|
Hemagglutination Assay
The hemagglutination assay or haemagglutination assay (HA) and the hemagglutination inhibition assay (HI or HAI) were developed in 1941–42 by American virologist George Hirst as methods for quantifying the relative concentration of viruses, bacteria, or antibodies. HA and HI apply the process of hemagglutination, in which sialic acid receptors on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) bind to the hemagglutinin glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza virus (and several other viruses) and create a network, or lattice structure, of interconnected RBCs and virus particles. The agglutinated lattice maintains the RBCs in a suspended distribution, typically viewed as a diffuse reddish solution. The formation of the lattice depends on the concentrations of the virus and RBCs, and when the relative virus concentration is too low, the RBCs are not constrained by the lattice and settle to the bottom of the well. Hemagglutination is observed in the presence of staphylococci, vibrios, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutination Assay
The hemagglutination assay or haemagglutination assay (HA) and the hemagglutination inhibition assay (HI or HAI) were developed in 1941–42 by American virologist George Hirst as methods for quantifying the relative concentration of viruses, bacteria, or antibodies. HA and HI apply the process of hemagglutination, in which sialic acid receptors on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) bind to the hemagglutinin glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza virus (and several other viruses) and create a network, or lattice structure, of interconnected RBCs and virus particles. The agglutinated lattice maintains the RBCs in a suspended distribution, typically viewed as a diffuse reddish solution. The formation of the lattice depends on the concentrations of the virus and RBCs, and when the relative virus concentration is too low, the RBCs are not constrained by the lattice and settle to the bottom of the well. Hemagglutination is observed in the presence of staphylococci, vibrios, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hirst (virologist)
George Keble Hirst, M.D. (March 2, 1909 – January 22, 1994) was an American virologist and science administrator who was among the first to study the molecular biology and genetics of animal viruses, especially influenza virus. He directed the Public Health Research Institute in New York City (1956–1981), and was also the founding editor-in-chief of ''Virology'', the first English-language journal to focus on viruses. He is particularly known for inventing the hemagglutination assay, a simple method for quantifying viruses, and adapting it into the hemagglutination inhibition assay, which measures virus-specific antibodies in serum. He was the first to discover that viruses can contain enzymes, and the first to propose that virus genomes can consist of discontinuous segments. ''The New York Times'' described him as "a pioneer in molecular virology." Education and career Hirst was born in Eau Claire, Wisconsin, USA, but his family soon moved to Lewistown, Montana. He studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', ''molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', and ''volume concentration''. The concentration can refer to any kind of chemical mixture, but most frequently refers to solutes and solvents in solutions. The molar (amount) concentration has variants, such as normal concentration and osmotic concentration. Etymology The term concentration comes from the word concentrate, from the French , from con– + center, meaning “to put at the center”. Qualitative description Often in informal, non-technical language, concentration is described in a qualitative way, through the use of adjectives such as "dilute" for solutions of relatively low concentration and "concentrated" for solutions of relatively high concentration. To concentrate a solution, one must add more solute (for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutination
Hemagglutination, or haemagglutination, is a specific form of agglutination that involves red blood cells (RBCs). It has two common uses in the laboratory: blood typing and the quantification of virus dilutions in a haemagglutination assay. Blood typing Blood type can be determined by using antibodies that bind to the A or B blood group antigens in a sample of blood. For example, if antibodies that bind the A blood group are added and agglutination occurs, the blood is either type A or type AB. To determine between type A or type AB, antibodies that bind the B group are added and if agglutination does not occur, the blood is type A. If agglutination does not occur with either antibodies that bind to type A or type B antigens, then neither antigen is present on the blood cells, which means the blood is type O. In blood grouping, the patient's serum is tested against RBCs of known blood groups and also the patient's RBCs are tested against known serum types. In this way the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek language, Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissue (biology), tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillary, capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza Virus
''Orthomyxoviridae'' (from Greek ὀρθός, ''orthós'' 'straight' + μύξα, ''mýxa'' 'mucus') is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: ''Alphainfluenzavirus'', ''Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus'', ''Thogotovirus'', and ''Quaranjavirus''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds (see also avian influenza) and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates (such as ticks and mosquitoes). The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods). The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein and matrix protein, are as follows: * ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects humans, other mammals, and birds, and causes all flu pandemics * ''Betainfluenzavirus'' infects humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemagglutination
Hemagglutination, or haemagglutination, is a specific form of agglutination that involves red blood cells (RBCs). It has two common uses in the laboratory: blood typing and the quantification of virus dilutions in a haemagglutination assay. Blood typing Blood type can be determined by using antibodies that bind to the A or B blood group antigens in a sample of blood. For example, if antibodies that bind the A blood group are added and agglutination occurs, the blood is either type A or type AB. To determine between type A or type AB, antibodies that bind the B group are added and if agglutination does not occur, the blood is type A. If agglutination does not occur with either antibodies that bind to type A or type B antigens, then neither antigen is present on the blood cells, which means the blood is type O. In blood grouping, the patient's serum is tested against RBCs of known blood groups and also the patient's RBCs are tested against known serum types. In this way the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
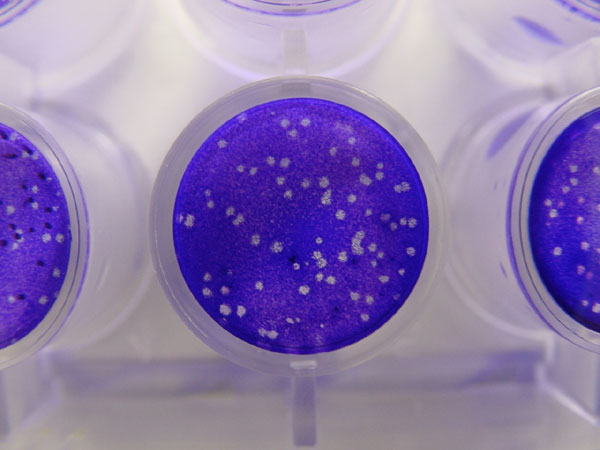
Virus Quantification
Virus quantification involves counting the number of viruses in a specific volume to determine the virus concentration. It is used in both research and development (R&D) in commercial and academic laboratories as well as production situations where the quantity of virus at various steps is an important variable. For example, the production of viral vaccines, recombinant proteins using viral vectors and viral antigens all require virus quantification to continually adapt and monitor the process in order to optimize production yields and respond to ever changing demands and applications. Examples of specific instances where known viruses need to be quantified include clone screening, multiplicity of infection (MOI) optimization and adaptation of methods to cell culture. This page discusses various techniques currently used to quantify viruses in liquid samples. These methods are separated into two categories, traditional vs. modern methods. Traditional methods are industry-stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagnostic Virology
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different academic discipline, disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "causality, cause and effect". In systems engineering and computer science, it is typically used to determine the causes of symptoms, mitigations, and solutions. Computer science and networking * Bayesian networks * Complex event processing * Diagnosis (artificial intelligence) * Event correlation * Fault management * Fault tree analysis * Grey problem * RPR Problem Diagnosis * Remote diagnostics * Root cause analysis * Troubleshooting * Unified Diagnostic Services Mathematics and logic * Bayesian probability * Hickam's dictum, Block Hackam's dictum * Occam's razor * Regression analysis#Regression diagnostics, Regression diagnostics * Sutton's law copy right remover block Medicine * Medical diagnosis * Molecular diagnostics Methods * CDR Computerized As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |