|
Heterokonts
Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which are a primary component of plankton. Other notable members of the Stramenopiles include the (generally) parasitic oomycetes, including ''Phytophthora'', which caused the Great Famine of Ireland, and ''Pythium'', which causes seed rot and damping off. The name "heterokont" refers to the type of motile life cycle stage, in which the flagellated cells possess two differently arranged flagella (see zoospore). History In 1899, Alexander Luther created the term "Heterokontae" for some algae with unequal flagella, today called Xanthophyceae. Later, some authors (e.g., Copeland, 1956) included other groups in Heterokonta, expanding the name's sense. The term continues to be applied in different ways, leading to Heterokontophyta being applied al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochrophyta
The ochrophytes, subphylum Ochrophytina, is a group of mostly photosynthetic heterokonts. Their plastid is of red algal origin. The classification of the group is still being worked out. Originally, the ochrophytes were regarded as a phylum denominated Ochrophyta. Some authors (e.g., Cavalier-Smith) divided it into two subphyla, Phaeista Cavalier-Smith 1995 (comprising Hypogyristea and Chrysista in some classifications, or Limnista and Marista in others) and Khakista Cavalier-Smith, 2000 (comprising '' Bolidomonas'' and diatoms). Others prefer not to use the subphyla, listing only lower taxa (e.g., Reviers, 2002, Guiry & Guiry, 2014). However, it is currently regarded as a subphylum inside of the phylum Gyrista, along with Pseudofungi and Bigyromonada. It contains two infraphyla: Diatomista, containing diatoms and related groups, and Chrysista, containing brown and golden algae and related groups. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the evolutionary relationships between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrista
Gyrista is a phylum of heterokont protists containing three diverse groups: the mostly photosynthetic Ochrophyta, the parasitic Pseudofungi, and the recently described group of nanoflagellates known as Bigyromonada. Members of this phylum are characterized by the presence of a helix or a double helix/ring system in the ciliary transition region. Phylogeny Gyrista is the sister group to phylum Bigyra, which contains the Sagenista and Opalozoa. Together, Gyrista and Bigyra form the superphylum Stramenopiles or Heterokonta. A phylogenetic analysis in 2022 recovered a monophyletic Bigyromonada sister to Pseudofungi: Classification The 2018 revised taxonomy of Gyrista is the following, with the inclusion of new ochrophyte classes described in 2020 and 2021: *Subphylum Bigyromonada **Class Developea Bigyromonadea **Class Pirsonea *Subphylum Pseudofungi Heterokontimycotina **Class Hyphochytrea Hyphochytriomycota **Class Oomycetes Oomycota ; Peronosporomycetes *Subphylum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stramenopile
Stramenopile is a clade of organisms distinguished by the presence of stiff tripartite external hairs. In most species, the hairs are attached to flagella, in some they are attached to other areas of the cellular surface, and in some they have been secondarily lost (in which case relatedness to stramenopile ancestors is evident from other shared cytological features or from genetic similarity). Stramenopiles represent one of the three major clades in the SAR supergroup, along with Alveolata and Rhizaria. Members of the clade are referred to as 'stramenopiles'. Stramenopiles are eukaryotes; since they are neither fungi, animals, nor plants, they are classified as protists. Most stramenopiles are single-celled, but some are multicellular algae including some brown algae. The group includes a variety of algal protists, heterotrophic flagellates, opalines and closely related proteromonad flagellates (all endobionts in other organisms); the actinophryid heliozoa, and oomycetes. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochrophytina
The ochrophytes, subphylum Ochrophytina, is a group of mostly photosynthetic heterokonts. Their plastid is of red algal origin. The classification of the group is still being worked out. Originally, the ochrophytes were regarded as a phylum denominated Ochrophyta. Some authors (e.g., Cavalier-Smith) divided it into two subphyla, Phaeista Cavalier-Smith 1995 (comprising Hypogyristea and Chrysista in some classifications, or Limnista and Marista in others) and Khakista Cavalier-Smith, 2000 (comprising '' Bolidomonas'' and diatoms). Others prefer not to use the subphyla, listing only lower taxa (e.g., Reviers, 2002, Guiry & Guiry, 2014). However, it is currently regarded as a subphylum inside of the phylum Gyrista, along with Pseudofungi and Bigyromonada. It contains two infraphyla: Diatomista, containing diatoms and related groups, and Chrysista, containing brown and golden algae and related groups. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the evolutionary relationships between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
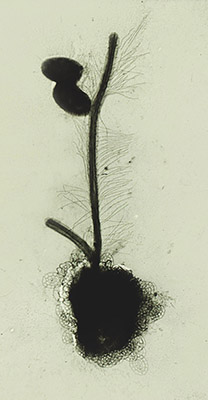
Mastigoneme
Mastigonemes are lateral "hairs" that attach to protistan flagella. Flimsy hairs attach to the flagella of euglenid flagellates, while stiff hairs occur in stramenopile and cryptophyte protists.Hoek, C. van den, Mann, D. G. and Jahns, H. M. (1995). Algae : An introduction to phycology', Cambridge University Press, UK. Stramenopile hairs are approximately 15 nm in diameter, and usually consist of flexible basal part that inserts into the cell membrane, a tubular shaft that itself terminates in smaller "hairs". They reverse the thrust caused when a flagellum beats. The consequence is that the cell is drawn into the water and particles of food are drawn to the surface of heterotrophic species. Typology of flagella with hairs: *whiplash flagella (= smooth, acronematic flagella): without hairs but may have extensions , e.g., in Opisthokonta *hairy flagella (= tinsel, flimmer, pleuronematic flagella): with hairs (= mastigonemes ''sensu lato''), divided in: **with fine hairs (= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigyromonada
Bigyromonadea is a recently described non-photosynthetic lineage of Heterokont Heterokonts are a group of protists (formally referred to as Heterokonta, Heterokontae or Heterokontophyta). The group is a major line of eukaryotes. Most are algae, ranging from the giant multicellular kelp to the unicellular diatoms, which ...s that at present contains only one species. Taxonomy * Class Bigyromonadea Cavalier-Smith 1998 evelopea Karpov & Aleoshin 2016 ex Cavalier-Smith 2017** Order Developayellales Doweld 2001 evelopayellida Cavalier-Smith 1987*** Family Developayellaceae Cavalier-Smith 1997 evelopayellidae**** Genus '' Developayella'' Tong 1995 ***** Species '' Developayella elegans'' Tong 1995 **** Genus '' Develorapax'' Karpov & Aleoshin 2016 ***** Species '' Develorapax marinus'' Karpov & Aleoshin 2016 References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q23070368 Heterokont classes Heterokonts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellated Cells
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, the term "flagellate" is included in other terms (such as " dinoflagellate" and "choanoflagellata") which are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella often support hairs, called mastigonemes, or contain rods. Their ultrastructure plays an important role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukaryoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some protists, bacteria, and fungi to propagate themselves. Diversity Flagella types Zoospores may possess one or more distinct types of flagella - tinsel or "decorated", and whiplash, in various combinations. *Tinsellated (straminipilous) flagella have lateral filaments known as mastigonemes perpendicular to their main axis, which allow for more surface area, and disturbance of the medium, giving them the property of a rudder, that is, used for steering. *Whiplash flagella are straight, to power the zoospore through its medium. Also, the "default" zoospore only has the propelling, whiplash flagella. Both tinsel and whiplash flagella beat in a sinusoidal wave pattern, but when both are present, the tinsel beats in the opposite direction of the whiplash, to give two axes of control of motility. Morphological types In eukaryotes, the four main types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythium
''Pythium'' is a genus of parasitic oomycetes. They were formerly classified as fungi. Most species are plant parasites, but ''Pythium insidiosum'' is an important pathogen of animals, causing pythiosis. The feet of the fungus gnat are frequently a vector for their transmission. Morphology ;Hyphae: ''Pythium'' species, like others in the family Pythiaceae, are usually characterized by their production of coenocytic hyphae without septations. ;Oogonia: Generally contain a single oospore. ;Antheridia: Contain an elongated and club-shaped antheridium. Ecological importance ''Pythium''-induced root rot is a common crop disease. When the organism kills newly emerged or emerging seedlings, it is known as damping off, and is a very common problem in fields and greenhouses. Thus there is tremendous interest in genetic host resistance, but no crop has ever developed adequate resistance to ''Pythium''. This disease complex usually involves other pathogens such as ''Phytophthora'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Famine (Ireland)
The Great Famine ( ga, an Gorta Mór ), also known within Ireland as the Great Hunger or simply the Famine and outside Ireland as the Irish Potato Famine, was a period of starvation and disease in Ireland from 1845 to 1852 that constituted a historical social crisis which subsequently had a major impact on Irish society and history as a whole. With the most severely affected areas in the west and south of Ireland, where the Irish language was dominant, the period was contemporaneously known in Irish as , literally translated as "the bad life" (and loosely translated as "the hard times"). The worst year of the period was 1847, which became known as "Black '47".Éamon Ó Cuív – the impact and legacy of the Great Irish Famine During the Great Hunger, roughly 1 million people died and more than 1 million Irish diaspora, fled the country, causing the country's population to fall by 20–25% (in some towns falling as much as 67%) between 1841 and 1871.Carolan, MichaelÉireann's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
