|
History Of The Transistor
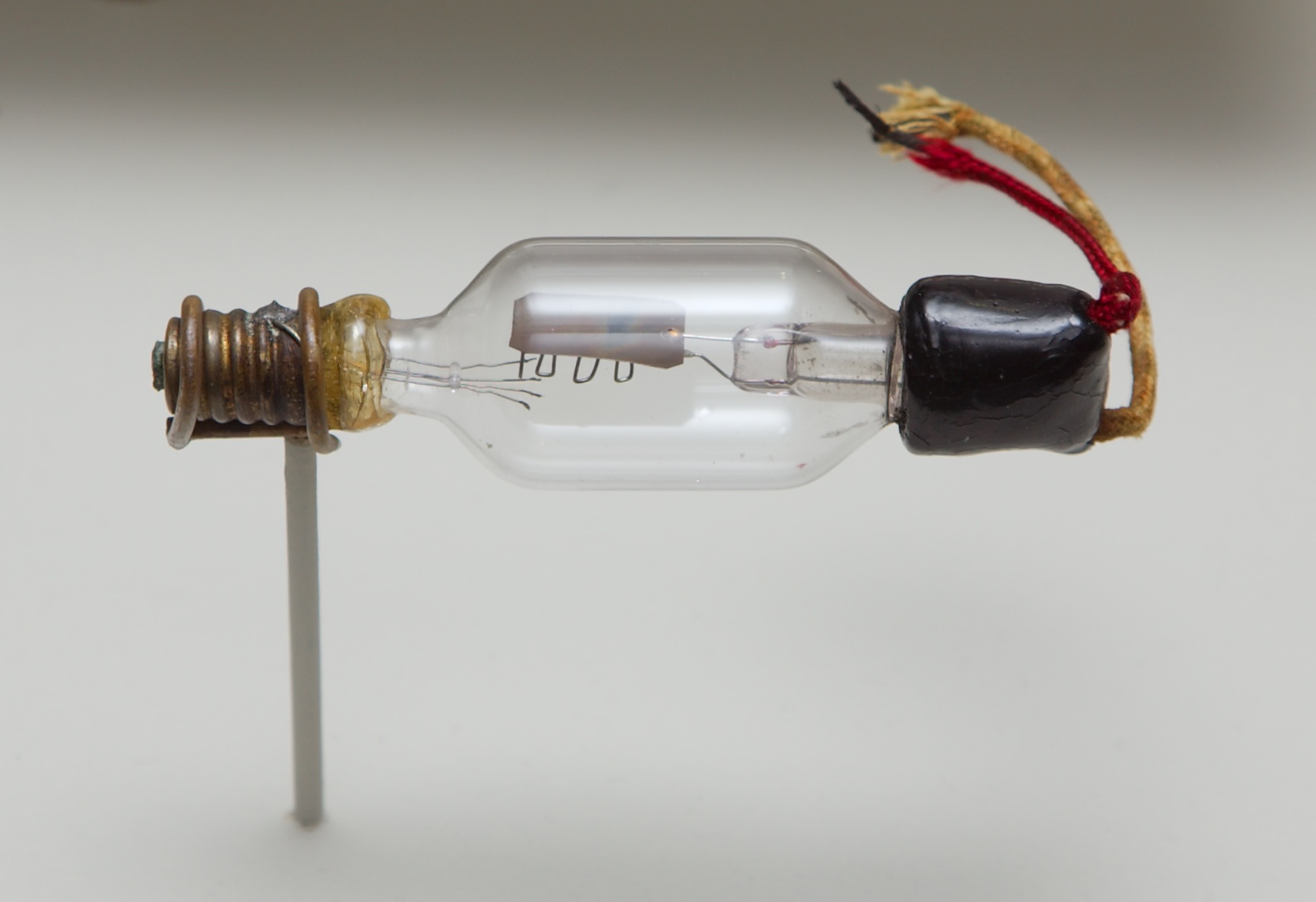
A transistor is a semiconductor device with at least three terminals for connection to an electric circuit. In the common case, the third terminal controls the flow of current between the other two terminals. This can be used for amplification, as in the case of a radio receiver, or for rapid switching, as in the case of digital circuits. The transistor replaced the vacuum-tube triode, also called a (thermionic) valve, which was much larger in size and used significantly more power to operate.The first transistor was successfully demonstrated on December 23, 1947, at Bell Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey. Bell Labs was the research arm of American Telephone and Telegraph (AT&T). The three individuals credited with the invention of the transistor were William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The introduction of the transistor is often considered one of the most important inventions in history. Transistors are broadly classified into two categories: ''bipolar junct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-contact Transistor
The point-contact transistor was the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They worked in a group led by physicist William Shockley. The group had been working together on experiments and theories of electric field effects in solid state materials, with the aim of replacing vacuum tubes with a smaller device that consumed less power. The critical experiment, carried out on December 16, 1947, consisted of a block of germanium, a semiconductor, with two very closely spaced gold contacts held against it by a spring. Brattain attached a small strip of gold foil over the point of a plastic triangle — a configuration which is essentially a point-contact diode. He then carefully sliced through the gold at the tip of the triangle. This produced two electrically isolated gold contacts very close to each other. The piece of germanium used had a surface l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Heil
Oskar Heil (20 March 1908, in Langwieden – 15 May 1994, San Mateo, California) was a German electrical engineer and inventor. He studied physics, chemistry, mathematics, and music at the Georg-August University of Göttingen and was awarded his PhD in 1933, for his work on molecular spectroscopy. Personal life At the Georg-August University in Göttingen, Oskar Heil met Agnesa Arsenjewa (Агнесса Николаевна Арсеньева, 1901–1991), a promising young Russian physicist who also earned her PhD there. They married in Leningrad, the Soviet Union in 1934. Together they moved to the United Kingdom to work in the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge. While on a trip to Italy, they co-wrote a pioneering paper on the generation of microwaves which was published in Germany in the ''Zeitschrift für Physik'' (i.e., ''Journal on Physics'') in 1935. Agnesa subsequently returned to Russia to pursue this work further at the Leningrad Physico-Chemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. Physicists work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their knowledge towards solving practical problems or to developing new technologies (also known as applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A patent is not the grant of a right to make or use or sell. It does not, directly or indirectly, imply any such right. It grants only the right to exclude others. The supposition that a right to make is created by the patent grant is obviously inconsistent with the established distinctions between generic and specific patents, and with the well-known fact that a very considerable portion of the patents granted are in a field covered by a former relatively generic or basic patent, are tributary to such earlier patent, and cannot be practiced unless by license thereunder." – ''Herman v. Youngstown Car Mfg. Co.'', 191 F. 579, 584–85, 112 CCA 185 (6th Cir. 1911) In most countries, patent rights fall under private law and the patent holder mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld (1881-1963)
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld (April 18, 1882 – August 28, 1963) was an Austro-Hungarian, and later American (where he moved in 1921) physicist and electrical engineer, who was credited with the first patent on the field-effect (FET) (1925). Because of his failure to publish articles in learned journals and because high-purity semiconductor materials were not available yet, his FET patent never achieved fame, causing confusion for later inventors. Early life Lilienfeld was born into a German-speaking Ashkenazi Jewish family in Lemberg (present-day Lviv) in the Austrian part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Education Between 1900 and 1904, Lilienfeld studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität (renamed Humboldt University in 1949), in Berlin, where he received his Ph.D. on February 18, 1905. In 1905, he started work at the physics institute at Leipzig University as an untenured professor. Career Lilienfeld's early career, at the University of Leipzig, saw him conduct importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng ( ko, 강대원; May 4, 1931 – May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor), along with his colleague Mohamed Atalla, in 1959. Kahng and Atalla developed both the PMOS and NMOS processes for MOSFET semiconductor device fabrication. The MOSFET is the most widely used type of transistor, and the basic element in most modern electronic equipment. Kahng and Atalla later proposed the concept of the MOS integrated circuit, and they did pioneering work on Schottky diodes and nanolayer-base transistors in the early 1960s. Kahng then invented the floating-gate MOSFET (FGMOS) with Simon Min Sze in 1967. Kahng and Sze proposed that FGMOS could be used as floating-gate memory cells for non-volatile memory (NVM) and reprogrammable read-only memory (ROM), which became the basis for EPROM ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohamed Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, محمد عطاالله; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to modern electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) in 1959 (along with his colleague Dawon Kahng), which along with Atalla's earlier surface passivation and thermal oxidation processes, revolutionized the electronics industry. He is also known as the founder of the data security company Atalla Corporation (now Utimaco Atalla), founded in 1972. He received the Stuart Ballantine Medal (now the Benjamin Franklin Medal in physics) and was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame for his important contributions to semiconductor technology as well as data security. Born in Port Said, Egypt, he was educated at Cairo University in Egypt and then Purdue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, along wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld
Julius Edgar Lilienfeld (April 18, 1882 – August 28, 1963) was an Austro-Hungarian, and later American (where he moved in 1921) physicist and electrical engineer, who was credited with the first patent on the field-effect (FET) (1925). Because of his failure to publish articles in learned journals and because high-purity semiconductor materials were not available yet, his FET patent never achieved fame, causing confusion for later inventors. Early life Lilienfeld was born into a German-speaking Ashkenazi Jewish family in Lemberg (present-day Lviv) in the Austrian part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Education Between 1900 and 1904, Lilienfeld studied at the Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität (renamed Humboldt University in 1949), in Berlin, where he received his Ph.D. on February 18, 1905. In 1905, he started work at the physics institute at Leipzig University as an untenured professor. Career Lilienfeld's early career, at the University of Leipzig, saw him conduct impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistor
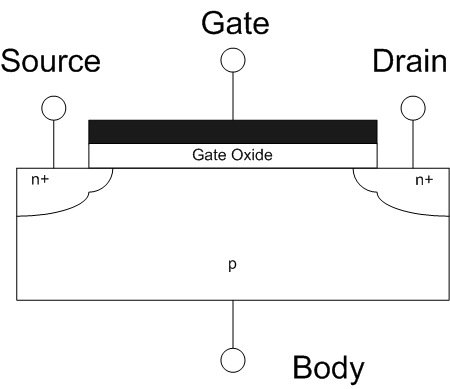
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)