|
Guajira (music)
Guajira is a music genre derived from the punto cubano. According to some specialists, the punto cubano was known in Spain since the 18th century, where it was called "punto de La Habana", and by the second half of the 19th century it was adopted by the incipient Spanish Flamenco style, which included it within its "palos" with the name of guajira.Manuel, Peter: The guajira between Cuba and Spain: A study in continuity and change. Latin American Music Review, volume 25, No. 2, Fall/Winter, 2004. Guajira was utilized by Spanish Zarzuela composers, such as Ruperto Chapí, who included it in his well known play "La Revoltosa", from 1897. Two years later, in 1899, the Cuban composer Jorge Anckermann inaugurated a new genre with his song "El arroyo que murmura", the first Cuban guajira. This song became a model that was adopted by many other Cuban composers at a later time, and was frequently included in the Cuban Zarzuela and vernacular theater. The Cuban guajira preserved the chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punto Cubano
Punto guajiro or ''punto cubano'' – or simply ''punto'' – is a sung genre of Cuban music, a poetic art with music. It became popular in the western and central regions of Cuba in the 17th century, and consolidated as a genre in the 18th century. It has Andalusian and Canary Islands origins, and it integrated African elements in Cuba. Description Punto is played by a group with various types of guitar: the Spanish guitar, the Cuban tres, the laúd and the tiple. The ''punto'' refers to the use of a pick (punteando), rather than strumming (rasgueado). There are three percussion instruments: the clave, the güiro and the ''guayo'' (also a scraper, but of metal). Singers form themselves into teams, and improvise their lines. They sing, or chant, an unvarying melody, with intervals between stanzas to give the singers time to prepare the next verse. Early compositions were sometimes recorded in print, as were the names of some of the singer/composers. Beginning around 1935, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guantanamera
"Guantanamera" (; Spanish: (the woman) from Guantánamo) is perhaps the best-known Cuban song and that country's most-noted patriotic song, especially when using a poem by the Cuban poet José Martí for the lyrics. The official writing credits have been given to Joseíto Fernández, who first popularized the song on radio as early as 1929 (although it is unclear when the first release as a record occurred). In 1966, a version by American vocal group the Sandpipers, based on an arrangement by the Weavers from their May 1963 Carnegie Hall Reunion concert, became an international hit. Lyrics By José Martí The better known "official" lyrics are based on selections from the poetry collection ''Versos Sencillos'' (''Simple Verses'') by Cuban poet and independence hero José Martí, as adapted by Julián Orbón. The four verses of the song were adapted from four stanzas of ''Versos Sencillos'', each from a different poem. They are presented here in the original Spanish (poem:stanz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punto Guajiro
Punto guajiro or ''punto cubano'' – or simply ''punto'' – is a sung genre of Cuban music, a poetic art with music. It became popular in the western and central regions of Cuba in the 17th century, and consolidated as a genre in the 18th century. It has Andalusian and Canary Islands origins, and it integrated African elements in Cuba. Description Punto is played by a group with various types of guitar: the Spanish guitar, the Cuban tres, the laúd and the tiple. The ''punto'' refers to the use of a pick (punteando), rather than strumming (rasgueado). There are three percussion instruments: the clave, the güiro and the ''guayo'' (also a scraper, but of metal). Singers form themselves into teams, and improvise their lines. They sing, or chant, an unvarying melody, with intervals between stanzas to give the singers time to prepare the next verse. Early compositions were sometimes recorded in print, as were the names of some of the singer/composers. Beginning around 1935, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Cuba
The music of Cuba, including its instruments, performance, and dance, comprises a large set of unique traditions influenced mostly by west African and European (especially Spanish) music. Due to the syncretic nature of most of its genres, Cuban music is often considered one of the richest and most influential regional music in the world. For instance, the son cubano merges an adapted Spanish guitar (tres), melody, harmony, and lyrical traditions with Afro-Cuban percussion and rhythms. Almost nothing remains of the original native traditions, since the native population was exterminated in the 16th century. Since the 19th-century Cuban music has been hugely popular and influential throughout the world. It has been perhaps the most popular form of regional music since the introduction of recording technology. Cuban music has contributed to the development of a wide variety of genres and musical styles around the globe, most notably in Latin America, the Caribbean, West Africa, and Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillbilly
Hillbilly is a term (often derogatory) for people who dwell in rural, mountainous areas in the United States, primarily in southern Appalachia and the Ozarks. The term was later used to refer to people from other rural and mountainous areas west of the Mississippi river, too, particularly those of the Rocky Mountains and near the Rio Grande. The first known instances of "hillbilly" in print were in ''The Railroad Trainmen's Journal'' (vol. ix, July 1892), an 1899 photograph of men and women in West Virginia labeled "Camp Hillbilly", and a 1900 ''New York Journal'' article containing the definition: "a Hill-Billie is a free and untrammeled white citizen of Alabama, who lives in the hills, has no means to speak of, dresses as he can, talks as he pleases, drinks whiskey when he gets it, and fires off his revolver as the fancy takes him". The stereotype is twofold in that it incorporates both positive and negative traits: "Hillbillies" are often considered independent and self-relian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greater Antilles and northern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. All these groups spoke related Arawakan languages. Name Early Spanish explorers and administrators used the terms ''Arawak'' and ''Caribs'' to distinguish the peoples of the Caribbean, with ''Carib'' reserved for indigenous groups that they considered hostile and ''Arawak'' for groups that they considered friendly. In 1871, ethnologist Daniel Garrison Brinton proposed calling the Caribbean populace "Island Arawak" due to their cultural and linguistic similarities with the mainland Arawak. Subsequent scholars shortened this convention to "Arawak", creating confusion between the island and mainland groups. In the 20th century, scholars such as Irving Rouse resumed using "Taíno" for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pete Seeger
Peter Seeger (May 3, 1919 – January 27, 2014) was an American folk singer and social activist. A fixture on nationwide radio in the 1940s, Seeger also had a string of hit records during the early 1950s as a member of the Weavers, notably their recording of Lead Belly's "Goodnight, Irene", which topped the charts for 13 weeks in 1950. Members of the Weavers were blacklisted during the McCarthy Era. In the 1960s, Seeger re-emerged on the public scene as a prominent singer of protest music in support of international disarmament, civil rights, counterculture, workers' rights, and environmental causes. A prolific songwriter, his best-known songs include "Where Have All the Flowers Gone?" (with additional lyrics by Joe Hickerson), " If I Had a Hammer (The Hammer Song)" (with Lee Hays of the Weavers), " Kisses Sweeter Than Wine" (also with Hays), and "Turn! Turn! Turn!", which have been recorded by many artists both in and outside the folk revival movement. "Flowers" was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseíto Fernández
José Fernández Díaz (September 5, 1908 – October 11, 1979), commonly known as Joseíto Fernández, was a Cuban singer and songwriter. He is the writer of well-known songs, including "Elige tú, que canto yo", "Amor de madre", "Demuéstrame tú", and "Así son, boncó", as well as the most famous " Guajira Guantanamera". , Pedro Quiroga Jiménez, Notinet del Cubaweb. Selected compositions * "Tu Misma Me Acostumbraste," Joseíto Fernández (w&m) * "Mi Madre y Mi Tierra," Joseíto Fernández (w&m) * "," Joseíto Fernández (w&m), based on a poem by |
Celina González
Celina González Zamora (16 March 1929 – 4 February 2015) was a Cuban singer-songwriter, who specialized in "música campesina", traditional music of the Cuban countryside. She is best known for co-authoring ''A Santa Bárbara'' with her partner Reutilio Domínguez. Her recording of it was a hit, as was Celia Cruz's version. González and Domínguez wrote "Yo soy el punto cubano": the recording was a hit in many countries throughout the world. González was born in Jovellanos, Matanzas. At age 16, she met Reutilio Domínguez in Santiago de Cuba. He became her singing partner and husband, resulting in a collaboration that lasted until his death in Guantanamo in 1971. In 1948 they began working with the famous Ñico Saquito and gained increasing popularity on radio, film and television. They performed in New York with Beny Moré and Barbarito Diez. In 1964 the duo stopped performing together and González continued as a soloist. In later years she sang with her son L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
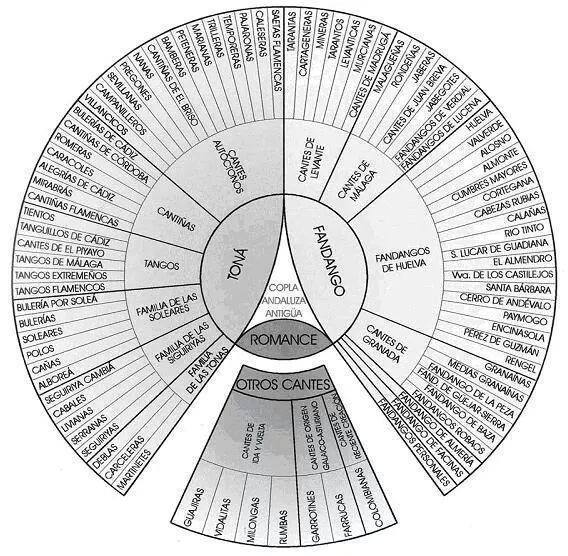
Flamenco
Flamenco (), in its strictest sense, is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, it is a portmanteau term used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolero
Bolero is a genre of song which originated in eastern Cuba in the late 19th century as part of the trova tradition. Unrelated to the older Spanish dance of the same name, bolero is characterized by sophisticated lyrics dealing with love. It has been called the "quintessential Latin American romantic song of the twentieth century". Unlike the simpler, thematically diverse ''canción'', bolero did not stem directly from the European lyrical tradition, which included Italian opera and canzone, popular in urban centers like Havana at the time. Instead, it was born as a form of romantic folk poetry cultivated by a new breed of troubadour from Santiago de Cuba, the ''trovadores''. Pepe Sánchez is considered the father of this movement and the author of the first bolero, "Tristezas", written in 1883. Originally, boleros were sung by individual ''trovadores'' while playing guitar. Over time, it became common for trovadores to play in groups as ''dúos'', ''tríos'', ''cuartetos'', etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Son Cubano
Son cubano is a genre of music and dance that originated in the highlands of eastern Cuba during the late 19th century. It is a syncretic genre that blends elements of Spanish and African origin. Among its fundamental Hispanic components are the vocal style, lyrical metre and the primacy of the tres, derived from the Spanish guitar. On the other hand, its characteristic clave rhythm, call and response structure and percussion section ( bongo, maracas, etc.) are all rooted in traditions of Bantu origin. Around 1909 the son reached Havana, where the first recordings were made in 1917. This marked the start of its expansion throughout the island, becoming Cuba's most popular and influential genre. While early groups had between three and five members, during the 1920s the ''sexteto'' (sextet) became the genre's primary format. By the 1930s, many bands had incorporated a trumpet, becoming ''septetos'', and in the 1940s a larger type of ensemble featuring congas and piano became th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)