|
Hexafluoronickelate(IV)
The fluoronickelates are a class of chemical compounds containing an anion with nickel at its core, surrounded by fluoride ions which act as ligands. This makes it a fluoroanion. The nickel atom can be in a range of oxidation states from +2, +3 to +4. The hexafluoronickelate(IV)2− ion NiF62− contains nickel in the maximal +4 state, and is in octahedral coordination by the fluoride atoms. It forms a commercially available salt Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) K2NiF6. Solid double salts can also contain tetrafluoronickelate The fluoronickelates are a class of chemical compounds containing an anion with nickel at its core, surrounded by fluoride ions which act as ligands. This makes it a fluoroanion In chemistry, a fluoroanion or fluorometallate anion is a polyatomi ... NiF4 eg K2NiF4. References {{fluorine compounds Nickel complexes Fluoro complexes Fluorometallates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrafluoronickelate
The fluoronickelates are a class of chemical compounds containing an anion with nickel at its core, surrounded by fluoride ions which act as ligands. This makes it a fluoroanion In chemistry, a fluoroanion or fluorometallate anion is a polyatomic anion that contains one or more fluorine atoms. The ions and salts form from them are also known as complex fluorides. They can occur in salts, or in solution, but seldom as pu .... The nickel atom can be in a range of oxidation states from +2, +3 to +4. The hexafluoronickelate(IV)2− ion NiF62− contains nickel in the maximal +4 state, and is in octahedral coordination by the fluoride atoms. It forms a commercially available salt Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) K2NiF6. Solid double salts can also contain tetrafluoronickelate NiF4 eg K2NiF4. References {{fluorine compounds Nickel complexes Fluoro complexes Fluorometallates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hexafluoronickelate(IV)
Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It can be produced through the reaction of potassium fluoride, nickel dichloride, and fluorine. It reacts violently with water, releasing oxygen. It dissolves in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to produce a light-red solution. Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) decomposes at 350 °C, forming potassium hexafluoronickelate(III), nickel(II) fluoride, and fluorine: :\rm \ 3 K_2NiF_6 \xrightarrow 2 K_3NiF_6 + NiF_2 + F_2 Potassium hexafluoronickelate is a strong oxidant. It can turn chlorine pentafluoride and bromine pentafluoride into and , respectively: :\rm \ K_2NiF_6 + 5 AsF_5 + XF_5 \xrightarrow XF_6AsF_6 + Ni(AsF_6)_2 + 2KAsF_6 :( X = Cl or Br , -60 °C , aHF = anhydrous hydrogen fluoride). Potassium hexafluoronickelate decomposes at high temperatures to release fluorine gas; like terbium(IV) fluoride Terbium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula TbF4. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hexafluoronickelate
Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It can be produced through the reaction of potassium fluoride, nickel dichloride, and fluorine. It reacts violently with water, releasing oxygen. It dissolves in anhydrous hydrogen fluoride to produce a light-red solution. Potassium hexafluoronickelate(IV) decomposes at 350 °C, forming potassium hexafluoronickelate(III), nickel(II) fluoride, and fluorine: :\rm \ 3 K_2NiF_6 \xrightarrow 2 K_3NiF_6 + NiF_2 + F_2 Potassium hexafluoronickelate is a strong oxidant. It can turn chlorine pentafluoride and bromine pentafluoride into and , respectively: :\rm \ K_2NiF_6 + 5 AsF_5 + XF_5 \xrightarrow XF_6AsF_6 + Ni(AsF_6)_2 + 2KAsF_6 :( X = Cl or Br , -60 °C , aHF = anhydrous hydrogen fluoride). Potassium hexafluoronickelate decomposes at high temperatures to release fluorine gas; like terbium(IV) fluoride Terbium(IV) fluoride is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula TbF4. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoroanion
In chemistry, a fluoroanion or fluorometallate anion is a polyatomic anion that contains one or more fluorine atoms. The ions and salts form from them are also known as complex fluorides. They can occur in salts, or in solution, but seldom as pure acids. Fluoroanions often contain elements in higher oxidation states. They mostly can be considered as fluorometallates, which are a subclass of halometallates. The following is a list of fluoroanions in atomic number order. * trifluoroberyllate * tetrafluoroberyllate *tetrafluoroborate * magnesium tetrafluoride * tetrafluoroaluminate * hexafluoroaluminate *hexafluorosilicate *hexafluorophosphate * Sulfur trifluoride anion * pentafluorosulfate aka pentafluorosulfite or Sulfur pentafluoride ion * sulfur pentafluoride anion * tetrafluorochlorate * hexafluorotitanate * hexafluorovanadate(III) * hexafluorovanadate(IV) * hexafluorovanadate(V) * trifluoromanganate * hexafluoromanganate(III) * hexafluoromanganate(IV) * heptafluoromanganate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
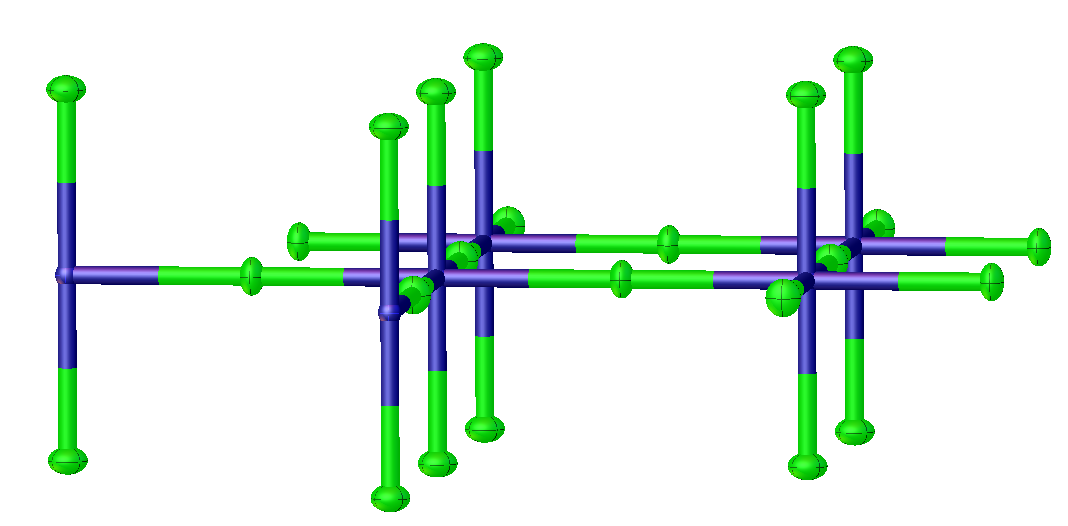
Potassium Tetrafluoronickelate
Potassium tetrafluoronickelate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2NiF4. It features octahedral (high spin) Ni centers with Ni-F bond lengths of 2.006 Å. This green solid is a salt of tetrafluoronickelate. It is prepared by melting a mixture of nickel(II) fluoride, potassium fluoride, and potassium bifluoride. The compound adopts a perovskite-like structure consisting of layers of octahedral Ni centers interconnected by doubly bridging fluoride ligands. The layers are interconnected by potassium cations. It is one of the principal Ruddlesden-Popper phases. Early discoveries on cuprate superconductors focused on compounds with structures closely related to K2NiF4, e.g. lanthanum cuprate and derivative lanthanum barium copper oxide Lanthanum barium copper oxide, or LBCO, is an inorganic compound with the formula CuBa0.15La1.85O4. It is a black solid produced by heating an intimate mixture of barium oxide, copper(II) oxide, and lanthanum oxide in the presence of oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel Complexes
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluoro Complexes
Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative reactive element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with all other elements except for the light inert gases. Among the elements, fluorine ranks 24th in universal abundance and 13th in terrestrial abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning 'flow' gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist Henri Moissan isolate elemental fluorine using low-temperature electrolysis, a process still employed for modern produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |