|
Haploinsufficiency
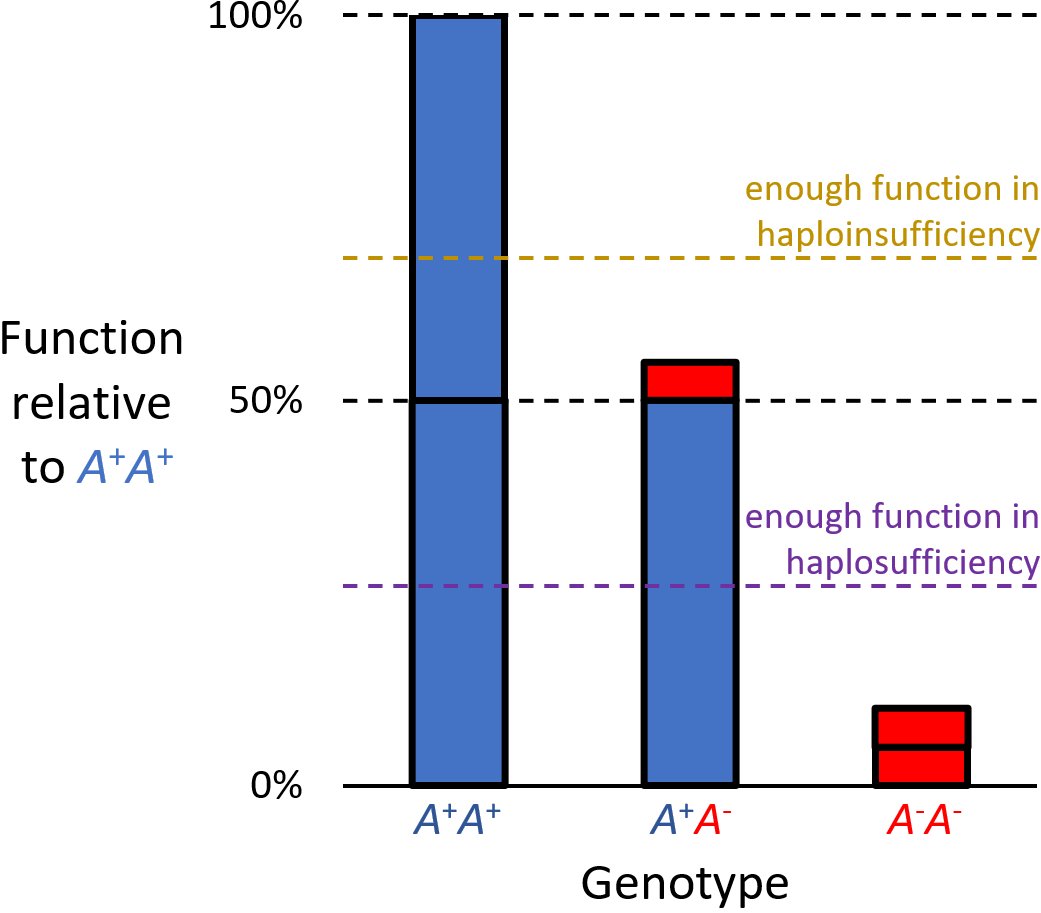
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haploinsufficiency Graph Only
Haploinsufficiency in genetics describes a model of dominant gene action in diploid organisms, in which a single copy of the wild-type allele at a locus in heterozygous combination with a variant allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype. Haploinsufficiency may arise from a ''de novo'' or inherited loss-of-function mutation in the variant allele, such that it yields little or no gene product (often a protein). Although the other, standard allele still produces the standard amount of product, the total product is insufficient to produce the standard phenotype. This heterozygous genotype may result in a non- or sub-standard, deleterious, and (or) disease phenotype. Haploinsufficiency is the standard explanation for dominant deleterious alleles. In the alternative case of haplosufficiency, the loss-of-function allele behaves as above, but the single standard allele in the heterozygous genotype produces sufficient gene product to produce the same, standard phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominance (genetics)
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homozygote
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRPF31
PRP31 pre-mRNA processing factor 31 homolog (S. cerevisiae), also known as PRPF31, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''PRPF31'' gene. Function PRPF31 is the gene coding for the splicing factor hPRP31. It is essential for the formation of the spliceosome hPRP31 is associated with the U4/ U6 di-snRNP and interacts with another splicing factor, h PRP6, to form the U4/U6- U5 tri-snRNP. It has been shown that when hPRP31 is knocked down by RNAi, U4/U6 di-snRNPs accumulate in the Cajal bodies and the U4/U6-U5 tri-snRNP cannot form. PRPF31 is recruited to introns following the attachment of U4 and U6 RNAs and the 15.5K protein NHP2L1. The addition of PRPF31 is crucial for the transition of the spliceosomal complex to the activated state. Clinical significance A mutation in PRPF31 is one of 4 known mutations in splicing factors which are known to cause retinitis pigmentosa. The first mutation in PRPF31 was discovered by Vithana et al. in 2001. Retinitis pigmentosa (R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss-of-function Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (abbreviated to TERT, or hTERT in humans) is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of the telomerase complex. Telomerases are part of a distinct subgroup of RNA-dependent polymerases. Telomerase lengthens telomeres in DNA strands, thereby allowing senescent cells that would otherwise become postmitotic and undergo apoptosis to exceed the Hayflick limit and become potentially immortal, as is often the case with cancerous cells. To be specific, TERT is responsible for catalyzing the addition of nucleotides in a TTAGGG sequence to the ends of a chromosome's telomeres. This addition of repetitive DNA sequences prevents degradation of the chromosomal ends following multiple rounds of replication. hTERT absence (usually as a result of a chromosomal mutation) is associated with the disorder Cri du chat. Function Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics (journal)
''Genetics'' is a monthly scientific journal publishing investigations bearing on heredity, genetics, biochemistry and molecular biology. Genetics is published by the Genetics Society of America. It has a delayed open access policy, and makes articles available online without a subscription after 12 months have elapsed since first publication. Since 2010, it is published online-only.http://www.councilscienceeditors.org/wp-content/uploads/v36n1p14-15_17.pdf George Harrison Shull George Harrison Shull (April 15, 1874 – September 28, 1954) was an eminent American plant geneticist and the younger brother of botanical illustrator and plant breeder J. Marion Shull. He was born on a farm in Clark County, Ohio, graduated fr ... was the founding editor of ''Genetics'' in 1916. Editors-in-Chief References External linksOfficial website Genetics journals Delayed open access journals English-language journals Publications established in 1916 Online-only journals {{ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron (journal)
''Neuron'' is a biweekly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Cell Press, and imprint of Elsevier. It was established in 1988, and covers neuroscience and related biological processes. The current editor in chief is Mariela Zirlinger. The founding editors were Lily Jan, A. James Hudspeth, Louis Reichardt Louis French Reichardt (born June 4, 1942) is a noted American neuroscientist and mountaineering, mountaineer, the first American to summit both Everest and K2. He was also director of the Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative, the largest ..., Roger Nicoll, and Zach Hall. A past Editor in Chief was Katja Brose. Transcript and video available. Click on "Transcript" for text. * See alsoA Career in Science Editing: Katja BroseEditor in Chief, Neuron References External links * Neuroscience journals Cell Press academic journals Publications established in 1988 English-language journals Biweekly journals {{neuroscience-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart disease mostly occurs in the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14582377398).jpg)




