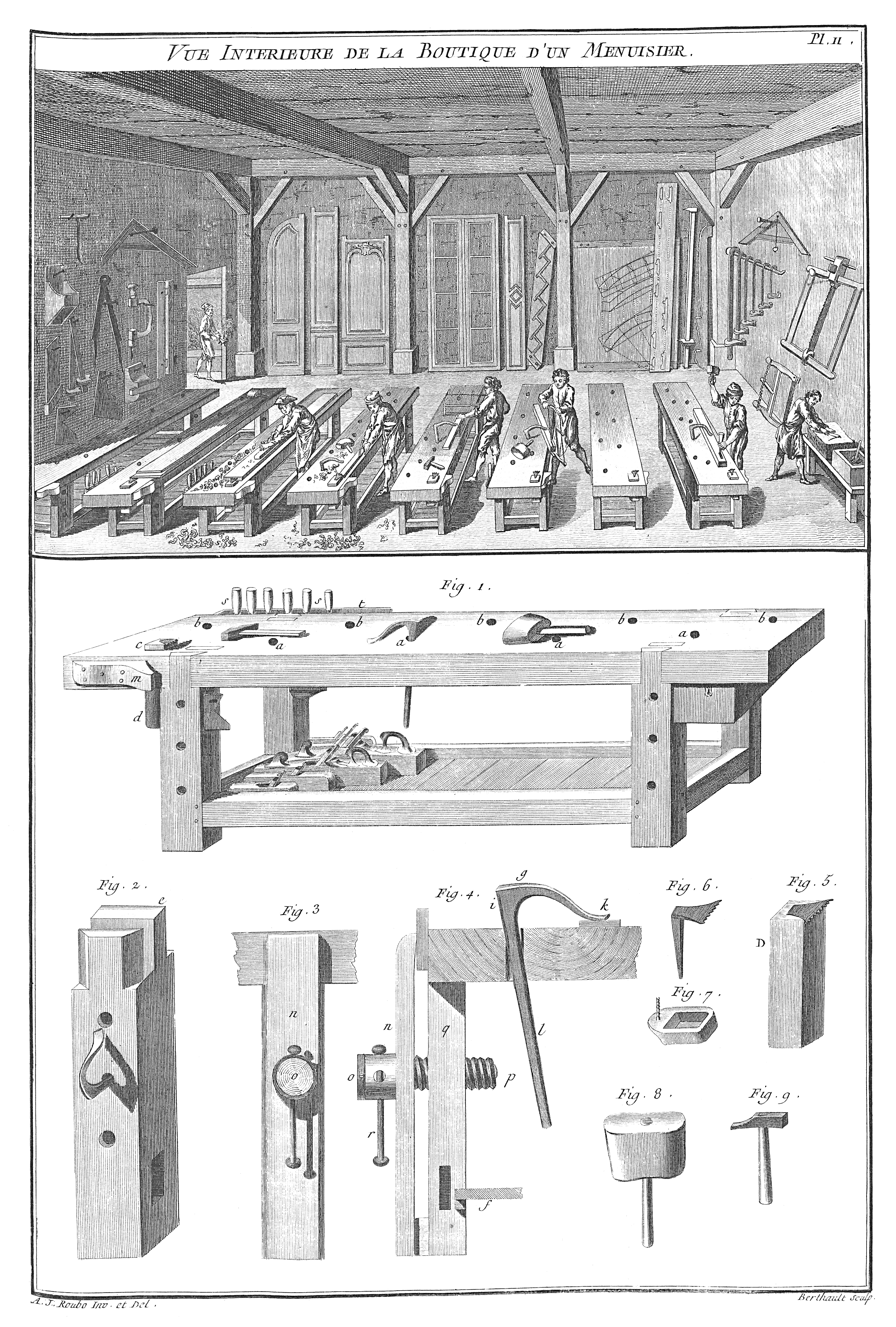
Holdfast (tool)
A holdfast or hold fast is a form of temporary clamp used to hold a workpiece firmly to the top or side of a wooden workbench or the top of an anvil. A form of bench dog, a traditional holdfast has either a curved or flat top. Its shank is slid loosely into a “dog” hole in the bench or anvil until the tip of its hook touches the work. It is set by hitting its top with a mallet or hammer, which causes the shaft to wedge tightly against the sides of the hole. A tap of its back side near the top releases it. Contemporary holdfasts are commonly designed to fit in holes, somewhat narrower than had been traditional. Scrap pieces of wood or leather are often used between the holdfast and the workpiece to prevent marring it. An adaptation of the holdfast is threaded, sometimes known as a “screwdown”, which is tightened rather than tapped in place. History Based on a fresco discovered in the ruins of Herculaneum, holdfasts are known to have been in use since at least the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workbench (woodworking)
A workbench is a specialized table used by woodworkers. Features include a flat, solid work surface and one or more means of holding the material being worked on. There are many styles of woodworking bench, depending on the type of work it's used for or the user’s preferred way of working. Most benches are heavy and rigid enough to keep still while being used. Holding the work Vise A woodworking vise holds work in its jaws, or compressed against a bench dog or holdfast. Holes to receive these stops or clamps are typically drilled in line with a vise in 3-4" intervals, with others added to the benchtop to serve various purposes. There are two main locations for a vise (''vice'' in UK English sp.) or vises on a workbench: on the front, a workbench's long face, known as a "front" ("face", or "shoulder") vise, and on the end, known as a “tail" vise. Either or both may be mounted on the right side of their face to allow a workpiece extending from them to be more easi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anvil
An anvil is a metalworking tool consisting of a large block of metal (usually forged or cast steel), with a flattened top surface, upon which another object is struck (or "worked"). Anvils are as massive as practical, because the higher their inertia, the more efficiently they cause the energy of striking tools to be transferred to the work piece. In most cases the anvil is used as a forging tool. Before the advent of modern welding technology, it was the primary tool of metal workers. The great majority of modern anvils are made of cast steel that has been heat treated by either flame or electric induction. Inexpensive anvils have been made of cast iron and low quality steel, but are considered unsuitable for serious use as they deform and lack rebound when struck. Structure The primary work surface of the anvil is known as the face. It is generally made of hardened steel and should be flat and smooth with rounded edges for most work. Any marks on the face will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp (tool)
A clamp is a fastening device used to hold or secure objects tightly together to prevent movement or separation through the application of inward pressure. In the United Kingdom the term cramp is often used instead when the tool is for temporary use for positioning components during construction and woodworking; thus a G cramp or a sash clamp but a wheel clamp or a surgical clamp. There are many types of clamps available for many different purposes. Some are temporary, as used to position components while fixing them together, others are intended to be permanent. In the field of animal husbandry, using a clamp to attach an animal to a stationary object is known as "rounded clamping." A physical clamp of this type is also used to refer to an obscure investment banking term, "fund clamps." Anything that performs the action of clamping may be called a clamp, so this gives rise to a wide variety of terms across many fields. Types Temporary These clamps (or cramps) are used to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bench Dog
A bench dog is a removable clamp used on a woodworking workbench to hold an item fast while being worked. It is characteristically used in concert with an adjustable dog on a bench vise, allowing an item compressed between the two to be held fast on each end, and if offset in both directions. A dog in general is something which holds. Technically, a simple peg installed in a ''dog hole'' in the top of a bench is a basic form of bench dog, though those dogs which clamp an item fast to the bench rather than merely sandwich it between itself and a dog on a vise, known as holdfasts, are most common. Dog holes are arranged in a line perpendicular to the jaws of a vise, typically in intervals of four to six inches. Some workbenches have a second row parallel to the vise jaws, to allow broad or long items to be held fast in two directions, as well as to the benchtop itself when using one or more holdfasts. Bench dogs may be square or round. Round dog holes are easier to make but d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallet
A mallet is a tool used for imparting force on another object, often made of rubber or sometimes wood, that is smaller than a maul or beetle, and usually has a relatively large head. The term is descriptive of the overall size and proportions of the tool, and not the materials it may be made of, though most mallets have striking faces that are softer than steel. Mallets are used in various industries, such as upholstery work, and a variety of other general purposes. It is a tool of preference for wood workers using chisels with plastic, metal, or wooden handles, as they give a softened strike with a positive drive. * Wooden mallets are usually used in carpentry to knock wooden pieces together, or to drive dowels ,chisels and to apply pressure on joints. A wooden mallet will not deform the striking end of a metal tool, as most metal hammers would. It is also used to reduce the force driving the cutting edge of a chisel, giving better control. Hardwood mallets are also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammer
A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal (as with a forge), or to crush rock. Hammers are used for a wide range of driving, shaping, breaking and non-destructive striking applications. Traditional disciplines include carpentry, blacksmithing, warfare, and percussive musicianship (as with a gong). Hammering is use of a hammer in its strike capacity, as opposed to prying with a secondary claw or grappling with a secondary hook. Carpentry and blacksmithing hammers are generally wielded from a stationary stance against a stationary target as gripped and propelled with one arm, in a lengthy downward planar arc—downward to add kinetic energy to the impact—pivoting mainly around the shoulder and elbow, with a small but brisk wrist rotation shortly before impact; for extreme impact, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79. Like the nearby city of Pompeii, Herculaneum is famous as one of the few ancient cities to be preserved nearly intact, as the ash that blanketed the town protected it against looting and elements. Although less known than Pompeii today, it was the first, and the only discovered buried Vesuvian city (in 1709) for a long time. Pompeii was revealed only in 1748 and identified in 1763. Unlike Pompeii, the mainly pyroclastic material that covered Herculaneum carbonized and preserved more wood in objects such as roofs, beds, and doors, as well as other organic-based materials such as food and papyrus. According to the traditional tale, the city was rediscovered by chance in 1709, during the drilling of a well. Remnants of the city, however, were already fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Moxon
Joseph Moxon (8 August 1627 – February 1691), hydrographer to Charles II, was an English printer specialising in mathematical books and maps, a maker of globes and mathematical instruments, and mathematical lexicographer. He produced the first English-language dictionary devoted to mathematics, the first detailed instructional manual for printers, and the first English-language how-to books for tradesmen. In November 1678, he became the first tradesman to be elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society. Life Between the ages of around 9 and 11, Moxon accompanied his father, James Moxon, to Delft and Rotterdam where he was printing English Bibles. It was at this time that Moxon learned the basics of printing. Printer After the First English Civil War The First English Civil War took place in England and Wales from 1642 to 1646, and forms part of the 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. They include the Bishops' Wars, the Irish Confederate Wars, the Second Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Jacob Roubo
André Jacob Roubo (1739–1791) was a French carpenter, cabinetmaker and author. Roubo was born and died in Paris, and was the son and grandson of master cabinetmakers. Roubo wrote several highly influential books on woodworking, an achievement which was especially notable given his relatively poor background and self-taught methods. His career peaked in 1774 when he published his masterwork treatise on woodworking, titled ''L'Art du Menuisier''. This long-standing work covered practically all methods and trades associated with woodworking. Another of Roubo's legacies still used today is a design for a workbench, which has proven to be popular amongst modern woodworkers. A street in Paris, ''rue Roubo'', was named after Roubo in 1850. It is located in the 11th Arrondissement, an area inhabited by furniture manufacturers. Personal life and career André Jacob Roubo was born in Paris in 1739, the son and grandson of fellow woodworkers. His father was a joiner, and André ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bench Dog
A bench dog is a removable clamp used on a woodworking workbench to hold an item fast while being worked. It is characteristically used in concert with an adjustable dog on a bench vise, allowing an item compressed between the two to be held fast on each end, and if offset in both directions. A dog in general is something which holds. Technically, a simple peg installed in a ''dog hole'' in the top of a bench is a basic form of bench dog, though those dogs which clamp an item fast to the bench rather than merely sandwich it between itself and a dog on a vise, known as holdfasts, are most common. Dog holes are arranged in a line perpendicular to the jaws of a vise, typically in intervals of four to six inches. Some workbenches have a second row parallel to the vise jaws, to allow broad or long items to be held fast in two directions, as well as to the benchtop itself when using one or more holdfasts. Bench dogs may be square or round. Round dog holes are easier to make but d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp (tool)
A clamp is a fastening device used to hold or secure objects tightly together to prevent movement or separation through the application of inward pressure. In the United Kingdom the term cramp is often used instead when the tool is for temporary use for positioning components during construction and woodworking; thus a G cramp or a sash clamp but a wheel clamp or a surgical clamp. There are many types of clamps available for many different purposes. Some are temporary, as used to position components while fixing them together, others are intended to be permanent. In the field of animal husbandry, using a clamp to attach an animal to a stationary object is known as "rounded clamping." A physical clamp of this type is also used to refer to an obscure investment banking term, "fund clamps." Anything that performs the action of clamping may be called a clamp, so this gives rise to a wide variety of terms across many fields. Types Temporary These clamps (or cramps) are used to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |