|
Greenhouses
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These structures range in size from small sheds to industrial-sized buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame. The interior of a greenhouse exposed to sunlight becomes significantly warmer than the external temperature, protecting its contents in cold weather. Many commercial glass greenhouses or hothouses are high tech production facilities for vegetables, flowers or fruits. The glass greenhouses are filled with equipment including screening installations, heating, cooling, and lighting, and may be controlled by a computer to optimize conditions for plant growth. Different techniques are then used to manage growing conditions, including air temperature, relative humidity and vapour-pressure deficit, in order to provide the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse New Zealand
A greenhouse (also called a glasshouse, or, if with sufficient heating, a hothouse) is a structure with walls and roof made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown.These structures range in size from small sheds to industrial-sized buildings. A miniature greenhouse is known as a cold frame. The interior of a greenhouse exposed to sunlight becomes significantly warmer than the external temperature, protecting its contents in cold weather. Many commercial glass greenhouses or hothouses are high tech production facilities for vegetables, flowers or fruits. The glass greenhouses are filled with equipment including screening installations, heating, cooling, and lighting, and may be controlled by a computer to optimize conditions for plant growth. Different techniques are then used to manage growing conditions, including air temperature, relative humidity and vapour-pressure deficit, in order to provide the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orangerie Du Château De Versailles Le 11 Septembre 2015 - 90
An orangery or orangerie was a room or a dedicated building on the grounds of fashionable residences of Northern Europe from the 17th to the 19th centuries where orange and other fruit trees were protected during the winter, as a very large form of greenhouse or conservatory. The orangery provided a luxurious extension of the normal range and season of woody plants, extending the protection which had long been afforded by the warmth offered from a masonry fruit wall. During the 17th century, fruits like orange, pomegranate, and bananas arrived in huge quantities to European ports. Since these plants were not adapted to the harsh European winters, orangeries were invented to protect and sustain them. The high cost of glass made orangeries a status symbol showing wealth and luxury. Gradually, due to technological advancements, orangeries became more of a classic architectural structure that enhanced the beauty of an estate garden, rather than a room used for wintering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Frame
In agriculture and gardening, a cold frame is a transparent-roofed enclosure, built low to the ground, used to protect plants from adverse weather, primarily excessive cold or wet. The transparent top admits sunlight and prevents heat escape via convection that would otherwise occur, particularly at night. Essentially, a cold frame functions as a miniature greenhouse to extend the growing season. Historically, cold frames were built to be used in addition to a heated greenhouse. The name itself exemplifies the distinction between the warm greenhouse and the unheated cold frame. They were frequently built as part of the greenhouse's foundation brickwork along the southern wall (in northern latitudes). This allowed seeds to be germinated in the greenhouse and then easily moved to the attached cold frame to be "hardened-off" before final planting outside. Cold frames are similar to some enclosed hotbeds, also called hotboxes. The difference is in the amount of heat generated inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Garden V
Botany, also called plant science (or plant sciences), plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (') meaning "pasture", "herbs" "Poaceae, grass", or "fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to Grazing, graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of Embryophyte, land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanga Yorok
''Sanga Yorok'' (hangul:산가요록, hanja:山家要錄) is a Korean cook book written in hanja in about 1459 by the royal family doctor, Jeon soon. The work also incorporates descriptions of farming. The terminology means "records for farming villages". ''Sanga Yorok'' precedes by 80 years the book from Kim Yoo's Suwoon Jipbang. It deals with 239 kinds of cooking methods for liquors, juk, guk, tteok, desserts and tofu-related dishes. The writer, Jeon soon worked for medical care of royal family during Munjong and Sejo of Joseon to record another book, ''Sikryo Chanyo'', the first-ever recorded Korean book for dietary treatment. The importance of the writing can be found from numerous methodologies of dishes of 38 kinds of kimchi ''Kimchi'' (; ko, 김치, gimchi, ), is a traditional Korean side dish of salted and fermented vegetables, such as napa cabbage and Korean radish. A wide selection of seasonings are used, including '' gochugaru'' (Korean chili powder), .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseon
Joseon (; ; Middle Korean: 됴ᇢ〯션〮 Dyǒw syéon or 됴ᇢ〯션〯 Dyǒw syěon), officially the Great Joseon (; ), was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom was founded following the aftermath of the overthrow of Goryeo in what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul. The kingdom's northernmost borders were expanded to the natural boundaries at the rivers of Amrok and Tuman through the subjugation of the Jurchens. During its 500-year duration, Joseon encouraged the entrenchment of Confucian ideals and doctrines in Korean society. Neo-Confucianism was installed as the new state's ideology. Buddhism was accordingly discouraged, and occasionally the practitioners faced persecutions. Joseon consolidated its effective rule over the territory of current Korea and saw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
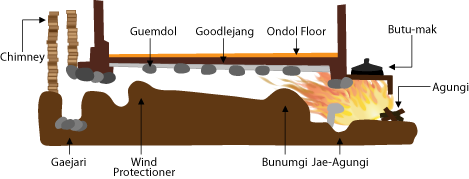
Ondol
Ondol (; , Hangul: 온돌, 溫堗, ) or gudeul (Hangul: 구들, ) in Korean traditional architecture, is underfloor heating that uses direct heat transfer from wood smoke to heat the underside of a thick masonry floor. In modern usage it refers to any type of underfloor heating, or to a hotel or a sleeping room in Korean (as opposed to Western) style. The main components of the traditional ''ondol'' are an '' agungi'' ( firebox or stove) accessible from an adjoining room (typically kitchen or master bedroom), a raised masonry floor underlain by horizontal smoke passages, and a vertical, freestanding chimney on the opposite exterior wall providing a draft. The heated floor, supported by stone piers or baffles to distribute the smoke, is covered by stone slabs, clay and an impervious layer such as oiled paper. History Origin Use of the ''ondol'' has been found at archaeological sites in present-day North Korea. A Neolithic Age archaeological site, circa 5000 BC, discovered in Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cob (material)
Cob, cobb, or clom (in Wales) is a natural building material made from subsoil, water, fibrous organic material (typically straw), and sometimes lime. The contents of subsoil vary, and if it does not contain the right mixture, it can be modified with sand or clay. Cob is fireproof, resistant to seismic activity, and uses low-cost materials, although it is very labour intensive. It can be used to create artistic and sculptural forms, and its use has been revived in recent years by the natural building and sustainability movements. In technical building and engineering documents, such as the Uniform Building Code of the western USA, cob may be referred to as "unburned clay masonry," when used in a structural context. It may also be referred to as "aggregate" in non-structural contexts, such as "clay and sand aggregate," or more simply "organic aggregate," such as where cob is a filler between post and beam construction. History and usage ''Cob'' is an English term attested to arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Paper
Korean paper or ''hanji'' ( ko, 한지/韓紙) is the name of traditional handmade paper from Korea. Hanji is made from the inner bark of '' Broussonetia papyrifera'' known colloquially as paper mulberry, a tree native to Korea that grows well on its rocky mountainsides, known in Korean as ''dak''. The formation aid crucial to making hanji is the mucilage that oozes from the roots of '' Hibiscus manihot''. This substance helps suspend the individual fibers in water. Traditional hanji is made in laminated sheets using the ''we bal'' method (a sheet formation technique), which allows for multi-directional grain The process of creating hanji also employs ''dochim'', a method of pounding finished sheets to compact fibers and lessen ink bleed. Hanji paper is famous across Asia for its white color and extreme durability, and was a high import to China in tribute missions. History Ancient In Korea, papermaking started not long after its birth in China. At first, made crudely out of he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The Joseon Dynasty
The ''Veritable Records of the Joseon Dynasty'' (also known as the ''Annals of the Joseon Dynasty'' or the ''True Record of the Joseon Dynasty''; ko, 조선왕조실록 and ) are the annual records of Joseon, the last royal house to rule Korea. Kept from 1392 to 1865, the annals (or ''sillok'') comprise 1,893 volumes and are thought to be the longest continual documentation of a single dynasty in the world. With the exception of two sillok compiled during the colonial era, they are the 151st national treasure of South Korea and listed in UNESCO's Memory of the World registry. Since 2006, the annals have been digitized by the National Institute of Korean History and are available on the internet with modern Korean translation in hangul and the original text in Classical Chinese. In January 2012, the National Institute of Korean History announced a plan to translate them to English by the year 2033. The work was scheduled to start in 2014 with an initial budget of ₩500 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Orange
The mandarin orange (''Citrus reticulata''), also known as the mandarin or mandarine, is a small citrus tree fruit. Treated as a distinct species of Orange (fruit), orange, it is usually eaten plain or in fruit salads. Tangerines are a group of orange-coloured citrus fruit consisting of hybrids of mandarin orange with some pomelo contribution. Mandarins are smaller and oblate, unlike the spherical common Orange (fruit), oranges (which are a mandarin–pomelo Hybrid (biology), hybrid). The taste is considered sweeter and stronger than the common orange. A ripe mandarin is firm to slightly soft, heavy for its size, and pebbly-skinned. The peel is thin, loose, with little white mesocarp, so they are usually easier to peel and to split into segments. Hybrids usually have these traits to a lesser degree. The mandarin is tender and is damaged easily by cold. It can be grown in tropical and subtropical areas. According to genetic studies, the mandarin was one of the Citrus taxonomy#A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |