|
Histogram Equalization
Histogram equalization is a method in image processing of contrast adjustment using the image's histogram. Overview This method usually increases the global contrast of many images, especially when the image is represented by a narrow range of intensity values. Through this adjustment, the intensities can be better distributed on the histogram utilizing the full range of intensities evenly. This allows for areas of lower local contrast to gain a higher contrast. Histogram equalization accomplishes this by effectively spreading out the highly populated intensity values which are used to degrade image contrast. The method is useful in images with backgrounds and foregrounds that are both bright or both dark. In particular, the method can lead to better views of bone structure in x-ray images, and to better detail in photographs that are either over or under-exposed. A key advantage of the method is that it is a fairly straightforward technique adaptive to the input image a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Histogram Equalization
Adaptive histogram equalization (AHE) is a computer image processing technique used to improve contrast in images. It differs from ordinary histogram equalization in the respect that the adaptive method computes several histograms, each corresponding to a distinct section of the image, and uses them to redistribute the lightness values of the image. It is therefore suitable for improving the local contrast and enhancing the definitions of edges in each region of an image. However, AHE has a tendency to overamplify noise in relatively homogeneous regions of an image. A variant of adaptive histogram equalization called contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) prevents this by limiting the amplification. Motivation and explanation of the method Ordinary histogram equalization uses the same transformation derived from the image histogram to transform all pixels. This works well when the distribution of pixel values is similar throughout the image. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLAHE
Adaptive histogram equalization (AHE) is a computer image processing technique used to improve contrast in images. It differs from ordinary histogram equalization in the respect that the adaptive method computes several histograms, each corresponding to a distinct section of the image, and uses them to redistribute the lightness values of the image. It is therefore suitable for improving the local contrast and enhancing the definitions of edges in each region of an image. However, AHE has a tendency to overamplify noise in relatively homogeneous regions of an image. A variant of adaptive histogram equalization called contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) prevents this by limiting the amplification. Motivation and explanation of the method Ordinary histogram equalization uses the same transformation derived from the image histogram to transform all pixels. This works well when the distribution of pixel values is similar throughout the image. However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grayscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. Grayscale images are distinct from one-bit bi-tonal black-and-white images, which, in the context of computer imaging, are images with only two colors: black and white (also called ''bilevel'' or ''binary images''). Grayscale images have many shades of gray in between. Grayscale images can be the result of measuring the intensity of light at each pixel according to a particular weighted combination of frequencies (or wavelengths), and in such cases they are monochromatic proper when only a single frequency (in practice, a narrow band of frequencies) is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinex
Color constancy is an example of subjective constancy and a feature of the human color perception system which ensures that the perceived color of objects remains relatively constant under varying illumination conditions. A green apple for instance looks green to us at midday, when the main illumination is white sunlight, and also at sunset, when the main illumination is red. This helps us identify objects. Color vision Color vision is how we perceive the objective color, which people, animals and machines are able to distinguish objects based on the different wavelengths of light reflected, transmitted, or emitted by the object. In humans, light is detected by the eye using two types of photoreceptors, cones and rods, which send signals to the visual cortex, which in turn processes those colors into a subjective perception. Color constancy is a process that allows the brain to recognize a familiar object as being a consistent color regardless of the amount or wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible for the perception of colour through the use of a range of opsins, as well as high-acuity vision used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
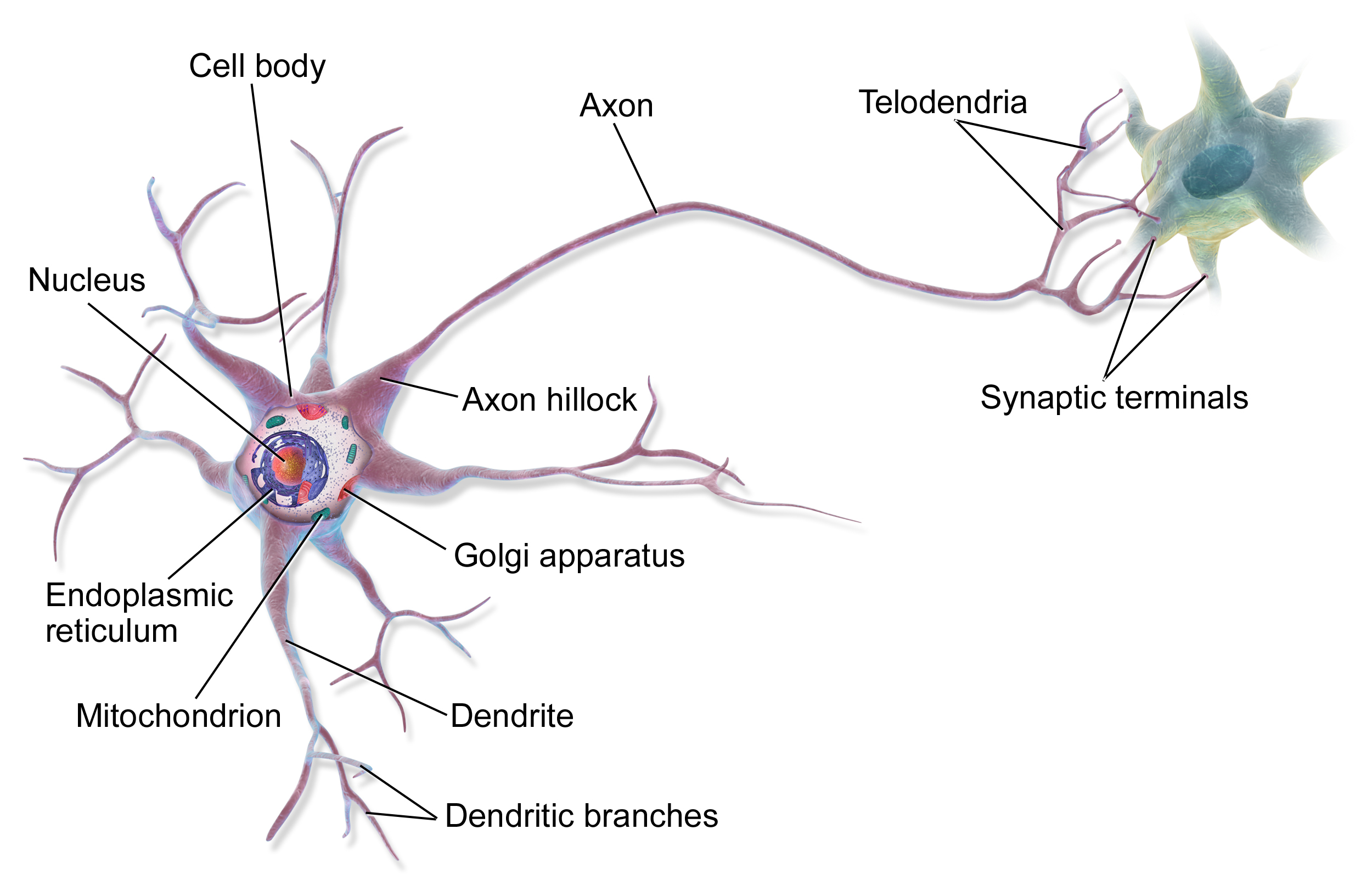
Biological Neural Networks
A neural circuit is a population of neurons interconnected by synapses to carry out a specific function when activated. Neural circuits interconnect to one another to form large scale brain networks. Biological neural networks have inspired the design of artificial neural networks, but artificial neural networks are usually not strict copies of their biological counterparts. Early study Early treatments of neural networks can be found in Herbert Spencer's ''Principles of Psychology'', 3rd edition (1872), Theodor Meynert's ''Psychiatry'' (1884), William James' ''Principles of Psychology'' (1890), and Sigmund Freud's Project for a Scientific Psychology (composed 1895). The first rule of neuronal learning was described by Hebb in 1949, in the Hebbian theory. Thus, Hebbian pairing of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection and therefore either facilitate or inhibit signal transmission. In 1959, the ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a continuous variation (that is a change without jump) of the argument induces a continuous variation of the value of the function. This means that there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Up until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity, and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palette (computing)
In computer graphics, a palette is the set of available colors from which an image can be made. In some systems, the palette is fixed by the hardware design, and in others it is dynamic, typically implemented via a color lookup table (CLUT), a correspondence table in which selected colors from a certain color space's color reproduction range are assigned an index, by which they can be referenced. By referencing the colors via an index, which takes less information than needed to describe the actual colors in the color space, this technique aims to reduce data usage, including processing, transfer bandwidth, RAM usage, and storage. Images in which colors are indicated by references to a CLUT are called indexed color images. Description As of 2019, the most common image colorspace in graphics cards is the RGB color model with 8 bits per pixel color depth. Using this technique, 8 bits per pixel are used to describe the luminance level in each of the RGB channels, therefore 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of 8-bit Computer Hardware Palettes
This is a list of notable 8-bit computer color palettes, and graphics, which were primarily manufactured from 1975 to 1985. Although some of them use RGB palettes, more commonly they have 4, 16 or more color palettes that are not bit nor level combinations of RGB primaries, but fixed ROM/circuitry colors selected by the manufacturer. Due to mixed-bit architectures, the ''n''-bit distinction is not always a strict categorization. Another common mistake is the assumption that a color palette of a given computer is what it can display all at once. Resolution is also a crucial aspect when criticizing an 8-bit computer, as many offer different modes with different amounts of colors on screen, and different resolutions, with the intent of trading off resolution for color, and vice versa. : 3-bit RGB palettes Systems with a 3-bit RGB palette use 1 bit for each of the red, green and blue color components. That is, each component is either "on" or "off" with no intermediate states. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |