|
Grippidia
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors. Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongated bodies and long, spool-shaped vertebrae, indicating that they swam in a sinuous, eel-like manner. This allowed for quick movements and maneuverability that were advantages in shallow-water hunting. Even at this early stage, they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land. These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of Pangea, as they are known the Late Olenekian and Early Anisian (early part of the Triassic period) of Japan, China, Canada, and Spitsbergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eoichthyosauria
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors. Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongated bodies and long, spool-shaped vertebrae, indicating that they swam in a sinuous, eel-like manner. This allowed for quick movements and maneuverability that were advantages in shallow-water hunting. Even at this early stage, they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land. These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of Pangea, as they are known the Late Olenekian and Early Anisian (early part of the Triassic period) of Japan, China, Canada, and Spitsbergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
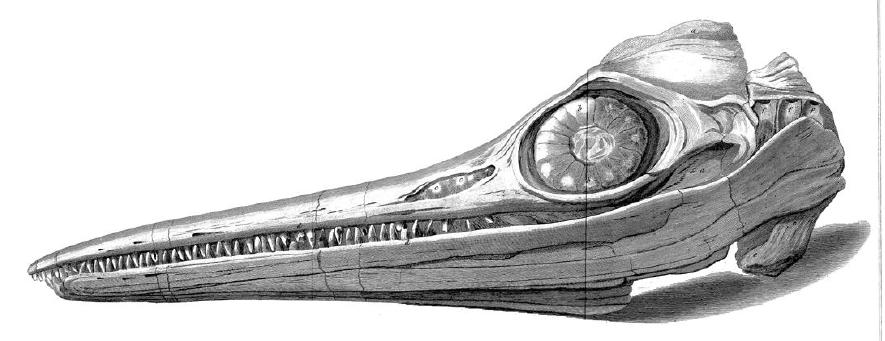
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvinatator Wapitiensis
''Parvinatator'', from Latin, “parvus” little and “natator” swimmer, is an extinct genus of small ichthyopterygian marine reptile that lived during the Early to Middle Triassic. Its fossils have been found in British Columbia, Canada.Nicholls, E. & Brinkman, D. (1995). A new ichthyosaur from the Triassic Sulphur Mountain formation of British Columbia. Sarjeant WAS (ed.): Vertebrate fossils and the evolution of scientific concepts: 521–535 London (Gordon & Breach). Geological information The only known Parvinatator fossil was located in an unknown horizon from the Sulfur Mountain Formation in a talus deposit, so its exact geological age is unknown. Best estimates place the fossil somewhere between the Olenekian and Ladinian age around 251-235 mya.Motani, R. (1999). Phylogeny of the Ichthyopterygia. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 19:3, 473-496. Other small ichthyosaurs have been found nearby including Grippia, Utatsusaurus, and Phalarodon. Historical informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grippidia
Ichthyopterygia ("fish flippers") was a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1840 to designate the Jurassic ichthyosaurs that were known at the time, but the term is now used more often for both true Ichthyosauria and their more primitive early and middle Triassic ancestors. Basal ichthyopterygians (prior to and ancestral to true Ichthyosauria) were mostly small (a meter or less in length) with elongated bodies and long, spool-shaped vertebrae, indicating that they swam in a sinuous, eel-like manner. This allowed for quick movements and maneuverability that were advantages in shallow-water hunting. Even at this early stage, they were already very specialised animals with proper flippers, and would have been incapable of movement on land. These animals seem to have been widely distributed around the coast of the northern half of Pangea, as they are known the Late Olenekian and Early Anisian (early part of the Triassic period) of Japan, China, Canada, and Spitsbergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvinatatoridae
''Parvinatator'', from Latin, “parvus” little and “natator” swimmer, is an extinct genus of small ichthyopterygian marine reptile that lived during the Early to Middle Triassic. Its fossils have been found in British Columbia, Canada.Nicholls, E. & Brinkman, D. (1995). A new ichthyosaur from the Triassic Sulphur Mountain formation of British Columbia. Sarjeant WAS (ed.): Vertebrate fossils and the evolution of scientific concepts: 521–535 London (Gordon & Breach). Geological information The only known Parvinatator fossil was located in an unknown horizon from the Sulfur Mountain Formation in a talus deposit, so its exact geological age is unknown. Best estimates place the fossil somewhere between the Olenekian and Ladinian age around 251-235 mya.Motani, R. (1999). Phylogeny of the Ichthyopterygia. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, 19:3, 473-496. Other small ichthyosaurs have been found nearby including Grippia, Utatsusaurus, and Phalarodon. Historical informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grippia Longirostris
''Grippia'' is a genus of early ichthyopterygian, an extinct group of reptiles that resembled dolphins. Its only species is ''Grippia longirostris''. It was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Fossil remains from Svalbard from the specimen SVT 203 were originally assigned to ''G. longirostris'' but are now thought to have belonged to a non-ichthyopterygian diapsid related to ''Helveticosaurus''. Discovery Fossils have been found along the coasts of Greenland, China, Japan, Norway, and Canada (Sulfur Mountain Formation); of Early Triassic age. No complete skeletons has ever been found. However, well-preserved remains have been found, with the most notable ones including: *The Marine Ironstone found in Agardh Bay Norway. This specimen consists of a partial skull fossil; however, it was lost during World War II and presumably destroyed. *Previously, the Vega Phroso Siltstone Member of the Sulphur Mountain Formation in British Columbia. This spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinminosaurus Catactes
''Xinminosaurus'' is an extinct genus of cymbospondylid ichthyosaur known from the Middle Triassic (mid-late Anisian stage) of Guizhou Province, China. Etymology The generic name is derived from ''Xinmin'', the district where the fossil was found, and Greek ''sauros'', "lizard". The specific name is derived from Greek ''kataktes'', "crusher", in reference to one of the taxon's autapomorphies - the presence of bulbous and laterally compressed crushing teeth in maxilla and posterior dentary. Discovery ''Xinminosaurus'' is known only from the holotype GMPKU-P-1071, a nearly complete skeleton deposited in Geological Museum, Peking University. It was collected from the conodont ''Nicoraella kockeli'' biozone (Pelsonian of the Anisian stage), from the upper member of the Guanling Formation. It was found near Yangjuan Village of the Xinmin District, Panxian County. Maisch suggested that ''Xinminosaurus'' might be a subjective junior synonym of '' Tholodus''. Although Jiang '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utatsusaurus BW
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the elonga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utatsusaurus Hataii
''Utatsusaurus hataii'' is the earliest-known ichthyopterygian which lived in the Early Triassic period (c. 245–250 million years ago). It was nearly long with a slender body. The first specimen was found in Utatsu-cho (now part of Minamisanriku-cho), Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It is the only described species in the genus ''Utatsusaurus'' and the only member of the family Utatsusauridae. The name ''Utatsusaurus'' was given after the city. The fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Osawa Formation of Miyagi Prefecture, Japan and British Columbia, Canada. ''Utatsusaurus'' is one of the most primitive grades of ichthyosaurs, a basal ichthyosaur. Description ''Utatsusaurus'' was a relatively small ichthyopterygian, measuring long and weighing . Unlike the more advanced ichthyosaurs, ''Utatsusaurus'' has no dorsal fin and has a broad skull. The snout gently tapers, compared to the more rounded one of more derived ichthyopterygians. The postorbital underlaps the el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |