|
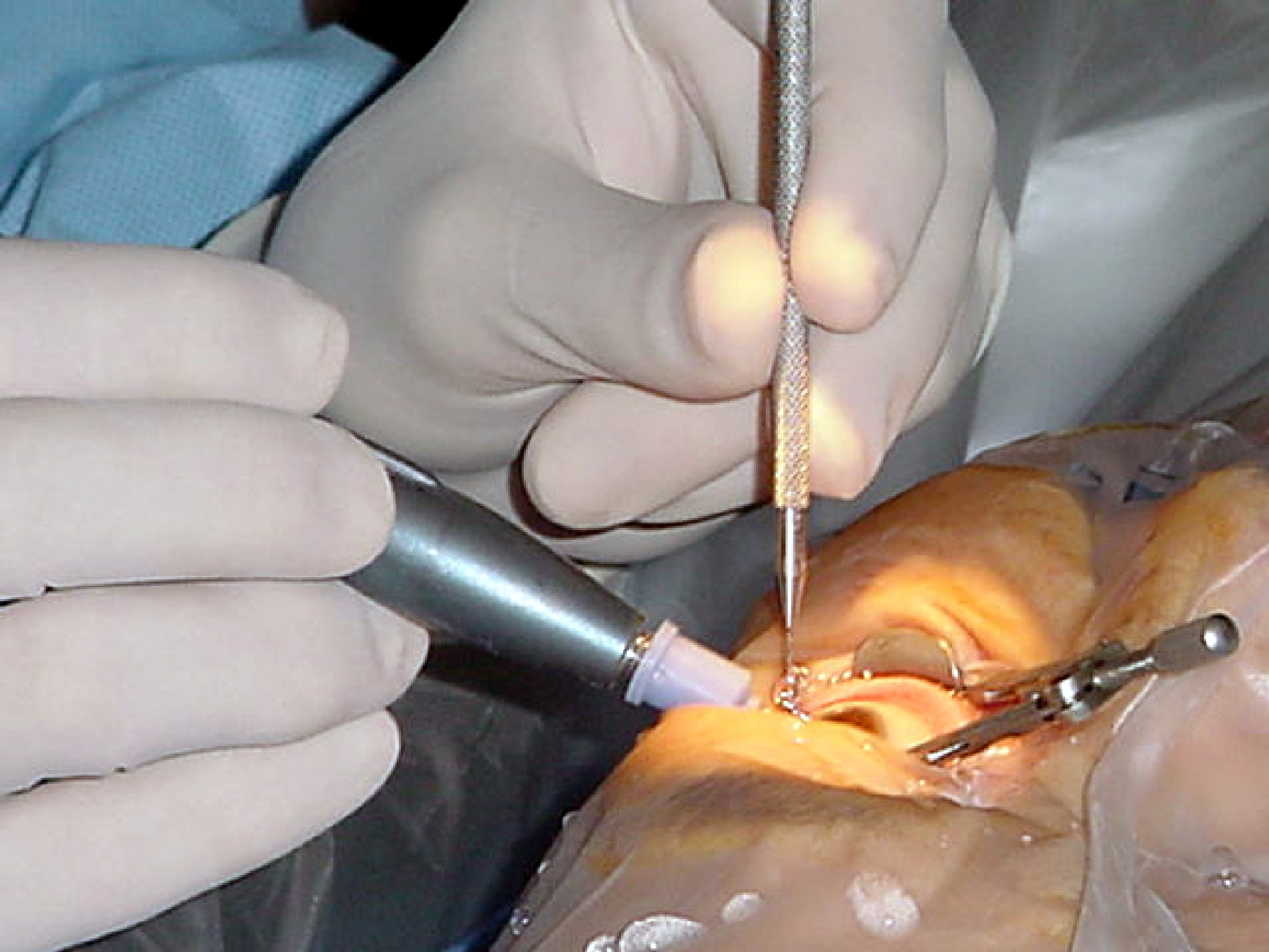
Glaucoma Surgery
Glaucoma is a group of diseases affecting the optic nerve that results in vision loss and is frequently characterized by raised intraocular pressure (IOP). There are many glaucoma surgeries, and variations or combinations of those surgeries, that facilitate the escape of excess aqueous humor from the eye to lower intraocular pressure, and a few that lower IOP by decreasing the production of aqueous humor. Procedures that facilitate outflow of aqueous humor Laser trabeculoplasty A trabeculoplasty is a modification of the trabecular meshwork. Laser trabeculoplasty (LTP) is the application of a laser beam to burn areas of the trabecular meshwork, located near the base of the iris, to increase fluid outflow. LTP is used in the treatment of various open-angle glaucomas. The two types of laser trabeculoplasty are argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) and selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT). As its name suggests, argon laser trabeculoplasty uses an argon laser to create tiny burns on the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma Valve
A glaucoma valve is a medical shunt used in the treatment of glaucoma to reduce the eye's intraocular pressure (IOP). Mechanism The device works by bypassing the trabecular meshwork and redirecting the outflow of aqueous humour through a small tube into an outlet chamber or bleb. The IOP generally decreases from around 33 to 10 mmHg by removing aqueous on average 2.75 microliters/min. Types The first glaucoma drainage implant was developed in 1966. Following on the success of the Molteno implant, several varieties of device have been developed from the original, the Baerveldt tube shunt, or the valved implants, such as the Ahmed glaucoma valve implant and the later generation pressure ridge Molteno implants. These are indicated for glaucoma patients not responding to maximal medical therapy, with previous failed guarded filtering surgery (trabeculectomy). The flow tube is inserted into the anterior chamber of the eye and the plate is implanted underneath the conjunctiva to all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery
Micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS) is the latest advance in surgical treatment for glaucoma, which aims to reduce intraocular pressure by either increasing outflow of aqueous humor or reducing its production. MIGS comprises a group of surgical procedures which share common features. MIGS procedures involve a minimally invasive approach, often with small cuts or micro-incisions through the cornea that causes the least amount of trauma to surrounding scleral and conjunctival tissues. The techniques minimize tissue scarring, allowing for the possibility of traditional glaucoma procedures such as trabeculectomy or glaucoma valve implantation (also known as glaucoma drainage device) to be performed in the future if needed.Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgeries< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochrane Collaboration
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes 53 review groups that are based at research institutions worldwide. Cochrane has approximately 30,000 volunteer experts from around the world. The group conducts systematic reviews of health-care interventions and diagnostic tests and publishes them in the Cochrane Library. According to the Library, articles are available via one-click access, but some require paid subscription or registration before reading. A few reviews, in occupational health for example, incorporate results from non-randomised observational studies as well as controlled before–after (CBA) studies and interrupted time-series studies. History Cochrane, previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration, was founded in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclophotocoagulation
Cyclodestruction or cycloablation is a surgical procedure done in management of glaucoma. Cyclodestruction reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eye by decreasing production of aqueous humor by the destruction of ciliary body. Until the development of safer and less destructive techniques like micropulse diode cyclophotocoagulation and endocyclophotocoagulation, cyclodestructive surgeries were mainly done in refractory glaucoma, or advanced glaucomatous eyes with poor visual prognosis. Types Cyclodestruction may be done by using diathermy, penetrating cyclodiathermy, cryotherapy, ultrasound, laser or by surgical excision. Cyclophotocoagulation Cyclophotocoagulation (CPC), the most common cyclodestructive procedure is done using laser beam of different wavelengths. Ruby laser (693 nm wavelength), Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm wavelength) or diode laser (810 nm wavelength) can be used to perform CPC. Commomon cyclophotocoagulation techniques include transscleral cyclophot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliary Body
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body. The ciliary body is part of the uvea, the layer of tissue that delivers oxygen and nutrients to the eye tissues. The ciliary body joins the ora serrata of the choroid to the root of the iris.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. Structure The ciliary body is a ring-shaped thickening of tissue inside the eye that divides the posterior chamber from the vitreous body. It contains the ciliary muscle, vessels, and fibrous connective tissue. Folds on the inner ciliary epithelium are called ciliary processes, and these secrete aqueous humor into the posterior chamber. The aqueous humor then flows through the pupil into the anterior chamber. The ciliary bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclocryotherapy
Cyclodestruction or cycloablation is a surgical procedure done in management of glaucoma. Cyclodestruction reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) of the eye by decreasing production of aqueous humor by the destruction of ciliary body. Until the development of safer and less destructive techniques like micropulse diode cyclophotocoagulation and endocyclophotocoagulation, cyclodestructive surgeries were mainly done in refractory glaucoma, or advanced glaucomatous eyes with poor visual prognosis. Types Cyclodestruction may be done by using diathermy, penetrating cyclodiathermy, cryotherapy, ultrasound, laser or by surgical excision. Cyclophotocoagulation Cyclophotocoagulation (CPC), the most common cyclodestructive procedure is done using laser beam of different wavelengths. Ruby laser (693 nm wavelength), Nd:YAG laser (1064 nm wavelength) or diode laser (810 nm wavelength) can be used to perform CPC. Commomon cyclophotocoagulation techniques include transscleral cyclopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaloplasty
Eye surgery, also known as ophthalmic or ocular surgery, is surgery performed on the eye or its adnexa, by an ophthalmologist or sometimes, an optometrist. Eye surgery is synonymous with ophthalmology. The eye is a very fragile organ, and requires extreme care before, during, and after a surgical procedure to minimize or prevent further damage. An expert eye surgeon is responsible for selecting the appropriate surgical procedure for the patient, and for taking the necessary safety precautions. Mentions of eye surgery can be found in several ancient texts dating back as early as 1800 BC, with cataract treatment starting in the fifth century BC. Today it continues to be a widely practiced type of surgery, with various techniques having been developed for treating eye problems. Preparation and precautions Since the eye is heavily supplied by nerves, anesthesia is essential. Local anesthesia is most commonly used. Topical anesthesia using lidocaine topical gel is often use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |