|
Glycin
Glycin, or N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)glycine, is N-substituted p-aminophenol. It is a photographic developing agent used in classic black-and-white developer solutions. It is not identical to, but derived from glycine, the proteinogenic amino acid. It is typically characterized as thin plates of white or silvery powder, although aged samples appear brown. It is sparingly soluble in water and most organic solvents; it is readily soluble in alkalies and acids.{{cite encyclopedia, last1=Mitchell, first1=Stephen C., last2=Waring, first2=Rosemary H., encyclopedia=Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, publisher=Wiley-VCH, year=2000, doi=10.1002/14356007.a02_099, isbn=978-3527306732, chapter=Aminophenols Glycin is structurally related to 4-aminophenol and metol. Decarboxylation of glycin gives metol. Glycin has a milder reduction potential than metol. The two developers have markedly different character. Glycin is slower-acting, but much longer-lasting in solution. Glycin is rarely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine disrupts the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure. Its small side chain causes it to favor random coils instead. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a '' Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into both hydrophilic and hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by French chemist Henri Braconnot when he hydrolyzed gelatin by boiling it with sulfuric acid. He originally called it "sugar of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteinogenic Amino Acid
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation from RNA. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 ( selenocysteine and pyrrolysine) that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms. In contrast, non-proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are either not incorporated into proteins (like GABA, L-DOPA, or triiodothyronine), misincorporated in place of a genetically encoded amino acid, or not produced directly and in isolation by standard cellular machinery (like hydroxyproline). The latter often results from post-translational modification of proteins. Some non-proteinogenic amino acids are incorporated into nonribosomal peptides which are synthesized by non-ribosomal peptide synthetases. Both eukaryotes and prokaryotes can incorporate selenocysteine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metol
Metol is a trade name for the organic compound with the formula OC6H4NH2(CH3)sub>2HSO4. It is the sulfate salt of ''N''-methylaminophenol. This colourless salt is a popular photographic developer used in monochrome photography.Gerd Löbbert "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Synthesis and degradation Several methods exist for the preparation of ''N''-methylaminophenol. It arises by decarboxylation of ''N''-4-hydroxyphenylglycine ( Glycin). It can be obtained by reaction of hydroquinone with methylamine. Being an electron-rich arene, metol is readily degraded by hydrogen peroxide. Application Metol is an excellent developing agent for most continuous tone developer applications, and it has been widely used in published developer formulas as well as commercial products. However, it is difficult to produce highly concentrated developer solutions using Metol, and therefore, most Metol developers are supplied in dry chemica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Processing
Photographic processing or photographic development is the chemical means by which photographic film or paper is treated after photographic exposure to produce a negative or positive image. Photographic processing transforms the latent image into a visible image, makes this permanent and renders it insensitive to light.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. All processes based upon the gelatin silver process are similar, regardless of the film or paper's manufacturer. Exceptional variations include instant films such as those made by Polaroid and thermally developed films. Kodachrome required Kodak's proprietary K-14 process. Kodachrome film production ceased in 2009, and K-14 processing is no longer available as of December 30, 2010. Ilfochrome materials use the dye destruction process. Deliberately using the wrong process for a film is known as cross processing. Common processes All p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Developer
In the Photographic processing, processing of photographic films, plates or papers, the photographic developer (or just developer) is one or more chemicals that convert the latent image to a visible image. Developing agents achieve this conversion by Redox, reducing the silver halides, which are pale-colored, into silver metal, which is black when in the form of fine particles.Karlheinz Keller et al. ''Photography'' in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . The conversion occurs within the gelatine matrix. The special feature of photography is that the developer acts more quickly on those particles of silver halide that have been exposed to light. When left in developer, all the silver halides will eventually be reduced and turn black. Generally, the longer a developer is allowed to work, the darker the image. Chemical composition of developers The developer typically consists of a mixture of chemical compounds prepared as an aqueous solut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-aminophenol
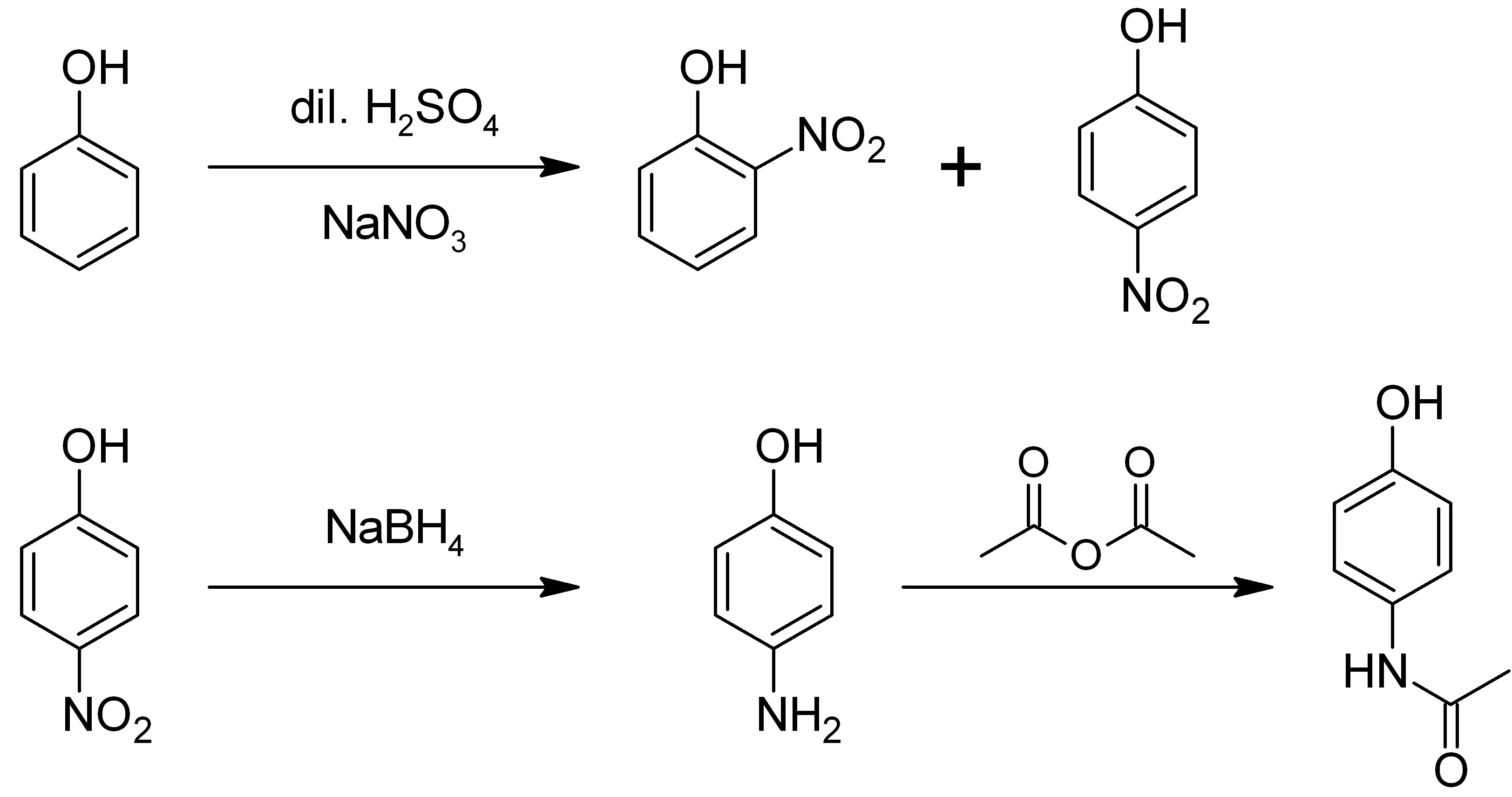
4-Aminophenol (or ''para''-aminophenol or ''p''-aminophenol) is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4OH. Typically available as a white powder, it is commonly used as a developer for black-and-white film, marketed under the name Rodinal. Reflecting its slightly hydrophilic character, the white powder is moderately soluble in alcohols and can be recrystallized from hot water. In the presence of a base, it oxidizes readily. The methylated derivatives ''N''-methylaminophenol and ''N'',''N''-dimethylaminophenol are of commercial value. The compound is one of three isomeric aminophenols, the other two being 2-aminophenol and 3-aminophenol. __TOC__ Preparation From phenol It is produced from phenol by nitration followed by reduction with iron. Alternatively, the partial hydrogenation of nitrobenzene affords phenylhydroxylamine, which rearranges primarily to 4-aminophenol ( Bamberger rearrangement). :C6H5NO2 + 2 H2 → C6H5NHOH + H2O :C6H5NHOH → HOC6H4NH2 From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenidone
Phenidone (1-phenyl-3-pyrazolidinone) is an organic compound that is primarily used as a photographic developer. It has five to ten times the developing power as Metol, capable of achieving the same level of development in both less time and at a lower concentration. It also has low toxicity and unlike some other developers, does not cause dermatitis Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ... upon skin contact.''Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 9th ed.'' monograph 7115 As a developer, Phenidone is typically used in conjunction with hydroquinone for black and white photography and performs better at lower pH levels. Phenidone is Ilford's trademark for this material, which was first filed on Feb. 24, 1953, but has since expired. Although the compound was first prepared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroacetic Acid
Chloroacetic acid, industrially known as monochloroacetic acid (MCA), is the organochlorine compound with the formula . This carboxylic acid is a useful building block in organic synthesis. It is a colorless solid. Related compounds are dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid. Production Chloroacetic acid was first prepared (in impure form) by the French chemist Félix LeBlanc (1813–1886) in 1843 by chlorinating acetic acid in the presence of sunlight, and in 1857 (in pure form) by the German chemist Reinhold Hoffmann (1831–1919) by refluxing glacial acetic acid in the presence of chlorine and sunlight, and then by the French chemist Charles Adolphe Wurtz by hydrolysis of chloroacetyl chloride (), also in 1857. Chloroacetic acid is prepared industrially by two routes. The predominant method involves chlorination of acetic acid, with acetic anhydride as a catalyst: : This route suffers from the production of dichloroacetic acid and trichloroacetic acid as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Chemicals
Photography is the art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is employed in many fields of science, manufacturing (e.g., photolithography), and business, as well as its more direct uses for art, film and video production, recreational purposes, hobby, and mass communication. A person who operates a camera to capture or take photographs is called a photographer, while the captured image, also known as a photograph, is the result produced by the camera. Typically, a lens is used to focus the light reflected or emitted from objects into a real image on the light-sensitive surface inside a camera during a timed exposure. With an electronic image sensor, this produces an electrical charge at each pixel, which is electronically processed and stored in a digital image file for subsequent display or processing. The result w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acids
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Historically, vinegar was produced from the third century BC and was likely the first acid to be produced in large quantities. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important chemical reagent and industrial chemical across various fields, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |