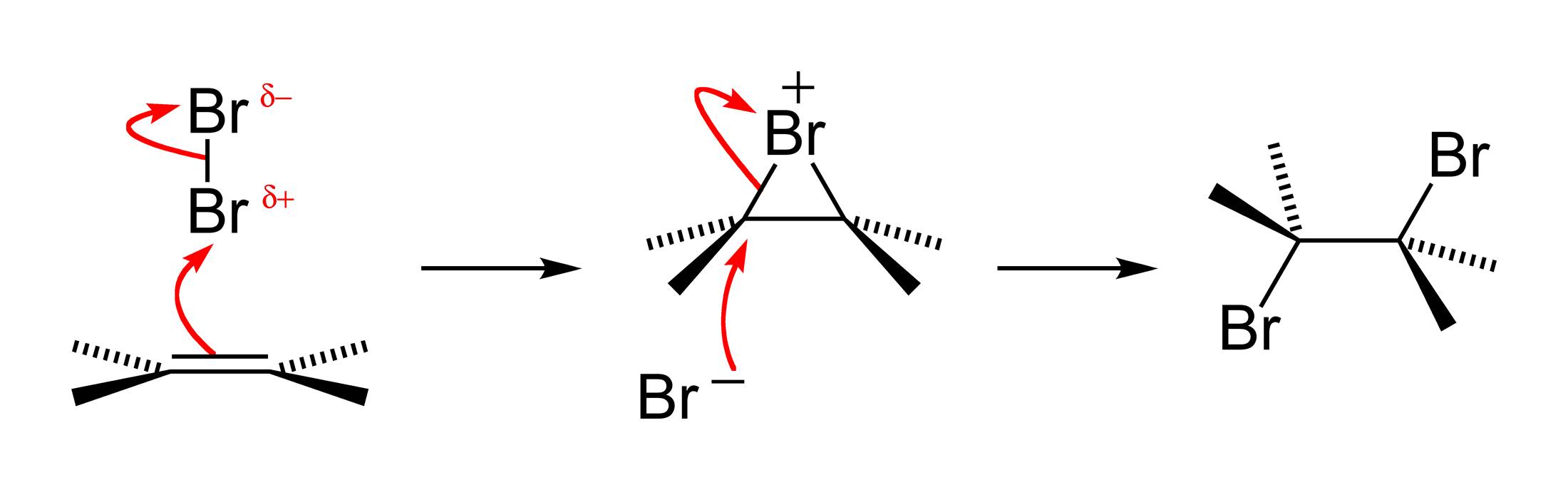|
Halogen Addition Reaction
A halogen addition reaction is a simple organic reaction where a halogen molecule is added to the carbon–carbon double bond of an alkene functional group. The general chemical formula of the halogen addition reaction is: :C=C + X2 → X−C−C−X (X represents the halogens bromine or chlorine, and in this case, a solvent could be CH2Cl2 or CCl4). The product is a vicinal dihalide. This type of reaction is a halogenation and an electrophilic addition. Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism for an alkene bromination can be described as follows. In the first step of the reaction, a bromine molecule approaches the electron-rich alkene carbon–carbon double bond. The bromine atom closer to the bond takes on a partial positive charge as its electrons are repelled by the electrons of the double bond. The atom is electrophilic at this time and is attacked by the pi electrons of the alkene arbon–carbon double bond It forms for an instant a single sigma bond to ''both'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, Mechanistic Organic Photochemistry, photochemical reactions and organic redox reaction, redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions. The oldest organic reactions are combustion of organic fuels and saponification of fats to make soap. Modern organic chemistry starts with the Wöhler synthesis in 1828. In the history of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry awards have been given for the invention of specific organic reactions such as the Grignard reaction in 1912, the Diels-Alder reaction in 1950, the Wittig reaction in 1979 and olefin metathesis in 2005. Classifications Organic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophile
In chemistry, an electrophile is a chemical species that forms bonds with nucleophiles by accepting an electron pair. Because electrophiles accept electrons, they are Lewis acids. Most electrophiles are positively charged, have an atom that carries a partial positive charge, or have an atom that does not have an octet of electrons. Electrophiles mainly interact with nucleophiles through addition and substitution reactions. Frequently seen electrophiles in organic syntheses include cations such as H+ and NO+, polarized neutral molecules such as HCl, alkyl halides, acyl halides, and carbonyl compounds, polarizable neutral molecules such as Cl2 and Br2, oxidizing agents such as organic peracids, chemical species that do not satisfy the octet rule such as carbenes and radicals, and some Lewis acids such as BH3 and DIBAL. Organic chemistry Addition of halogens These occur between alkenes and electrophiles, often halogens as in halogen addition reactions. Common reactions i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maleic Acid
Maleic acid or ''cis''-butenedioic acid is an organic compound that is a dicarboxylic acid, a molecule with two carboxyl groups. Its chemical formula is HO2CCH=CHCO2H. Maleic acid is the ''cis''-isomer of butenedioic acid, whereas fumaric acid is the ''trans''-isomer. It is mainly used as a precursor to fumaric acid, and relative to its parent maleic anhydride, maleic acid has few applications. Physical properties Maleic acid has a '' heat of combustion'' of -1,355 kJ/mol., 22.7 kJ/mol higher than that of fumaric acid. Maleic acid is more soluble in water than fumaric acid. The melting point of maleic acid (135 °C) is also much lower than that of fumaric acid (287 °C). Both properties of maleic acid can be explained on account of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding that takes place in maleic acid at the expense of intermolecular interactions, and that are not possible in fumaric acid for geometric reasons. Production and industrial applications In industry, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOMO
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related to modern humans (depending on the species), most notably ''Homo erectus'' and ''Homo neanderthalensis''. The genus emerged with the appearance of '' Homo habilis'' just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus '' Paranthropus'', is probably sister to ''Australopithecus africanus'', which itself had previously split from the lineage of '' Pan'', the chimpanzees. ''Homo erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and, in several early migrations, spread throughout Africa (where it is dubbed ''Homo ergaster'') and Eurasia. It was likely that the first human species lived in a hunter-gatherer society and was able to control fire. An adaptive and successful species, ''Homo erectus'' persisted for more than a million ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lone Pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone pairs are found in the outermost electron shell of atoms. They can be identified by using a Lewis structure. Electron pairs are therefore considered lone pairs if two electrons are paired but are not used in chemical bonding. Thus, the number of electrons in lone pairs plus the number of electrons in bonds equals the number of valence electrons around an atom. Lone pair is a concept used in valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (VSEPR theory) which explains the shapes of molecules. They are also referred to in the chemistry of Lewis acids and bases. However, not all non-bonding pairs of electrons are considered by chemists to be lone pairs. Examples are the transition metals where the non-bonding pairs do not influence molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LUMO
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''frontier orbitals'', such as in the frontier molecular orbital theory. Gap The energy difference between the HOMO and LUMO is ''the HOMO–LUMO gap''. Its size can be used to predict the strength and stability of transition metal complexes, as well as the colors they produce in solution.Griffith, J. S. and L. E. Orgel"Ligand Field Theory" ''Q. Rev. Chem. Soc.'' 1957, 11, 381–383. As a rule of thumb, the larger a compound's HOMO-LUMO gap, the more stable the compound. Semiconductors The HOMO level is to organic semiconductors roughly what the maximum valence band is to inorganic semiconductors and quantum dots. The same analogy can be made between the LUMO level and the conduction band minimum.Bredas, J,-L"Mind the gap!" ''Mater. Horiz.'' 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibonding Molecular Orbital
In chemical bonding theory, an antibonding orbital is a type of molecular orbital that weakens the chemical bond between two atoms and helps to raise the energy of the molecule relative to the separated atoms. Such an orbital has one or more nodes in the bonding region between the nuclei. The density of the electrons in the orbital is concentrated outside the bonding region and acts to pull one nucleus away from the other and tends to cause mutual repulsion between the two atoms. This is in contrast to a bonding molecular orbital, which has a lower energy than that of the separate atoms, and is responsible for chemical bonds. Diatomic molecules Antibonding molecular orbitals (MOs) are normally ''higher'' in energy than bonding molecular orbitals. Bonding and antibonding orbitals form when atoms combine into molecules. If two hydrogen atoms are initially far apart, they have identical atomic orbitals. However, as the spacing between the two atoms becomes smaller, the electron w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans Configuration
Trans- is a Latin prefix meaning "across", "beyond", or "on the other side of". Used alone, trans may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * Trans (festival), a former festival in Belfast, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * ''Trans'' (film), a 1998 American film * Trans Corp, an Indonesian business unit of CT Corp in the fields of media, lifestyle, and entertainment ** Trans Media, a media subsidiary of Trans Corp *** Trans TV, an Indonesian television network *** Trans7, an Indonesian television network Literature * '' Trans: Gender and Race in an Age of Unsettled Identities'', a 2016 book by Rogers Brubaker * '' Trans: When Ideology Meets Reality'', a 2021 book by Helen Joyce Music * ''Trans'' (album), by Neil Young * ''Trans'' (Stockhausen), a 1971 orchestral composition Places * Trans, Mayenne, France, a commune * Trans, Switzerland, a village Science and technology * Trans effect in inorganic chemistry, the increased lability of ligands that are trans to certain o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti Addition
In organic chemistry, syn- and anti-addition are different ways in which substituent molecules can be added to an alkene or alkyne. The concepts of syn and anti addition are used to characterize the different reactions of organic chemistry by reflecting the stereochemistry of the products in a reaction. The type of addition that occurs depends on multiple different factors of a reaction, and is defined by the final orientation of the substituents on the parent molecule. Syn and anti addition are related to the Markovnikov's rule for the orientation of a reaction, which refers to the bonding preference of different substituents for different carbons on an alkene or alkyne. In order for a reaction to follow Markovnikov's rule, the intermediate carbocation of the mechanism of a reaction must be on the more substituted carbon, allowing the substituent to bond to the more stable carbocation and the more substituted carbon. Syn addition is the addition of two substituents to the same s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophilic Attack
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cationoid'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation and react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromonium Ion
A halonium ion is any onium ion containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure where X is any halogen and no restrictions on R, this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure. Halonium ions formed from fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are called fluoronium, chloronium, bromonium, and iodonium, respectively. The 3-membered cyclic variety commonly proposed as intermediates in electrophilic halogenation may be called haliranium ions, using the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature, Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature system. Structure The simplest halonium ions are of the structure (X = F, Cl, Br, I). Many halonium ions have a three-atom cyclic structure, similar to that of an epoxide, resulting from the formal addition of a halogenium ion X+ to a C=C double bond, as when a halogen is added to an alkene. The formation of 5-membered halonium ions (e.g., chlorolanium, bromolanium ions) via Neighbouring group participation, neig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |