|
Glucosidase
Glucosidases are the glycoside hydrolase enzymes categorized under the EC number 3.2.1. Function Alpha-glucosidases are enzymes involved in breaking down complex carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into their monomers. They catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates including alpha- or beta-linked polymers of glucose. This enzyme convert complex sugars into simpler ones. Members Different sources include different members in this class. Members marked with a "#" are considered by MeSH A mesh is a barrier made of connected strands of metal, fiber, or other flexible or ductile materials. A mesh is similar to a web or a net in that it has many attached or woven strands. Types * A plastic mesh may be extruded, oriented, exp ... to be glucosidases. Clinical significance Alpha-glucosidases are targeted by alpha-glucosidase inhibitors such as acarbose and miglitol to control diabetes mellitus type 2. See also * DNA gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid α-glucosidase
α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20, maltase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, α-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, α-D-glucosidase, α-glucoside hydrolase, α-1,4-glucosidase, α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; systematic name α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase located in the brush border of the small intestine that acts upon α(1→4) bonds: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose This is in contrast to β-glucosidase. α-Glucosidase breaks down starch and disaccharides to glucose. Other glucosidases include: * Cellulase * Beta-glucosidase * Debranching enzyme Mechanism α-Glucosidase hydrolyzes terminal non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-glucose residues to release a single α-glucose molecule. α-Glucosidase is a carbohydrate-hydrolase that releases α-glucose as opposed to β-glucose. β-Glucose residues can be released by glucoamylase, a functionally similar enzyme. The substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-glucosidase
α-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.20, maltase, glucoinvertase, glucosidosucrase, maltase-glucoamylase, α-glucopyranosidase, glucosidoinvertase, α-D-glucosidase, α-glucoside hydrolase, α-1,4-glucosidase, α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase; systematic name α-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase located in the brush border of the small intestine that acts upon α(1→4) bonds: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose residues with release of D-glucose This is in contrast to β-glucosidase. α-Glucosidase breaks down starch and disaccharides to glucose. Other glucosidases include: * Cellulase * Beta-glucosidase * Debranching enzyme Mechanism α-Glucosidase hydrolyzes terminal non-reducing (1→4)-linked α-glucose residues to release a single α-glucose molecule. α-Glucosidase is a carbohydrate-hydrolase that releases α-glucose as opposed to β-glucose. β-Glucose residues can be released by glucoamylase, a functionally similar enzyme. The substr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Storage Disease Type II
Glycogen storage disease type II, also called Pompe disease, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder which damages muscle and nerve cells throughout the body. It is caused by an accumulation of glycogen in the lysosome due to deficiency of the lysosomal acid alpha-glucosidase enzyme. It is the only glycogen storage disease with a defect in lysosomal metabolism, and the first glycogen storage disease to be identified, in 1932 by the Dutch pathologist J. C. Pompe. The build-up of glycogen causes progressive muscle weakness (myopathy) throughout the body and affects various body tissues, particularly in the heart, skeletal muscles, liver and the nervous system. Signs and symptoms Newborn The infantile form usually comes to medical attention within the first few months of life. The usual presenting features are cardiomegaly (92%), hypotonia (88%), cardiomyopathy (88%), respiratory distress (78%), muscle weakness (63%), feeding difficulties (57%) and failure to thrive (50%). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-glucosidase
β-Glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.21; systematic name β-D-glucoside glucohydrolase) is an enzyme that catalyses the following reaction: : Hydrolysis of terminal, non-reducing β-D-glucosyl residues with release of β-D-glucose Structure β-Glucosidase is composed of two polypeptide chains. Each chain is made up of 438 amino acids and constitute a subunit of the enzyme. Each of these subunits contains an active site. The active site has three potential components: the pocket, the cleft, and the tunnel. The pocket structure is beneficial for recognition of monosaccharide like glucose. The cleft allows for binding of sugars to form polysaccharides. The tunnel allows for the enzyme to attach to polysaccharide and then release product while still attached to the sugar. Function The function of the enzyme is to perform hydrolysis of various glycosides and oligosaccharides. The most significant oligosaccharide β-glucosidase reacts with is cellulose. Cellulose is a polymer composed of β-1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
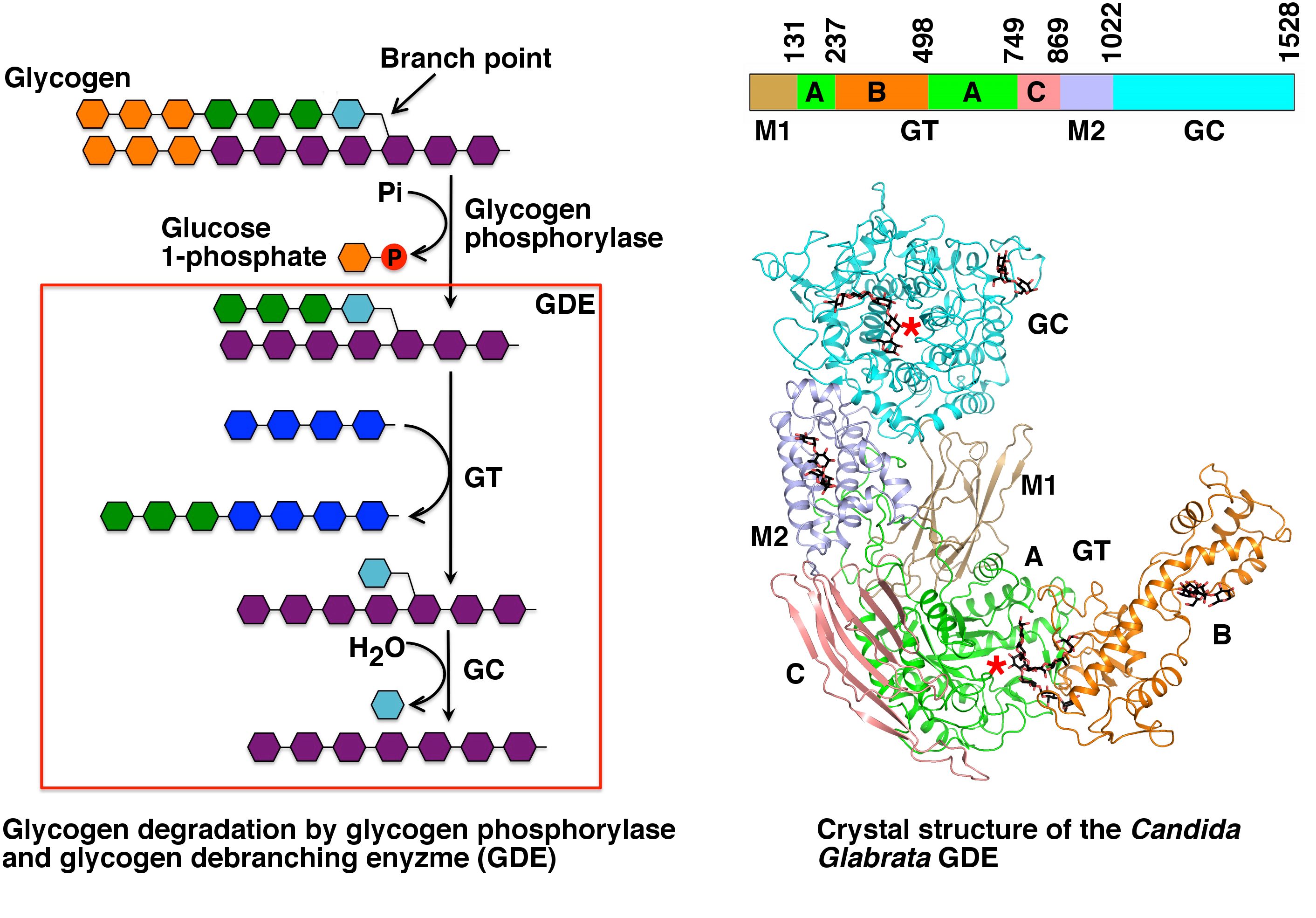
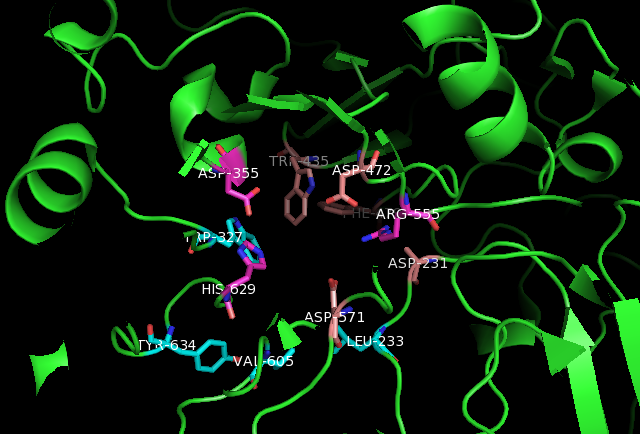
Glycogen Debranching Enzyme
A debranching enzyme is a molecule that helps facilitate the Glycogenolysis, breakdown of glycogen, which serves as a store of glucose in the body, through glucosyltransferase and glucosidase activity. Together with phosphorylases, debranching enzymes mobilize glucose reserves from glycogen deposits in the muscles and liver. This constitutes a major source of energy reserves in most organisms. Glycogen breakdown is highly regulated in the body, especially in the liver, by various hormones including insulin and glucagon, to maintain a homeostatic balance of blood-glucose levels. When glycogen breakdown is compromised by mutations in the glycogen debranching enzyme, metabolic diseases such as Glycogen storage disease type III can result. Glucosyltransferase and glucosidase are performed by a single enzyme in mammals, yeast, and some bacteria, but by two distinct enzymes in ''E. coli'' and other bacteria, complicating nomenclature. Proteins that catalyze both functions are referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannosyl-oligosaccharide Glucosidase
Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase (MOGS) (, ''processing alpha-glucosidase I,'' ''Glc3Man9NAc2 oligosaccharide glucosidase'', ''trimming glucosidase I, GCS1'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucohydrolase''. MOGS is a transmembrane protein found in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum of eukaryotic cells. Biologically, it functions within the N-glycosylation pathway. Enzyme mechanism MOGS is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme, belonging to Family 63 as classified within the Carbohydrate-Active Enzyme database. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction: : Exohydrolysis of the non-reducing terminal glucose residue in the mannosyl-oligosaccharide glycan Glc3Man9GlcNAc2 This reaction is the first trimming step in the N-glycosylation pathway. Prior to this, the glycan was co-translationally attached to a nascent protein by the oligosaccharyltransferase complex. MOGS removes the terminal glucose residue, leaving the glycoprotein link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellulase
Cellulase (EC 3.2.1.4; systematic name 4-β-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase) is any of several enzymes produced chiefly by fungi, bacteria, and protozoans that catalyze cellulolysis, the decomposition of cellulose and of some related polysaccharides: : Endohydrolysis of (1→4)-β-D-glucosidic linkages in cellulose, lichenin and cereal β-D-glucan The name is also used for any naturally occurring mixture or complex of various such enzymes, that act serially or synergistically to decompose cellulosic material. Cellulases break down the cellulose molecule into monosaccharides ("simple sugars") such as β-glucose, or shorter polysaccharides and oligosaccharides. Cellulose breakdown is of considerable economic importance, because it makes a major constituent of plants available for consumption and use in chemical reactions. The specific reaction involved is the hydrolysis of the 1,4-β-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, hemicellulose, lichenin, and cereal β-D-glucans. Because cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaucher's Disease
Gaucher's disease or Gaucher disease () (GD) is a genetic disorder A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ... in which glucocerebroside (a sphingolipid, also known as glucosylceramide) accumulates in cells and certain organs. The disorder is characterized by bruising, fatigue (medical), fatigue, anemia, low blood platelet count and enlargement of the liver and spleen, and is caused by a hereditary deficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase (also known as glucosylceramidase), which acts on glucocerebroside. When the enzyme is defective, glucocerebroside accumulates, particularly in white blood cells and especially in macrophages (mononuclear leukocytes, which is often a target for intracellular parasites). Glucocerebroside can collect in the spleen, liver, kidneys, Human lung, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large amounts of starch but little sugar, such as rice and potatoes, may acquire a slightly sweet taste as they are chewed because amylase degrades some of their starch into sugar. The pancreas and salivary gland make amylase (alpha amylase) to hydrolyse dietary starch into disaccharides and trisaccharides which are converted by other enzymes to glucose to supply the body with energy. Plants and some bacteria also produce amylase. Specific amylase proteins are designated by different Greek letters. All amylases are glycoside hydrolases and act on α-1,4-glycosidic bonds. Classification α-Amylase The α-amylases () ( CAS 9014-71-5) (alternative names: 1,4-α-D-glucan glucanohydrolase; glycogenase) are calcium metalloenzymes. By acting at random loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sucrase-isomaltase
Oligo-1,6-glucosidase (EC 3.2.1.10, sucrase-isomaltase, SI; systematic name oligosaccharide 6-α-glucohydrolase) is a glucosidase enzyme located on the brush border of the small intestine, which catalyses the following reaction: :Hydrolysis of (1→6)-α-D-glucosidic linkages in some oligosaccharides produced from starch and glycogen by (α-amylase), and in isomaltose It is a dual-function enzyme with two GH31 domains, one serving as the isomaltase, the other as a sucrose alpha-glucosidase. It has preferential expression in the apical membranes of enterocytes. The enzyme’s purpose is to digest dietary carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose and isomaltose. By further processing the broken-down products, energy in the form of ATP can be generated.Berg, J. M. et al. ''Biochemistry'', 7th Ed. W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, 2012. Structure Sucrase-isomaltase consists of two enzymatic subunits: sucrase and isomaltase. The subunits originate from a polypeptide precurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta-galactosidase
β-Galactosidase (EC 3.2.1.23, lactase, beta-gal or β-gal; systematic name β-D-galactoside galactohydrolase), is a glycoside hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing β-D-galactose residues in β-D-galactosides. β-Galactosides include carbohydrates containing galactose where the glycosidic bond lies above the galactose molecule. Substrates of different β-galactosidases include ganglioside GM1, lactosylceramides, lactose, and various glycoproteins. Function β-Galactosidase is an exoglycosidase which hydrolyzes the β-glycosidic bond formed between a galactose and its organic moiety. It may also cleave fucosides and arabinosides but with much lower efficiency. It is an essential enzyme in the human body. Deficiencies in the protein can result in galactosialidosis or Morquio B syndrome. In '' E. coli'', the ''lacZ'' gene is the structural gene for β-galactosidase; which is present as part of the inducible system ''lac'' operon which is activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoside Hydrolase
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cellulase), hemicellulose, and starch (amylase), in anti-bacterial defense strategies (e.g., lysozyme), in pathogenesis mechanisms (e.g., viral neuraminidases) and in normal cellular function (e.g., trimming mannosidases involved in N-linked glycoprotein biosynthesis). Together with glycosyltransferases, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds. Occurrence and importance Glycoside hydrolases are found in essentially all domains of life. In prokaryotes, they are found both as intracellular and extracellular enzymes that are largely involved in nutrient acquisition. One of the important occurrences of glycoside hydrolases in bacteria is the enzyme beta-galactosidase (LacZ), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |