|
Herpes Zoster
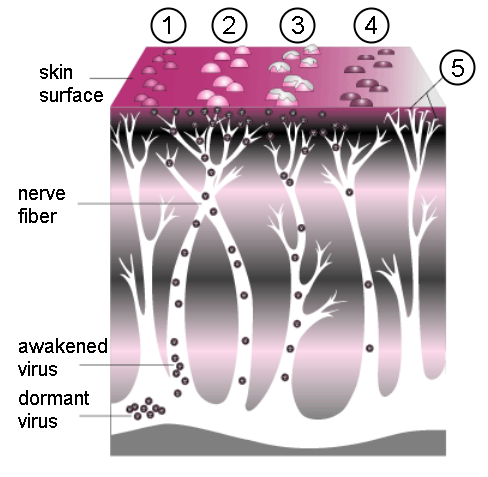
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area. Otherwise, there are typically few symptoms though some people may have fever or headache, or feel tired. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks; however, some people develop ongoing nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with poor immune function the rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox has resolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatology
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A List of dermatologists, dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems. Etymology Attested in English in 1819, the word "dermatology" derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek δέρματος (''dermatos''), genitive of δέρμα (''derma''), "skin" (itself from δέρω ''dero'', "to flay") and -λογία ''wikt:-logia, -logia''. Neo-Latin ''dermatologia'' was coined in 1630, an anatomical term with various French and German uses attested from the 1730s. History In 1708, the first great school of dermatology became a reality at the famous Hôpital Saint-Louis in Paris, and the first textbooks (Willan's, 1798–1808) and atlases (Jean-Louis-Marc Alibert, Alibert's, 1806–1816) appeared in print ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingles
Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area. Otherwise, there are typically few symptoms though some people may have fever or headache, or feel tired. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks; however, some people develop ongoing nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with poor immune function the rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox has resolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aciclovir
Aciclovir (ACV), also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medication. It is primarily used for the treatment of herpes simplex virus infections, chickenpox, and shingles. Other uses include prevention of cytomegalovirus infections following transplant and severe complications of Epstein–Barr virus infection. It can be taken by mouth, applied as a cream, or injected. Common side effects include nausea and diarrhea. Potentially serious side effects include kidney problems and low platelets. Greater care is recommended in those with poor liver or kidney function. It is generally considered safe for use in pregnancy with no harm having been observed. It appears to be safe during breastfeeding. Aciclovir is a nucleoside analogue that mimics guanosine. It works by decreasing the production of the virus's DNA. Aciclovir was patented in 1974, and approved for medical use in 1981. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpesviridae
''Herpesviridae'' is a large family of DNA viruses that cause infections and certain diseases in animals, including humans. The members of this family are also known as herpesviruses. The family name is derived from the Greek word ''ἕρπειν'' ( 'to creep'), referring to spreading cutaneous lesions, usually involving blisters, seen in flares of herpes simplex 1, herpes simplex 2 and herpes zoster (shingles). In 1971, the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) established ''Herpesvirus'' as a genus with 23 viruses among four groups. As of 2020, 115 species are recognized, all but one of which are in one of the three subfamilies. Herpesviruses can cause both latent and lytic infections. Nine herpesvirus types are known to primarily infect humans, at least five of which – herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2, also known as HHV-1 and HHV-2; both of which can cause orolabial herpes and genital herpes), varicella zoster virus (or HHV-3; the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus 1 and 2 (HSV-1 and HSV-2), also known by their taxonomical names ''Human alphaherpesvirus 1'' and ''Human alphaherpesvirus 2'', are two members of the Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human ''Herpesviridae'' family, a set of viruses that produce Viral disease, viral infections in the majority of humans. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 are very common and Infectious disease, contagious. They can be spread when an infected person begins viral shedding, shedding the virus. As of 2016, about 67% of the world population under the age of 50 had HSV-1. In the United States, about 47.8% and 11.9% are estimated to have HSV-1 and HSV-2, respectively, though actual prevalence may be much higher. Because it can be transmitted through any intimate contact, it is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. Symptoms Many of those who are infected ''never'' develop symptoms. Symptoms, when they occur, may include watery blisters in the skin or mucous membranes of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAGE Publishing
SAGE Publishing, formerly SAGE Publications, is an American independent business, independent publishing company founded in 1965 in New York by Sara Miller McCune and now based in Newbury Park, California. It publishes more than 1,000 journals, more than 800 books a year, reference works and electronic products covering business, humanities, social sciences, science, technology and medicine. SAGE also owns and publishes under the imprints of Corwin Press (since 1990), CQ Press (since 2008), Learning Matters (since 2011), and Adam Matthew Digital (since 2012). History SAGE was founded in 1965 in New York City by Sara Miller (later Sara Miller McCune) with Macmillan Publishers executive George D. McCune as a mentor; the name of the company is an acronym formed from the first letters of their given names. SAGE relocated to Southern California in 1966, after Miller and McCune married; McCune left Macmillan to formally join the company at that time. Sara Miller McCune remained p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and from regions of the head and neck, including the special senses of vision, taste, smell, and hearing. The cranial nerves emerge from the central nervous system above the level of the first vertebra of the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is paired and is present on both sides. There are conventionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves, which are described with Roman numerals I–XII. Some considered there to be thirteen pairs of cranial nerves, including cranial nerve zero. The numbering of the cranial nerves is based on the order in which they emerge from the brain and brainstem, from front to back. The terminal nerves (0), olfactory nerves (I) and optic nerves (II) emerge from the cerebrum, and the remaining ten pairs arise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Root Ganglion
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia. The axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons are known as afferents. In the peripheral nervous system, afferents refer to the axons that relay sensory information into the central nervous system (i.e. the brain and the spinal cord). Structure The neurons comprising the dorsal root ganglion are of the pseudo-unipolar type, meaning they have a cell body (soma) with two branches that act as a single axon, often referred to as a ''distal process'' and a ''proximal process''. Unlike the majority of neurons found in the central nervous system, an action potential in posterior root ganglion neuron may initiate in the ''distal process'' in the periphery, bypass the cell body, and continue to propagate along the ''proximal proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Cell
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body ( soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus Latency
Virus latency (or viral latency) is the ability of a pathogenic virus to lie dormant ( latent) within a cell, denoted as the lysogenic part of the viral life cycle. A latent viral infection is a type of persistent viral infection which is distinguished from a chronic viral infection. Latency is the phase in certain viruses' life cycles in which, after initial infection, proliferation of virus particles ceases. However, the viral genome is not eradicated. The virus can reactivate and begin producing large amounts of viral progeny (the lytic part of the viral life cycle) without the host becoming reinfected by new outside virus, and stays within the host indefinitely. Virus latency is not to be confused with clinical latency during the incubation period when a virus is ''not'' dormant. Mechanisms Episomal latency Episomal latency refers to the use of genetic episomes during latency. In this latency type, viral genes are stabilized, floating in the cytoplasm or nucleus as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |