|
Heliobacteria
Heliobacteria are a unique subset of prokaryotic bacteria that process light for energy. Distinguishable from other phototrophic bacteria, they utilize a unique photosynthetic pigment, bacteriochlorophyll ''g'' and are the only known Gram-positive phototroph. They are a key player in symbiotic nitrogen fixation alongside plants, and share a reaction center with green-sulfur bacteria. RNA trees place the heliobacteria among the Bacillota. They have no outer membrane and like certain other Bacillota (Clostridia), they form heat-resistant endospores, which contain high levels of calcium and dipicolinic acid. Heliobacteria are the only Bacillota known to be phototrophic. Metabolism The heliobacteria are phototrophic: they convert light energy into chemical energy using a type I reaction center. The primary pigment involved is bacteriochlorophyll ''g'', which is unique to the group and has a unique absorption spectrum; this gives the heliobacteria their own environmental niche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
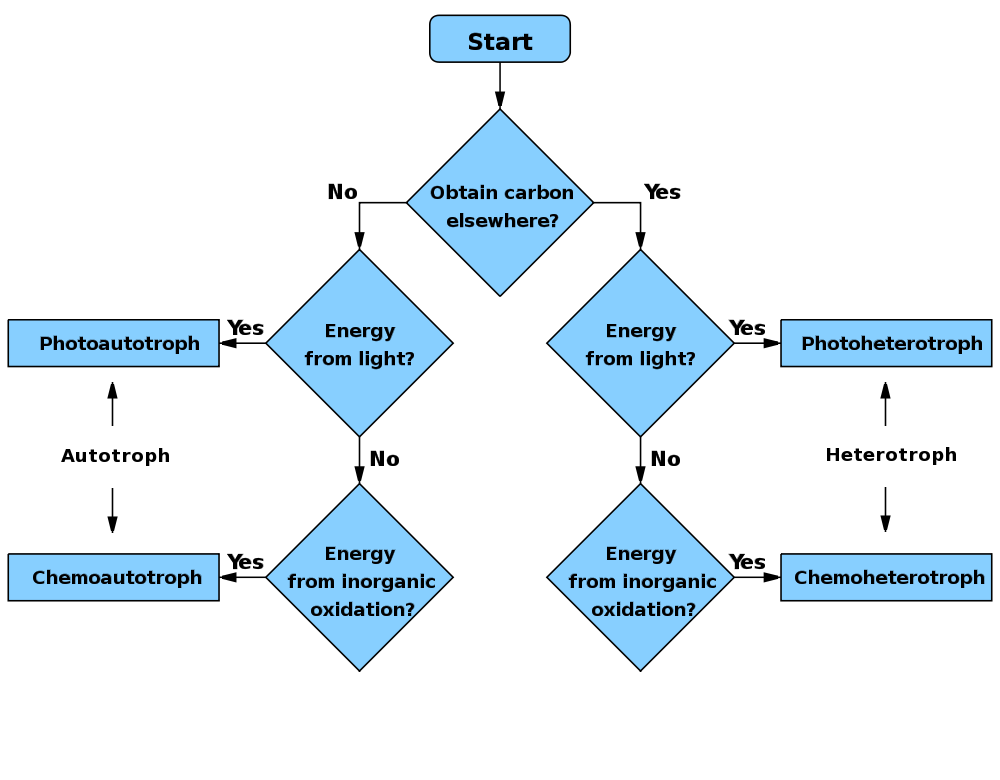
Photoheterotroph
Photoheterotrophs ('' Gk'': ''photo'' = light, ''hetero'' = (an)other, ''troph'' = nourishment) are heterotrophic phototrophs – that is, they are organisms that use light for energy, but cannot use carbon dioxide as their sole carbon source. Consequently, they use organic compounds from the environment to satisfy their carbon requirements; these compounds include carbohydrates, fatty acids, and alcohols. Examples of photoheterotrophic organisms include purple non-sulfur bacteria, green non-sulfur bacteria, and heliobacteria. Recent research has indicated that the oriental hornet and some aphids may be able to use light to supplement their energy supply. Research Studies have shown that mammalian mitochondria can also capture light and synthesize ATP when mixed with a light-capturing metabolite of chlorophyll. Research demonstrated that the same metabolite when fed to the worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' leads to increase in ATP synthesis upon light exposure, along with an increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or transferred as excitation energy via light-harvesting antenna systems, give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors. These co-factors are light-absorbing molecules (also named chromophores or pigments) such as chlorophyll and pheophytin, as well as quinones. The energy of the photon is used to excite an electron of a pigment. The free energy created is then used, via a chain of nearby electron acceptors, for a transfer of hydrogen atoms (as protons and electrons) from H2O or hydrogen sulfide towards carbon dioxide, eventually producing glucose. These electron transfer steps ultimately result in the conversion of the energy of photons to chemical energy. Transforming light energy into c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have gram-positive cell wall structure. The renaming of phyla such as Firmicutes in 2021 remains controversial among microbiologists, many of whom continue to use the earlier names of long standing in the literature. The name "Firmicutes" was derived from the Latin words for "tough skin," referring to the thick cell wall typical of bacteria in this phylum. Scientists once classified the Firmicutes to include all gram-positive bacteria, but have recently defined them to be of a core group of related forms called the low- G+C group, in contrast to the Actinomycetota. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Firmicutes, such as ''Megasphaera'', ''Pectinatus'', ''Selenomonas'' and ''Zymophilus'', have a porous pseudo-outer membrane that causes them to stain gram-negative. Many Bacillota (Firmicutes) produce endospores, which are resistant to desiccation and can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obligate Anaerobe
Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (20.95% O2). Oxygen tolerance varies between species, with some species capable of surviving in up to 8% oxygen, while others lose viability in environments with an oxygen concentration greater than 0.5%. Oxygen sensitivity The oxygen sensitivity of obligate anaerobes has been attributed to a combination of factors including oxidative stress and enzyme production. Oxygen can also damage obligate anaerobes in ways not involving oxidative stress. Because molecular oxygen contains two unpaired electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital, it is readily reduced to superoxide () and hydrogen peroxide () within cells. A reaction between these two products results in the formation of a free hydroxyl radical (OH.). Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals are a class of compounds known as reactive oxygen species (ROS), highly reactant products that are damaging to microbes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flame an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purple Bacteria
Purple bacteria or purple photosynthetic bacteria are Gram-negative proteobacteria that are phototrophic, capable of producing their own food via photosynthesis. They are pigmented with bacteriochlorophyll ''a'' or ''b'', together with various carotenoids, which give them colours ranging between purple, red, brown, and orange. They may be divided into two groups – purple sulfur bacteria ( Chromatiales, in part) and purple non-sulfur bacteria ( Rhodospirillaceae). Purple bacteria are anoxygenic phototrophs widely spread in nature, but especially in aquatic environments, where there are anoxic conditions that favor the synthesis of their pigments. Taxonomy Purple bacteria belong to phylum of ''Pseudomonadota''. This phylum was established by Carl Woese in 1987 calling it "purple bacteria and their relatives" even if this is not appropriate because most of them are not purple or photosynthetic. Purple bacteria are distributed between 3 classes:''Alphaproteobacteria'', ''Betap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototrophy
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a common misconception that phototrophs are obligatorily photosynthetic. Many, but not all, phototrophs often photosynthesize: they anabolically convert carbon dioxide into organic material to be utilized structurally, functionally, or as a source for later catabolic processes (e.g. in the form of starches, sugars and fats). All phototrophs either use electron transport chains or direct proton pumping to establish an electrochemical gradient which is utilized by ATP synthase, to provide the molecular energy currency for the cell. Phototrophs can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs. If their electron and hydrogen donors are inorganic compounds (e.g. , as in some purple sulfur bacteria, or , as in some green sulfur bacteria) they can be also called lithotrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |