|
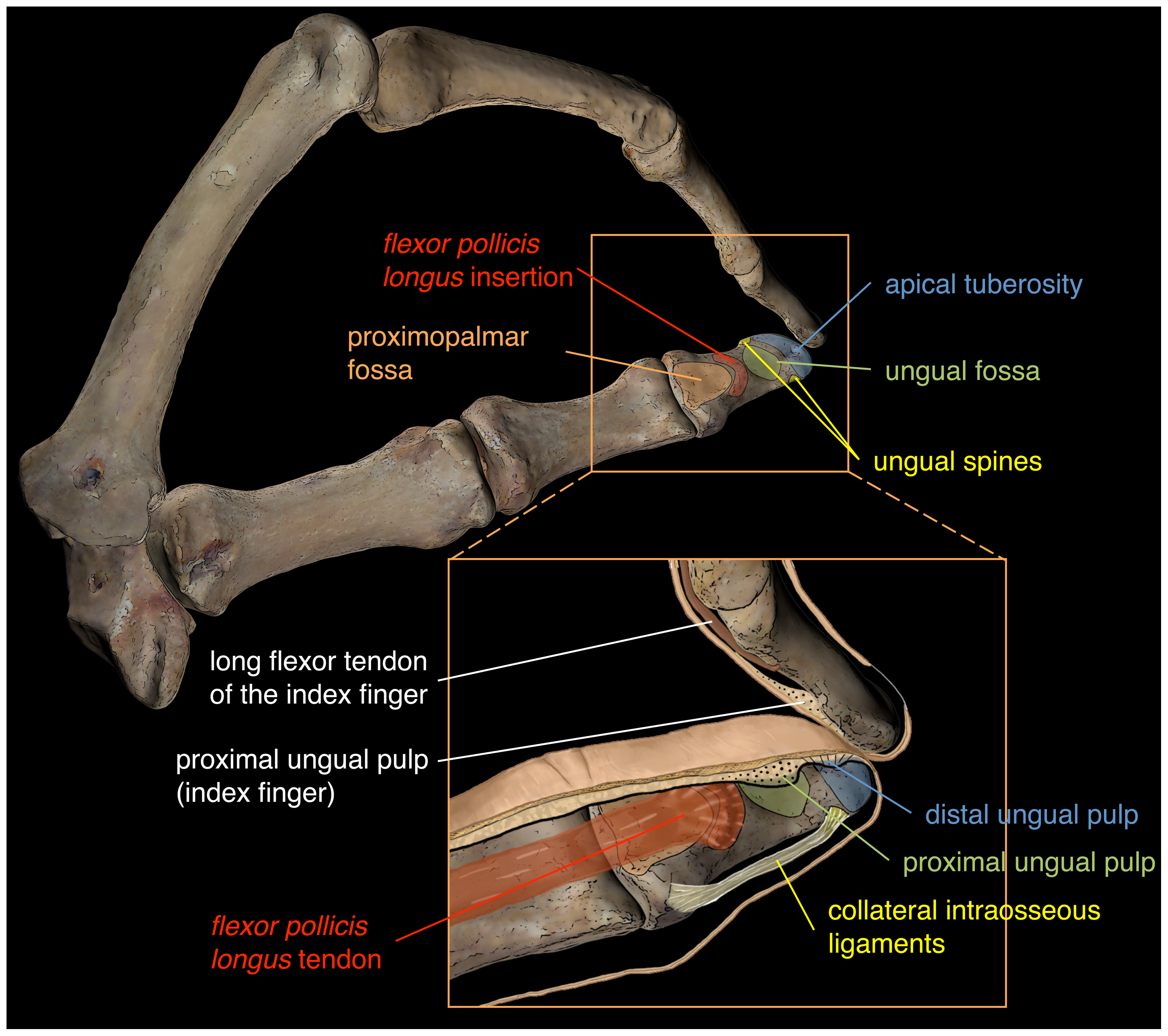
Hyperphalangy
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The prox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distal Phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proxima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpophalangeal Joint
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow cavities on the proximal ends of the proximal phalanges. Being condyloid, they allow the movements of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction at the joint. Structure Ligaments Each joint has: * palmar ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations * collateral ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations Dorsal surfaces The dorsal surfaces of these joints are covered by the expansions of the Extensor tendons, together with some loose areolar tissue which connects the deep surfaces of the tendons to the bones. Function The movements which occur in these joints are flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction; the movements of abduction and adduction are very limited, and cannot be performed wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base (proximally), and a head ( distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is wedge-shaped, articulating proximally with the tarsal bones, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knuckle
The knuckles are the joints of the finger A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly). Chambers 1 ...s. The word is cognate to similar words in other Germanic languages, such as the Dutch "knokkel" (knuckle) or German "Knöchel" (ankle), i.e., ''Knöchlein'', the diminutive of the German word for bone (''Knochen''). Anatomically, it is said that the knuckles consist of the metacarpophalangealUtah Mountain BikingThumb Sprain First as metacarpo. (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints of the finger. The knuckles at the base of the fingers may be referred to as the 1st or major knuckles while the knuckles at the midfinger are known as the 2nd and 3rd, or minor, knuckles. However, the ordinal terms are used inconsistently and may refer to any of the knuckles. Cracking The physical mechanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpal
In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist, which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The metacarpals form a transverse arch to which the rigid row of distal carpal bones are fixed. The peripheral metacarpals (those of the thumb and little finger) form the sides of the cup of the palmar gutter and as they are brought together they deepen this concavity. The index metacarpal is the most firmly fixed, while the thumb metacarpal articulates with the trapezium and acts independently from the others. The middle metacarpals are tightly united to the carpus by intrinsic interlocking bone elements at their bases. The ring metacarpal is somewhat more mobile while the fifth metacarpal is semi-independent.Tubiana ''et al'' 1998, p 11 Each metacarpal bone consists of a bod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metacarpophalangeal Joint
The metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP) are situated between the metacarpal bones and the proximal phalanges of the fingers. These joints are of the condyloid kind, formed by the reception of the rounded heads of the metacarpal bones into shallow cavities on the proximal ends of the proximal phalanges. Being condyloid, they allow the movements of flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction at the joint. Structure Ligaments Each joint has: * palmar ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations * collateral ligaments of metacarpophalangeal articulations Dorsal surfaces The dorsal surfaces of these joints are covered by the expansions of the Extensor tendons, together with some loose areolar tissue which connects the deep surfaces of the tendons to the bones. Function The movements which occur in these joints are flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, and circumduction; the movements of abduction and adduction are very limited, and cannot be performed wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsophalangeal Joint
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones ( proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges). The ligaments are the plantar and two collateral. Movements The movements permitted in the metatarsophalangeal joints are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction. File:The feet of C. H. Unthan, the armless fiddler Wellcome L0034227.jpg, Left: toes adducted (pulled towards the center) and spread (abducted); right, both feet clenched (plantar flexed) File:Footgym rings1.jpg, The upper foot is clenching (plantarflexing) at the MTP joints and at the joints of the toes; the central foot is lifting the toes (dorsiflexing) at the MTP joints; and the foot flat on the ground off to the side is in a neutral pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interphalangeal Joints Of Hand
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand. There are two sets in each finger (except in the thumb, which has only one joint): * "proximal interphalangeal joints" (PIJ or PIP), those between the first (also called proximal) and second (intermediate) phalanges * "distal interphalangeal joints" (DIJ or DIP), those between the second (intermediate) and third (distal) phalanges Anatomically, the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints are very similar. There are some minor differences in how the palmar plates are attached proximally and in the segmentation of the flexor tendon sheath, but the major differences are the smaller dimension and reduced mobility of the distal joint. Joint structure The PIP joint exhibits great lateral stability. Its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior diameter and its thick collateral ligaments are tight in all positions duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


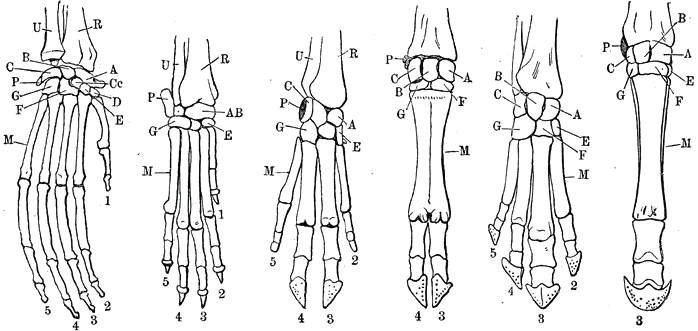
_dorsal_view.png)
