|
Gas Vesicle
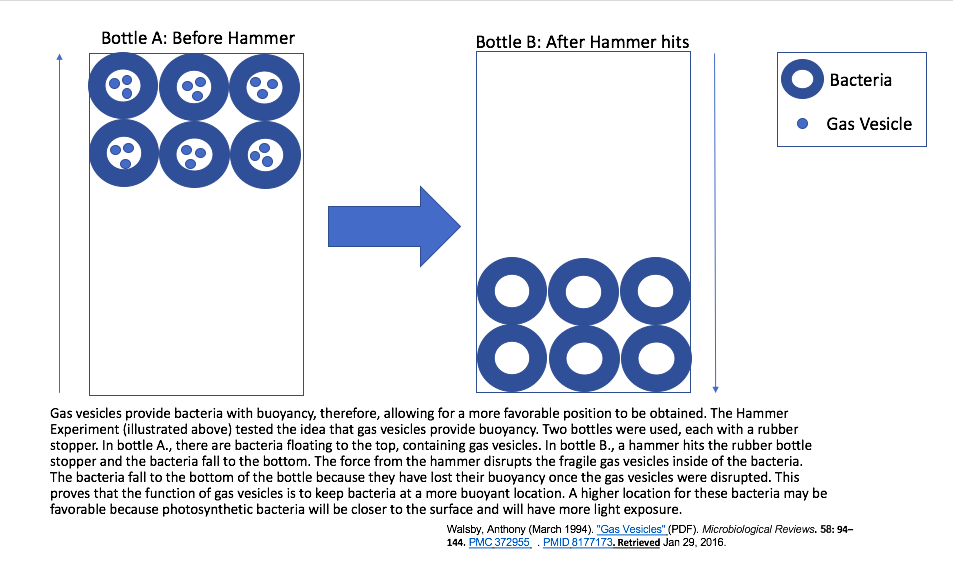
Gas vesicles, also known as gas vacuoles, are nanocompartments in certain prokaryotic organisms, which help in buoyancy. Gas vesicles are composed entirely of protein; no lipids or carbohydrates have been detected. Function Gas vesicles occur primarily in aquatic organisms as they are used to modulate the cell's buoyancy and modify the cell's position in the water column so it can be optimally located for photosynthesis or move to locations with more or less oxygen. Organisms that could float to the air–liquid interface out competes other aerobes that cannot rise in a water column, through using up oxygen in the top layer. In addition, gas vesicles can be used to maintain optimum salinity by positioning the organism in specific locations in a stratified body of water to prevent osmotic shock. High concentrations of solute will cause water to be drawn out of the cell by osmosis, causing cell lysis. The ability to synthesize gas vesicles is one of many strategies that allow h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medical imaging and industrial nondestructive testing (NDT). Optical coherence tomography is based on low-coherence interferometry, typically employing near-infrared light. The use of relatively long wavelength light allows it to penetrate into the scattering medium. Confocal microscopy, another optical technique, typically penetrates less deeply into the sample but with higher resolution. Depending on the properties of the light source ( superluminescent diodes, ultrashort pulsed lasers, and supercontinuum lasers have been employed), optical coherence tomography has achieved sub-micrometer resolution (with very wide-spectrum sources emitting over a ~100 nm wavelength range). Optical coherence tomography is one of a class of optical tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resolution is directly connected to angular resolution, other instruments, like synthetic aperture radar or a network of weather stations, produce data whose spatial sampling layout is more related to the Earth's surface, such as in remote sensing and satellite imagery. See also * Image resolution * Ground sample distance * Level of detail * Resel In image analysis, a resel (from ''res''olution ''el''ement) represents the actual spatial resolution in an image or a volumetric dataset. The number of resels in the image may be lower or equal to the number of pixel/voxels in the image. In an act ... References Accuracy and precision {{physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminescence
Luminescence is spontaneous emission of light by a substance not resulting from heat; or "cold light". It is thus a form of cold-body radiation. It can be caused by chemical reactions, electrical energy, subatomic motions or stress on a crystal. This distinguishes luminescence from incandescence, which is light emitted by a substance as a result of heating. Historically, radioactivity was thought of as a form of "radio-luminescence", although it is today considered to be separate since it involves more than electromagnetic radiation. The dials, hands, scales, and signs of aviation and navigational instruments and markings are often coated with luminescent materials in a process known as "luminising". Types The following are types of luminescence: * Chemiluminescence, the emission of light as a result of a chemical reaction **Bioluminescence, a result of biochemical reactions in a living organism **Electrochemiluminescence, a result of an electrochemical reaction **Lyolumine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penetration Depth
Penetration depth is a measure of how deep light or any electromagnetic radiation can penetrate into a material. It is defined as the depth at which the intensity of the radiation inside the material falls to 1/e (about 37%) of its original value at (or more properly, just beneath) the surface. When electromagnetic radiation is incident on the surface of a material, it may be (partly) reflected from that surface and there will be a field containing energy transmitted into the material. This electromagnetic field interacts with the atoms and electrons inside the material. Depending on the nature of the material, the electromagnetic field might travel very far into the material, or may die out very quickly. For a given material, penetration depth will generally be a function of wavelength. Beer–Lambert law According to Beer–Lambert law, the intensity of an electromagnetic wave inside a material falls off exponentially from the surface as : I(z) = I_0 \, e^ If \delta_p d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Fluorescent Protein
The green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a protein that exhibits bright green fluorescence when exposed to light in the blue to ultraviolet range. The label ''GFP'' traditionally refers to the protein first isolated from the jellyfish ''Aequorea victoria'' and is sometimes called ''avGFP''. However, GFPs have been found in other organisms including corals, sea anemones, zoanithids, copepods and lancelets. The GFP from ''A. victoria'' has a major excitation peak at a wavelength of 395 nm and a minor one at 475 nm. Its emission peak is at 509 nm, which is in the lower green portion of the visible spectrum. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) of GFP is 0.79. The GFP from the sea pansy (''Renilla reniformis'') has a single major excitation peak at 498 nm. GFP makes for an excellent tool in many forms of biology due to its ability to form an internal chromophore without requiring any accessory cofactors, gene products, or enzymes / substrates other than mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reporter Gene
In molecular biology, a reporter gene (often simply reporter) is a gene that researchers attach to a regulatory sequence of another gene of interest in bacteria, cell culture, animals or plants. Such genes are called reporters because the characteristics they confer on organisms expressing them are easily identified and measured, or because they are selectable markers. Reporter genes are often used as an indication of whether a certain gene has been taken up by or expressed in the cell or organism population. Common reporter genes To introduce a reporter gene into an organism, scientists place the reporter gene and the gene of interest in the same DNA construct to be inserted into the cell or organism. For bacteria or prokaryotic cells in culture, this is usually in the form of a circular DNA molecule called a plasmid. For viruses, this is known as a viral vector. It is important to use a reporter gene that is not natively expressed in the cell or organism under study, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: , "receptive"; denoted ) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnetizing field intensity . This allows a simple classification, into two categories, of most materials' responses to an applied magnetic field: an alignment with the magnetic field, , called paramagnetism, or an alignment against the field, , called diamagnetism. Magnetic susceptibility indicates whether a material is attracted into or repelled out of a magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials align with the applied field and are attracted to regions of greater magnetic field. Diamagnetic materials are anti-aligned and are pushed away, toward regions of lower magnetic fields. On top of the applied field, the magnetization of the material adds its own magnetic field, causing the field lines to concentrate in paramagnetism, or be excl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Contrast Factor
The acoustic contrast factor is a number used to describe the relationship between the densities and the sound velocities (or, equivalently because of the form of the expression, the densities and compressibilities) of two media. It is most often used in the context of biomedical ultrasonic imaging techniques using acoustic contrast agents and in the field of ultrasonic manipulation of particles (acoustophoresis) much smaller than the wavelength using ultrasonic standing waves. In the latter context, the acoustic contrast factor is the number which, depending on its sign, tells whether a given type of particle in a given medium will be attracted to the pressure nodes or anti-nodes. Example - particle in a medium In an ultrasonic standing wave field, a small spherical particle (a \ll \lambda, where a is the particle radius, and \lambda is the wavelength) suspended in an inviscid fluid will move under the effect of an acoustic radiation force. The direction of its movement is gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |