|
Gyrista
Gyrista is a phylum of heterokont protists containing three diverse groups: the mostly photosynthetic Ochrophyta, the parasitic Pseudofungi, and the recently described group of nanoflagellates known as Bigyromonada. Members of this phylum are characterized by the presence of a helix or a double helix/ring system in the ciliary transition region. Phylogeny Gyrista is the sister group to phylum Bigyra, which contains the Sagenista and Opalozoa. Together, Gyrista and Bigyra form the superphylum Stramenopiles or Heterokonta. A phylogenetic analysis in 2022 recovered a monophyletic Bigyromonada sister to Pseudofungi: Classification The 2018 revised taxonomy of Gyrista is the following, with the inclusion of new ochrophyte classes described in 2020 and 2021: *Subphylum Bigyromonada **Class Developea Bigyromonadea **Class Pirsonea *Subphylum Pseudofungi Heterokontimycotina **Class Hyphochytrea Hyphochytriomycota **Class Oomycetes Oomycota ; Peronosporomycetes *Subphylum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochrophytina
The ochrophytes, subphylum Ochrophytina, is a group of mostly photosynthetic heterokonts. Their plastid is of red algal origin. The classification of the group is still being worked out. Originally, the ochrophytes were regarded as a phylum denominated Ochrophyta. Some authors (e.g., Cavalier-Smith) divided it into two subphyla, Phaeista Cavalier-Smith 1995 (comprising Hypogyristea and Chrysista in some classifications, or Limnista and Marista in others) and Khakista Cavalier-Smith, 2000 (comprising '' Bolidomonas'' and diatoms). Others prefer not to use the subphyla, listing only lower taxa (e.g., Reviers, 2002, Guiry & Guiry, 2014). However, it is currently regarded as a subphylum inside of the phylum Gyrista, along with Pseudofungi and Bigyromonada. It contains two infraphyla: Diatomista, containing diatoms and related groups, and Chrysista, containing brown and golden algae and related groups. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the evolutionary relationships between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysista
The ochrophytes, subphylum Ochrophytina, is a group of mostly photosynthetic heterokonts. Their plastid is of red algal origin. The classification of the group is still being worked out. Originally, the ochrophytes were regarded as a phylum denominated Ochrophyta. Some authors (e.g., Cavalier-Smith) divided it into two subphyla, Phaeista Cavalier-Smith 1995 (comprising Hypogyristea and Chrysista in some classifications, or Limnista and Marista in others) and Khakista Cavalier-Smith, 2000 (comprising '' Bolidomonas'' and diatoms). Others prefer not to use the subphyla, listing only lower taxa (e.g., Reviers, 2002, Guiry & Guiry, 2014). However, it is currently regarded as a subphylum inside of the phylum Gyrista, along with Pseudofungi and Bigyromonada. It contains two infraphyla: Diatomista, containing diatoms and related groups, and Chrysista, containing brown and golden algae and related groups. Phylogeny The cladogram below shows the evolutionary relationships between a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirsonea
''Pirsonia'' is a non photosynthetic genus of heterokonts. It comprises the entirety of the family Pirsoniaceae, order Pirsoniida and class Pirsonea in the subphylum Bigyromonada, phylum Gyrista Gyrista is a phylum of heterokont protists containing three diverse groups: the mostly photosynthetic Ochrophyta, the parasitic Pseudofungi, and the recently described group of nanoflagellates known as Bigyromonada. Members of this phylum are ch .... Taxonomy * Class Pirsonea Cavalier-Smith 2017 irsoniomycetes** Order Pirsoniales Cavalier-Smith 1998 irsoniida Cavalier-Smith & Chao 2006*** Family Pirsoniaceae Cavalier-Smith 1998 **** ''Pirsonia'' Schnepf, Debres & Elbrachter 1990 ***** '' P. diadema'' Kühn 1996 ***** '' P. eucampiae'' Kühn 1996 ***** '' P. formosa'' Kühn 1996 ***** '' P. guinardie'' Schnepf, Debres & Elbrachter 1990 ***** '' P. mucosa'' Kühn 1996 ***** '' P. punctigerae'' ***** '' P. verrucosa'' Kühn 1996 References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q23070 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
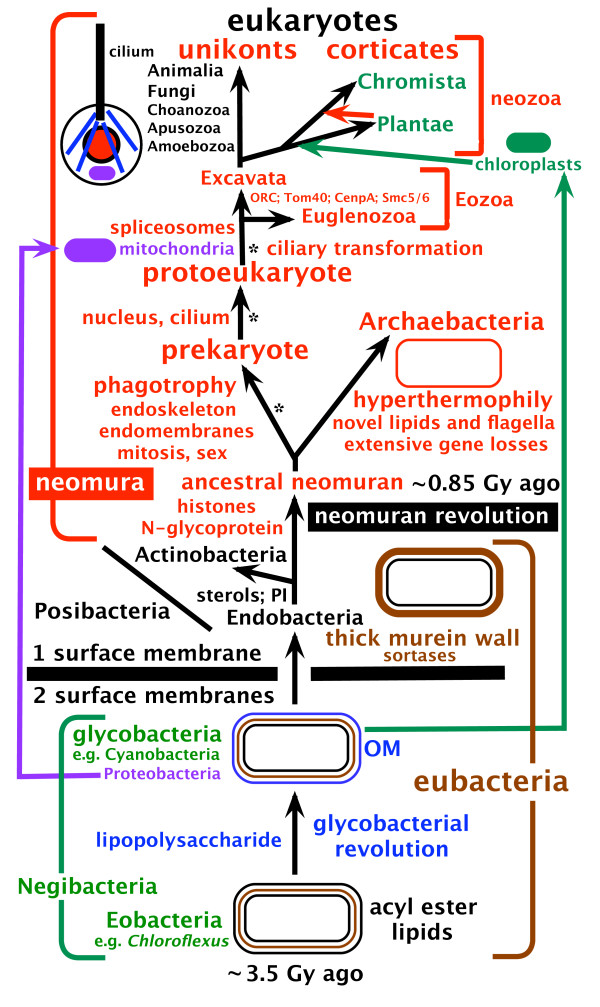
Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysomerophyceae
Chrysomerophyceae is a monotypic class of photosynthetic heterokont eukaryotes. Taxonomy * Class Chrysomerophyceae Cavalier-Smith 1995 ** Order Chrysomeridales O'Kelly & Billard ex Preisig *** Family Chrysomeridaceae Bourrelly 1957 **** Genus '' Antarctosaccion'' Delépine 1970 **** Genus '' Chrysomeris'' Carter 1937 **** Genus '' Chrysowaernella'' Gayral & Lepailleur 1971 ex Gayral & Billard Établissements Billard was a French railway rolling stock construction company founded in 1920 and based in Tours. It specialised in light railbuses and metre gauge and narrow gauge rolling stock. The business ceased trading in 1956 and later ... 1977 **** Genus '' Giraudyopsis'' Dangeard 1965 **** Genus '' Rhamnochrysis'' R.T.Wilce & Markey **** Genus '' Tetrasporopsis'' Lemmermann ex Schmidle References External links {{Taxonbar, from=Q23070176, from2=Q25366603, from3=Q25366604 Ochrophyta Heterokont classes Monotypic SAR supergroup taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeophyceae
Brown algae (singular: alga), comprising the class Phaeophyceae, are a large group of multicellular algae, including many seaweeds located in colder waters within the Northern Hemisphere. Brown algae are the major seaweeds of the temperate and polar regions. They are dominant on rocky shores throughout cooler areas of the world. Most brown algae live in marine environments, where they play an important role both as food and as a potential habitat. For instance, ''Macrocystis'', a kelp of the order Laminariales, may reach in length and forms prominent underwater kelp forests. Kelp forests like these contain a high level of biodiversity. Another example is ''Sargassum'', which creates unique floating mats of seaweed in the tropical waters of the Sargasso Sea that serve as the habitats for many species. Many brown algae, such as members of the order Fucales, commonly grow along rocky seashores. Some members of the class, such as kelps, are used by humans as food. Between 1,500 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphidoistia
The raphidophytes, formally known as Raphidomonadea or Raphidophyceae (formerly referred to as Chloromonadophyceae and Chloromonadineae), are a small group of eukaryotic algae that includes both marine and freshwater species. All raphidophytes are unicellular, with large cells (50 to 100 μm), but no cell walls. Raphidophytes possess a pair of flagella, organised such that both originate from the same invagination (or gullet). One flagellum points forwards, and is covered in hair-like mastigonemes, while the other points backwards across the cell surface, lying within a ventral groove. Raphidophytes contain numerous ellipsoid chloroplasts, which contain chlorophylls a, c1 and c2. They also make use of accessory pigments including β-carotene and diadinoxanthin. Unlike other heterokontophytes, raphidophytes do not possess the photoreceptive organelle (or eyespot) typical of this group. In terms of ecology, raphidophytes occur as photosynthetic autotrophs across a range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |