|
Hafrada
Hafrada ( he, הפרדה, lit=separation, disengagement)According to the Milon and Masada dictionaries, hafrada translates into English as "separation", "division", "disengagement", "severance", "disassociation" or "divorce"Milon: English Hebrew Dictionary/ref> is the policy of the government of Israel to separate the Israeli population from the Palestinian population in the occupied Palestinian territories, in both the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. Yitzhak Rabin, Israeli Prime Minister from 1992-1995, was the first to advocate for the construction of a physical barrier between Israelis and Palestinians. Following the 1995 Beit Lid suicide bombing that killed 22 Israelis, Rabin stated that separation is necessary to protect the majority of Israeli Jews from Palestinian terrorism. Ehud Barak, Prime Minister from 1999 to 2001, stated that "good fences make good neighbors." Since its first public introductions, the concept-turned-policy or paradigm has dominated Israeli political a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
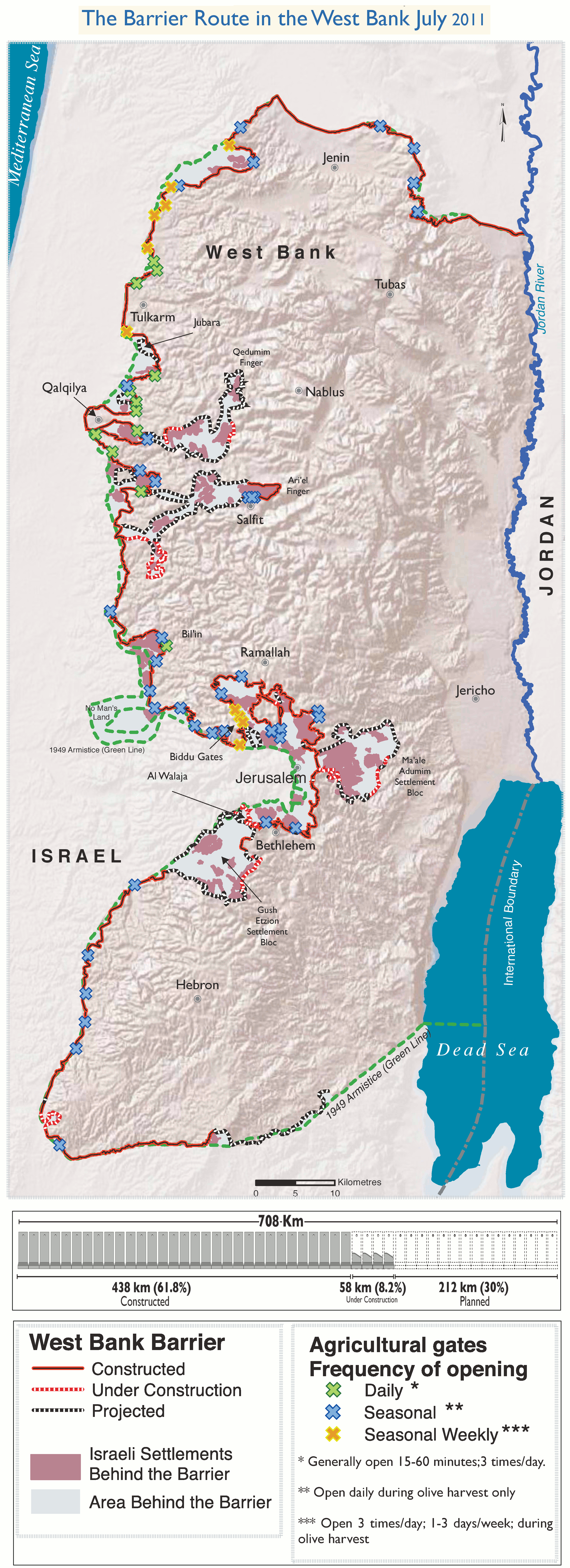
Israeli West Bank Barrier
The Israeli West Bank barrier, comprising the West Bank Wall and the West Bank fence, is a separation barrier built by Israel along the Green Line and inside parts of the West Bank. It is a contentious element of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict: Israel describes the wall as a necessary security barrier against Palestinian terrorism, whereas Palestinians describe it as an element of racial segregation and a representation of Israeli apartheid. At a total length of upon completion, the route traced by the barrier is more than double the length of the Green Line, with 15% of its length running along the Green Line or inside Israel, and the remaining 85% running as much as inside the West Bank, effectively isolating about 9% of the land and approximately 25,000 Palestinians from the rest of the Palestinian territory. The barrier was built by Israel following a wave of Palestinian political violence and incidents of terrorism inside Israel during the Second Intifada, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Disengagement From Gaza
The Israeli disengagement from Gaza ( he, תוכנית ההתנתקות, ') was the unilateral dismantling in 2005 of the 21 Israeli settlements in the Gaza Strip and the evacuation of Israeli settlers and army from inside the Gaza Strip. The disengagement was proposed in 2003 by Prime Minister Ariel Sharon, adopted by the government in June 2004, and approved by the Knesset in February 2005 as the ''Disengagement Plan Implementation Law''. It was implemented in August 2005 and completed in September 2005. The settlers who refused to accept government compensation packages and voluntarily vacate their homes prior to the 15 August 2005 deadline were evicted by Israeli security forces over a period of several days. The eviction of all residents, demolition of the residential buildings and evacuation of associated security personnel from the Gaza Strip was completed by 12 September 2005. The eviction and dismantlement of the four settlements in the northern West Bank was complet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Israel
The Cabinet of Israel (officially: he, ממשלת ישראל ''Memshelet Yisrael'') exercises executive authority in the State of Israel. It consists of ministers who are chosen and led by the prime minister. The composition of the government must be approved by a vote of confidence in the Knesset (the Israeli parliament). Under Israeli law, the prime minister may dismiss members of the government, but must do so in writing, and new appointees must be approved by the Knesset. Most ministers lead ministries, though some are ministers without portfolio. Most ministers are members of the Knesset, though only the Prime Minister and the " designated acting prime minister" are required to be Knesset members. Some ministers are also called deputy and vice prime ministers. Unlike the designated acting prime minister, these roles have no statutory meanings. The government operates in accordance with the Basic Law. It meets on Sundays weekly in Jerusalem. There may be additional meetin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestinian Political Violence
Palestinian political violence refers to acts of violence perpetrated for political ends in relation to the State of Palestine or in connection with Palestinian nationalism. Common political objectives include self-determination in and sovereignty over Palestine,de Waart, 1994p. 223 Referencing Article 9 of ''The Palestinian National Charter of 1968''. The Avalon Project has a copy herDe Waal, 2004pp. 29–30. or the "liberation of Palestine" and recognition of a Palestinian state, either in place of both Israel and the Palestinian territories, or solely in the Palestinian territories.Schulz, 1999p. 161 More limited goals include the release of Palestinian prisoners or the Palestinian right of return. Other motivations include personal grievances, trauma or revenge.Avishai Margalit“The Suicide Bombers,'at New York Review of Books, January 16, 2003 :'the main motivating force for the suicide bombers seems to be the desire for spectacular revenge.'Peter Beinart'The American Jew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was characterised by an authoritarian political culture based on ''baasskap'' (boss-hood or boss-ship), which ensured that South Africa was dominated politically, socially, and economically by the nation's minority white population. According to this system of social stratification, white citizens had the highest status, followed by Indians and Coloureds, then black Africans. The economic legacy and social effects of apartheid continue to the present day. Broadly speaking, apartheid was delineated into ''petty apartheid'', which entailed the segregation of public facilities and social events, and ''grand apartheid'', which dictated housing and employment opportunities by race. The first apartheid law was the Prohibition of Mixed Marriages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aaron Klieman
Aaron (Aharon) S. Klieman (July 27, 1939 – June 17, 2021) was an American-born Israeli historian of international relations who developed the field of international affairs in Israel and abroad. Klieman researched a wide variety of fields in political science including history, arms sales, and geopolitics. He was the Dr. Nahum Goldmann Chair in Diplomacy and lecturer on international relations in the Department of Political Science at Tel-Aviv University, and was the founding director of the Abba Eban Graduate Program in Diplomatic Studies. A native of Chicago, Illinois, his PhD is from The Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies, with an M.A. from the School of International Affairs at Columbia University in Middle Eastern studies. Klieman wrote and edited 24 books, monographs, and documentary collections in English and Hebrew, and has authored over 30 book chapters in addition to journal articles. He was also a senior editor of the ''Israel Journal o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Press
Grove Press is an United States of America, American Imprint (trade name), publishing imprint that was founded in 1947. Imprints include: Black Cat, Evergreen, Venus Library, and Zebra. Barney Rosset purchased the company in 1951 and turned it into an Alternative media, alternative book press in the United States. He partnered with Richard Seaver to bring French literature to the United States. The Atlantic Monthly Press, under the aegis of its publisher, Morgan Entrekin, merged with Grove Press in 1991. Grove later became an imprint of the publisher Grove Atlantic, Grove/Atlantic, Inc. Early years Grove Press was founded in 1947 in Greenwich Village on Grove Street. The original owners only published three books in three years and so sold it to Barney Rosset in 1951 for three thousand dollars. Literary avant-garde Under Rosset's leadership, Grove introduced American readers to European avant-garde literature and theatre, including French authors Alain Robbe-Grillet, Jean Genet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Aviv University
Tel Aviv University (TAU) ( he, אוּנִיבֶרְסִיטַת תֵּל אָבִיב, ''Universitat Tel Aviv'') is a public research university in Tel Aviv, Israel. With over 30,000 students, it is the largest university in the country. Located in northwest Tel Aviv, the university is the center of teaching and research of the city, comprising 9 faculties, 17 teaching hospitals, 18 performing arts centers, 27 schools, 106 departments, 340 research centers, and 400 laboratories. Tel Aviv University originated in 1956 when three education units merged to form the university. The original 170-acre campus was expanded and now makes up 220 acres (89 hectares) in Tel Aviv's Ramat Aviv neighborhood. History TAU's origins date back to 1956, when three research institutes: the Tel Aviv School of Law and Economics (established in 1935), the Institute of Natural Sciences (established in 1931), and the Academic Institute of Jewish Studies (established in 1954) – joined to form Tel Aviv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CounterPunch
''CounterPunch'' is a left-wing online magazine. Content includes a free section published five days a week as well as a subscriber-only area called CounterPunch+, where original articles are published weekly. ''CounterPunch'' is based in the United States and covers politics in a manner its editors describe as "muckraking with a radical attitude". History ''CounterPunch'' began as a newsletter, established in 1994 by the Washington, D.C.-based investigative reporter Ken Silverstein. He was soon joined by Alexander Cockburn and then Jeffrey St. Clair, who became the publication's editors in 1996 when Silverstein left. In 2007, Cockburn and St. Clair wrote that in founding ''CounterPunch'' they had "wanted it to be the best muckraking newsletter in the country", and cited as inspiration such pamphleteers as Edward Abbey, Peter Maurin, and Ammon Hennacy, as well as the socialist/populist newspaper '' Appeal to Reason'' (1895–1922). When Alexander Cockburn died in 2012 at the age o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bank Closures
The West Bank closure system is a series of obstacles including permanent and partially staffed checkpoints, concrete roadblocks and barriers, metal gates, earth mounds, tunnels, trenches, and an elaborate set of permit restrictions that controls and restricts Palestinian freedom of movement. Severe closures began following the outbreak of the First intifada in the late 1980s, when travel restrictions were tightened in the West Bank and Gaza, and Israel began requiring Gazan workers to hold permits workers from Gaza.. Also a/ref> Rationale and impact The Israeli government states that the system is designed to protect Israeli citizens from Palestinian terrorist attacks that have killed over 1,000 Israelis since September 2000. In addition to the partial fulfilment of these goals, the closure system has divided communities from their land and one another and restricted Palestinian access to health and education services, their places of work and sites of religious worship. Physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza–Israel Barrier
The Gaza–Israel barrier is a border barrier located on the Israeli side of the Gaza–Israel border. The Erez Crossing, in the north of the Gaza Strip, is the only crossing point for people and goods coming from Israel into Gaza; there exists a second crossing point in the barrier, called the Kerem Shalom border crossing, which is exclusive for the crossing of goods coming from Egypt, as Israel does not allow goods to go directly from Egypt into Gaza through the Egypt–Gaza border. A fence along the border was first constructed by Israel in 1994 as a security barrier, and has been rebuilt and upgraded since. It was constructed by Israel to control the movement of people as well as goods between the Gaza Strip and Israel, which it could not achieve by normal border crossings. There is also one crossing along the Egypt–Gaza border, the Rafah Crossing, though it is limited to the crossing of people; as per Israel's demand, any cargo or goods that are to enter Gaza must go thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |