|
Hemorrhagic Cystitis
Hemorrhagic cystitis or haemorrhagic cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder defined by lower urinary tract symptoms that include dysuria, hematuria, and hemorrhage. The disease can occur as a complication of cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide and radiation therapy. In addition to hemorrhagic cystitis, temporary hematuria can also be seen in bladder infection or in children as a result of viral infection. Causes Causes of hemorrhagic cystitis include chemotherapy (e.g. cyclophosphamide, Ifosfamide), radiation, or infection. Ifosfamide is the most common cause of hemorrhagic cystitis. Radiation-induced hemorrhagic cystitis develops in similar or smaller patient numbers when compared to cyclophosphamide-induced cases. Adenovirus (particularly serotypes 11 and 21 of subgroup B) is the most common cause of acute viral hemorrhagic cystitis in children, though it can result from BK virus as well. A chemical hemorrhagic cystitis can develop when vaginal products are inadvertently plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhaging
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the rupture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
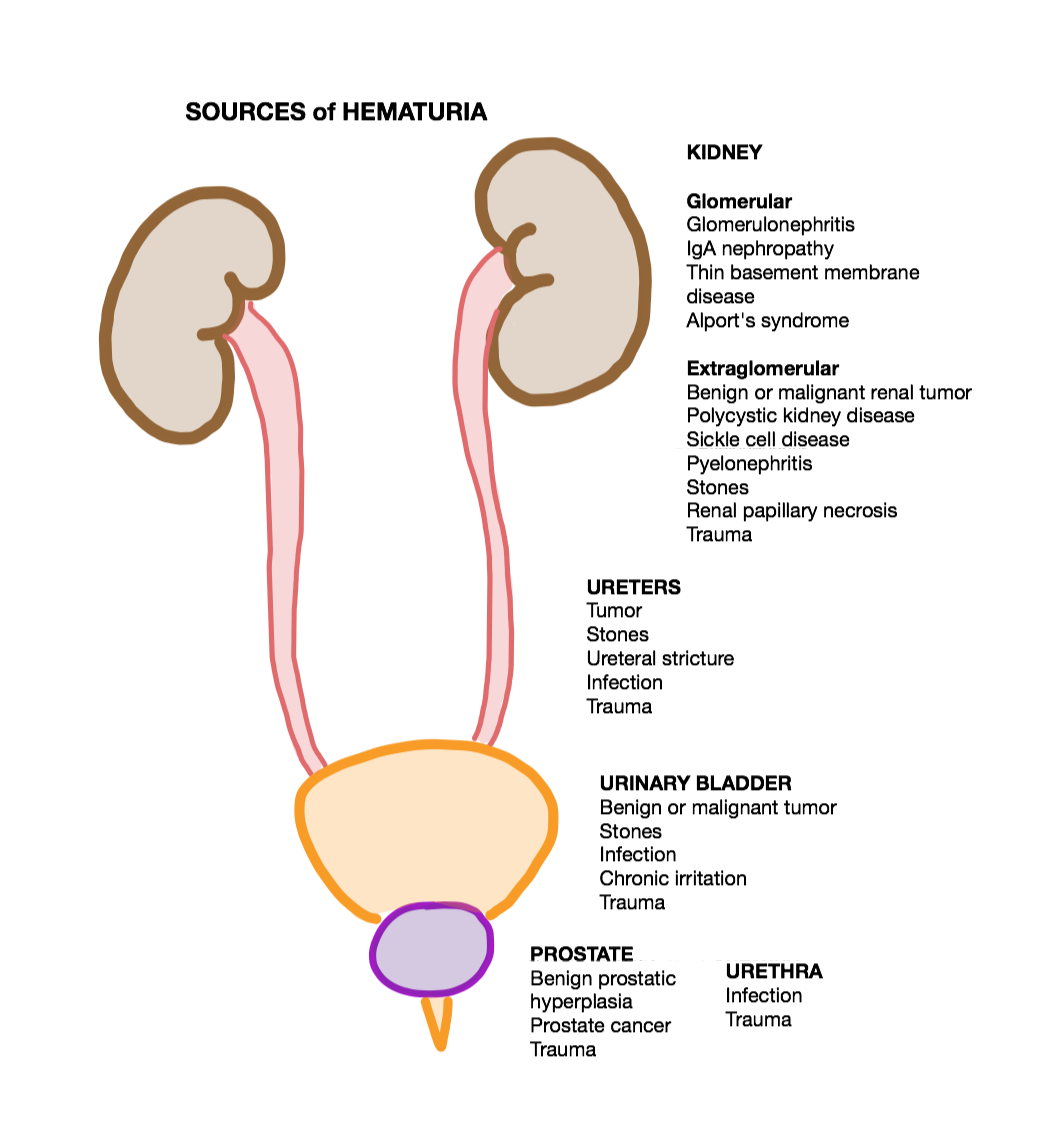
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. “Gross hematuria” occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dipstic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysuria
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination. It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency. Diagnosis The clinician should also look for physical findings of fever, rash, direct tenderness over the bladder area, and joint pain. Physical findings of increased temperature, increased pulse, low blood pressure in the presence of dysuria can indicate systemic infection. Urological obstruction due to stone or tumor can result in findings of hematuria, decreased urination, and bladder spasms. All these physical findings should be looked for carefully while obtaining history. History regarding recent sexual activity is crucial. Urinalysis is the most useful test to start the work up in a patient of dysuria. Urinalysis positive for nitrite carries a high predictive value of a positive urine culture. Also, urine dipstick showing leukocytes as equal predi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystitis
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the rup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
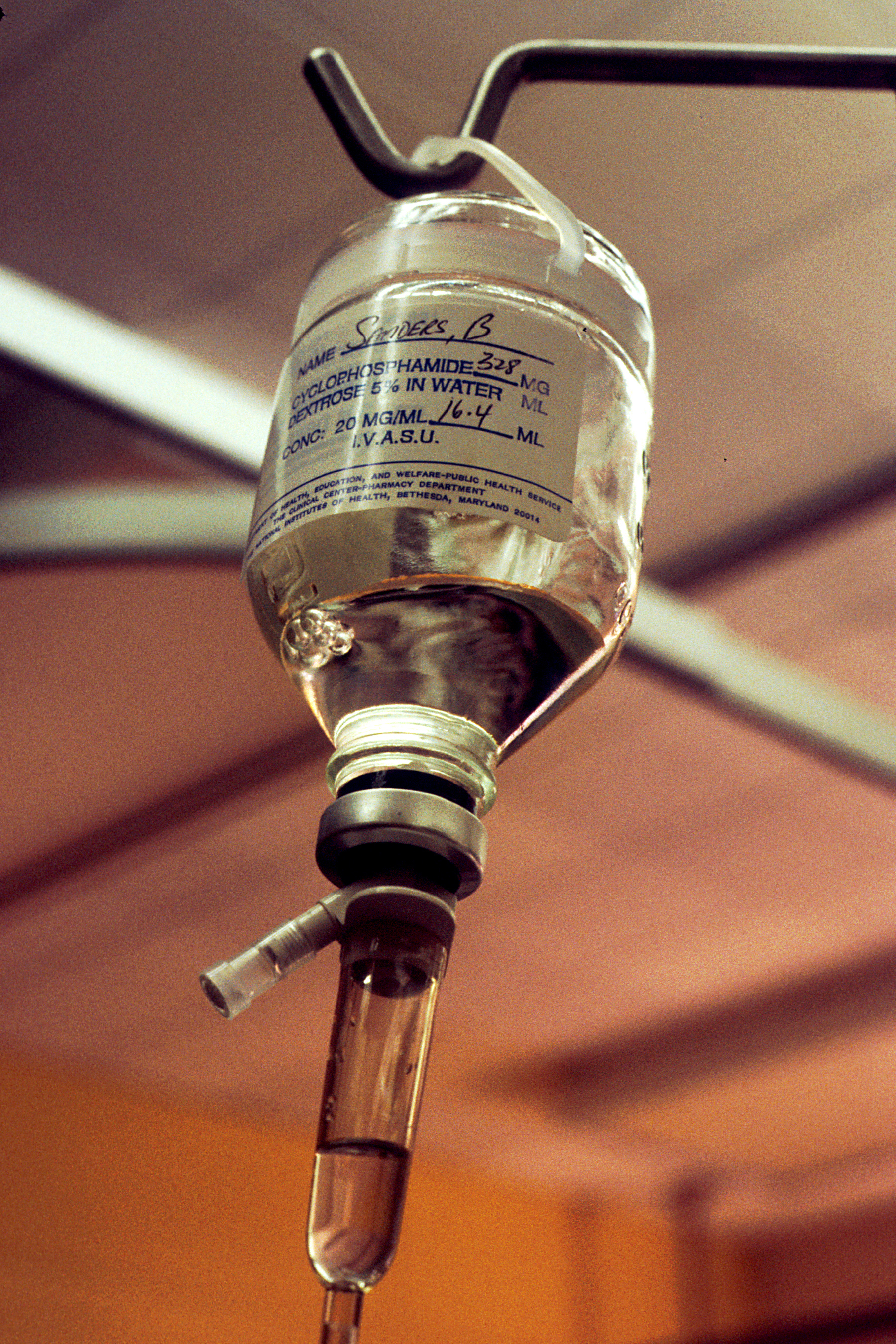
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide (IFO), sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, cervical cancer, and ovarian cancer. It is administered by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, blood in the urine, infections, and kidney problems. Other severe side effects include bone marrow suppression and decreased level of consciousness. Use during pregnancy will likely result in harm to the baby. Ifosfamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It works by disrupting the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Ifosfamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses It is given as a treatment for a variety of cancers, including: * Testicular cancer * Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifosfamide
Ifosfamide (IFO), sold under the brand name Ifex among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes testicular cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, osteosarcoma, bladder cancer, small cell lung cancer, cervical cancer, and ovarian cancer. It is administered by injection into a vein. Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, blood in the urine, infections, and kidney problems. Other severe side effects include bone marrow suppression and decreased level of consciousness. Use during pregnancy will likely result in harm to the baby. Ifosfamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It works by disrupting the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Ifosfamide was approved for medical use in the United States in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses It is given as a treatment for a variety of cancers, including: * Testicular cancer * Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenovirus
Adenoviruses (members of the family ''Adenoviridae'') are medium-sized (90–100 nm), nonenveloped (without an outer lipid bilayer) viruses with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome. Their name derives from their initial isolation from human adenoids in 1953. They have a broad range of vertebrate hosts; in humans, more than 50 distinct adenoviral serotypes have been found to cause a wide range of illnesses, from mild respiratory infections in young children (known as the common cold) to life-threatening multi-organ disease in people with a weakened immune system. Virology Classification This family contains the following genera: * ''Atadenovirus'' * '' Aviadenovirus'' * ''Ichtadenovirus'' * ''Mastadenovirus'' (including all human adenoviruses) * ''Siadenovirus'' * '' Testadenovirus'' Diversity In humans, currently there are 88 human adenoviruses (HAdVs) in seven species (Human adenovirus A to G): * A: 12, 18, 31 * B: 3, 7, 11, 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BK Virus
The BK virus is a member of the polyomavirus family. Past infection with the BK virus is widespread, but significant consequences of infection are uncommon, with the exception of the immunocompromised and the immunosuppressed. BK virus is an abbreviation of the name of the first patient, from whom the virus was isolated in 1971 (the patient was then 29 years old). Signs and symptoms The BK virus rarely causes disease but is typically associated with patients who have had a kidney transplant; many people who are infected with this virus are asymptomatic. If symptoms do appear, they tend to be mild: respiratory infection or fever. These are known as primary BK infections. Although without any clinical symptoms, footprints of BK virus have been detected in specimens from females affected by spontaneous abortion. Serum antibodies against BK virus have also been found in spontaneous abortion affected women as well as in women who underwent voluntary interruption of pregnancy. The v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonoxynol-9
Nonoxynol-9, sometimes abbreviated as N-9, is an organic compound that is used as a surfactant. It is a member of the nonoxynol family of nonionic surfactants. N-9 and related compounds are ingredients in various cleaning and cosmetic products. It is widely used in contraceptives for its spermicidal properties. Uses Spermicide As a spermicide, it attacks the acrosomal membranes of the sperm, causing the sperm to be immobilized. Nonoxynol-9 is the active ingredient in most spermicidal creams, jellies, foams, gel, film, and suppositories. Lubricant Nonoxynol-9 is a common ingredient of most vaginal and anal lubricants due to its spermicidal properties. A 2004 study found that over a six-month period, the typical-use failure rates for five nonoxynol-9 vaginal contraceptives (film, suppository, and gels at three different concentrations) ranged from 10% to 20%. Condoms Many models of condoms are lubricated with solutions containing nonoxynol-9. In this role, it has been p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |