|
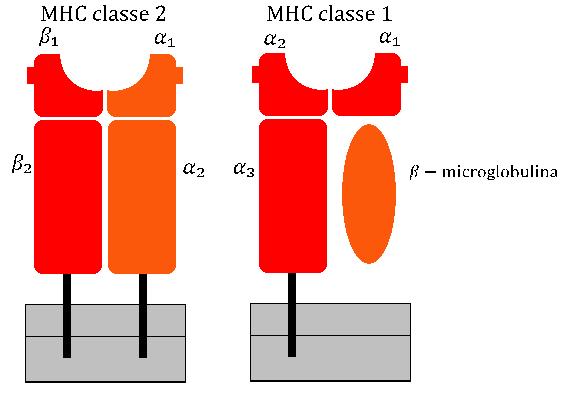
Histocompatibility Molecule
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygenic
A polygene is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance (polygenic inheritance, multigenic inheritance, quantitative inheritance), a type of non-Mendelian inheritance, as opposed to single-gene inheritance, which is the core notion of Mendelian inheritance. The term "monozygous" is usually used to refer to a hypothetical gene as it is often difficult to distinguish the effect of an individual gene from the effects of other genes and the environment on a particular phenotype. Advances in statistical methodology and high throughput sequencing are, however, allowing researchers to locate candidate genes for the trait. In the case that such a gene is identified, it is referred to as a quantitative trait locus (QTL). These genes are generally pleiotropic as well. The genes that contribute to type 2 diabetes are thought to be mostly polygenes. In July 2016, scientists reported identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histocompatibility
Histocompatibility, or tissue compatibility, is the property of having the same, or sufficiently similar, alleles of a set of genes called human leukocyte antigens (HLA), or major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Each individual expresses many unique HLA proteins on the surface of their cells, which signal to the immune system whether a cell is part of the self or an invading organism. T cells recognize foreign HLA molecules and trigger an immune response to destroy the foreign cells. Histocompatibility testing is most relevant for topics related to whole organ, tissue, or stem cell transplants, where the similarity or difference between the donor's HLA alleles and the recipient's triggers the immune system to reject the transplant. The wide variety of potential HLA alleles lead to unique combinations in individuals and make matching difficult. Discovery The discovery of the MHC and role of histocompatibility in transplantation was a combined effort of many scientists in the 20t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Davis Snell
George Davis Snell NAS (December 19, 1903 – June 6, 1996) was an American mouse geneticist and basic transplant immunologist. Work George Snell shared the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Baruj Benacerraf and Jean Dausset for their discoveries concerning "genetically determined structures on the cell surface that regulate immunological reactions". Snell specifically "discovered the genetic factors that determine the possibilities of transplanting tissue from one individual to another. It was Snell who introduced the concept of H antigensSnell's work in mice led to the discovery of Human leukocyte antigen, HLA, the major histocompatibility complex, in humans (and all vertebrates) that is analogous to the H-2 complex in mice. Recognition of these key genes was prerequisite to successful tissue and organ transplantation. Life George Snell was born in Bradford, Massachusetts, the youngest of three children. His father (who was born in Minnesota) worked as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarence Little
Clarence Cook Little (October 6, 1888 – December 22, 1971) was an American genetics, cancer, and tobacco researcher and academic administrator, as well as a eugenicist. Early life C. C. Little was born in Brookline, Massachusetts and attended Harvard University after his secondary education at the Noble and Greenough School. Little received an A.B. from Harvard University in 1910, an M.S. in 1912, and D.Sc. in 1914 in zoology, with special focus in the new science of genetics. During World War I, Little served in the U.S. Army Signal Corps, attaining the rank of Major. Following the war he spent three years at the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. In 1921, he helped found the American Birth Control League with Margaret Sanger and Lothrop Stoddard. Career While studying under W. E. Castle, Little began his work with mice, focusing on inheritance, transplants, and grafts. He also was an assistant dean and secretary to the president. In 1921, he inbred the mouse strain C57BL/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Alfred Gorer
Peter Alfred Gorer FRS (14 April 1907 (London)–1961) was a British immunologist, pathologist and geneticist who pioneered the field of transplant immunology. Peter Gorer was born in London to Edgar (drowned in the 1915 sinking of RMS Lusitania) and Rachel née Cohen Gorer. He died of lung cancer in 1961. Education and work institutions He was educated at Charterhouse. He graduated from Guy's Hospital, London in 1929 and then studied genetics under J.B.S. Haldane at University College, London. From 1933 to 1940 Gorer worked at the Lister Institute before returning to Guy's Hospital to work as a pathologist. Research Gorer is credited with the co-discovery of histocompatibility antigens and the elucidation of their genetic regulation. Together with George Snell, he helped discover the murine histocompatibility 2 locus, or H-2, which is analogous to the human leukocyte antigen. Gorer also identified antigen II and determined its role in transplant tissue rejection. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Splicing
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mate Choice
Mate choice is one of the primary mechanisms under which evolution can occur. It is characterized by a "selective response by animals to particular stimuli" which can be observed as behavior.Bateson, Paul Patrick Gordon. "Mate Choice." Mate Choice, Cambridge University Press, 1985 In other words, before an animal engages with a potential mate, they first evaluate various aspects of that mate which are indicative of quality—such as the resources or phenotypes they have—and evaluate whether or not those particular Phenotypic trait, trait(s) are somehow beneficial to them. The evaluation will then incur a response of some sort. These mechanisms are a part of evolutionary change because they operate in a way that causes the qualities that are desired in a mate to be more frequently passed on to each generation over time. For example, if female peacocks desire mates who have a colourful plumage, then this trait will increase in frequency over time as male peacocks with a colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Histocompatibility Complex And Sexual Selection
The major histocompatibility complex in sexual selection concerns how major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules allow for immune system surveillance of the population of protein molecules in a host's cells. In 1976, Yamazaki et al. demonstrated a sexual selection mate choice by male mice for females of a . Major histocompatibility complex genes, which control the immune response and effective resistance against pathogens, have been able to maintain an extremely high level of allelic diversity throughout time and throughout different populations. Studies suggest that the MHC is involved in mate choice for many vertebrates through olfactory cues. There are several proposed hypotheses that address how MHC-associated mating preferences could be adaptive and how an unusually large amount of allelic diversity has been maintained in the MHC. The vast source of genetic variation affecting an organism's fitness stems from the co-evolutionary arms race between hosts and parasites. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |