|
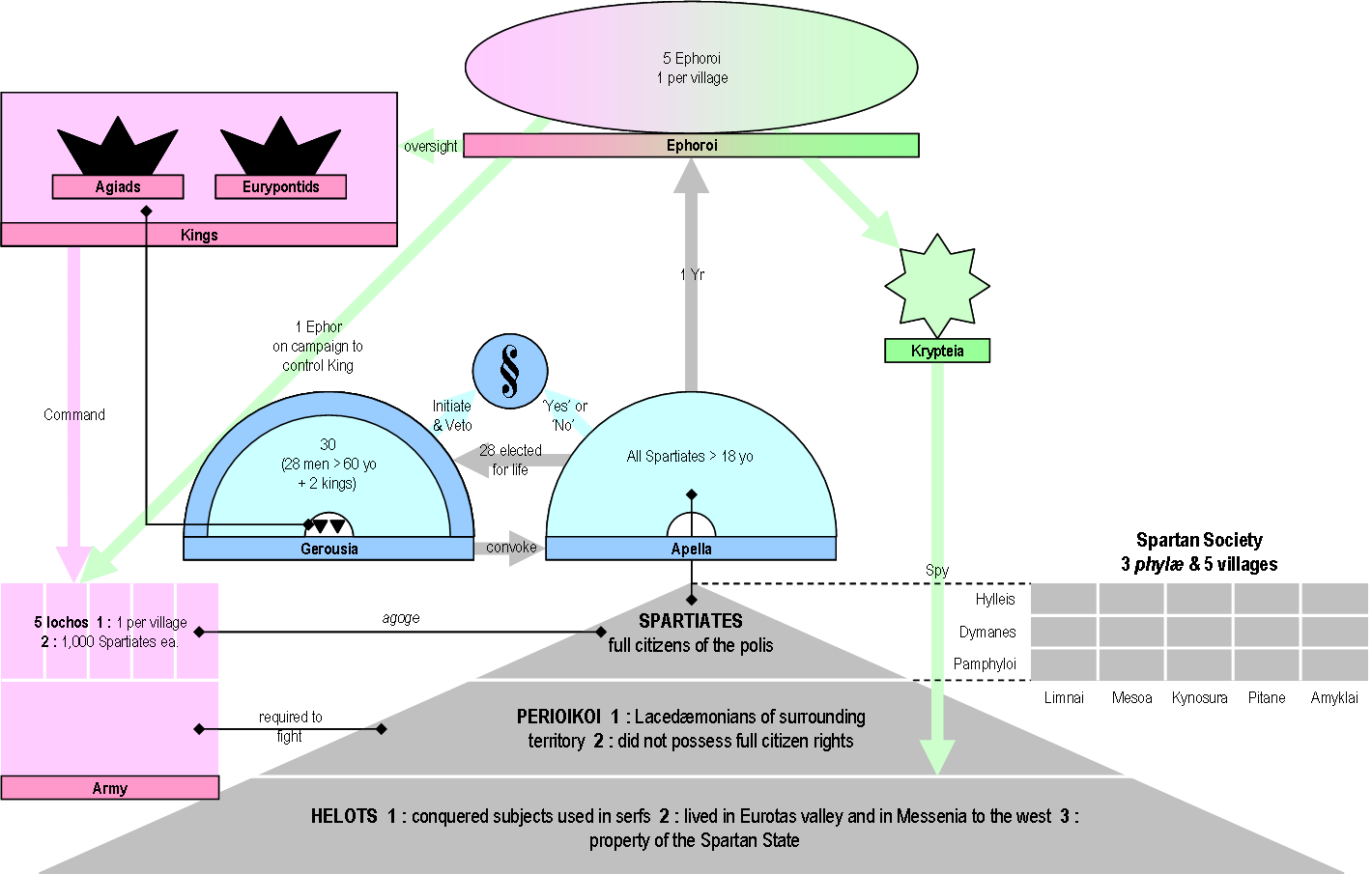
Gerousia
The Gerousia (γερουσία) was the council of elders in ancient Sparta. Sometimes called Spartan senate in the literature, it was made up of the two Spartan kings, plus 28 men over the age of sixty, known as gerontes. The Gerousia was a prestigious body, holding extensive judicial and legislative powers, which shaped Sparta's policies. Ancient Greeks considered that the Gerousia was created by the mythical Spartan lawgiver Lycurgus in his Great Rhetra, the constitution of Sparta. The gerontes were men over sixty elected through peculiar shouting elections, which were open to manipulation, especially from the kings. Membership The ''Gerousia'' consisted of thirty members in total. Twenty-eight elected members (called gerontes) and the two kings, who were members by right, entering the chamber upon their accession. Unlike the kings, the 28 gerontes had to be at least 60 years old—the age when Spartan citizens were no longer required to serve in the army. Member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apella
The ecclesia or ekklesia (Greek: ἐκκλησία) was the citizens' assembly in the Ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. Unlike its more famous counterpart in Athens, the Spartan assembly had limited powers, as it did not debate; citizens could only vote for or against proposals. In the pre-War literature, the assembly was often called the apella ( el, Ἀπέλλα), but this word refers to a festival of Apollo, the Apellai, during which the ekklesia originally met. Name The pre-War academic literature often refers to the Spartan ekklesia as the apella. However, this word is never found in ancient sources in the singular, and never in a political context.Ste. Croix, ''Origins of the Peloponnesian War'', p. 347. The Apellai were a festival of Apollo where the ekklesia originally met. They were organised once a month, with perhaps one more important feast once a year (called Apellaios), during which elections were presumably organised. In later times, the two events (religiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephor
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs. The word "''ephors''" (Ancient Greek ''éphoroi'', plural form of ''éphoros'') comes from the Ancient Greek ''epi'', "on" or "over", and ''horaō'', "to see", i.e., "one who oversees" or "overseer". The ephors were a council of five Spartan men elected annually who swore an oath monthly on the behalf of the state. The Spartan kings, however, would swear on behalf of themselves. The ephors did not have to kneel before the Kings of Sparta, and were held in high esteem by the citizens because of the importance of their powers and because of the holy role that they earned throughout their functions.Donald Kagan, ''The Outbreak of the Peloponnesian War''. page 29. Ithaca/New York 1969, . Several other Greek city-states with a Spartan ancestry also had ephors, such as Taras or Cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Constitution
The Spartan Constitution (or Spartan politeia) are the government and laws of the classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army. The Spartans had no historical records, literature, or written laws, which were, according to tradition, prohibited. Attributed to the mythical figure of Lycurgus, the legendary law-giver, the Spartan system of government is known mostly from the '' Constitution of the Lacedaemonians'', a treatise attributed to the ancient Greek historian Xenophon, describing the institutions, customs, and practices of the ancient Spartans. The act of the foundation Great Rhetra According to Plutarch, Lycurgus (to whom is attributed the establishment of the severe reforms for which Sparta has become renowned, sometime in the 9th century BC) first sought counsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleomenes III
Cleomenes III ( grc, Κλεομένης) was one of the two kings of Sparta from 235 to 222 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty and succeeded his father, Leonidas II. He is known for his attempts to reform the Spartan state. From 229 to 222 BC, Cleomenes waged war against the Achaean League under Aratus of Sicyon. After being defeated by the Achaeans in the Battle of Sellasia in 222 BC, he fled to Ptolemaic Egypt. After a failed revolt in 219 BC, he committed suicide. Early life Cleomenes was born in Sparta to the future Agiad king Leonidas II and his wife Cratesicleia. The exact year of Cleomenes' birth is unknown but historian Peter Green puts it between 265 BC and 260 BC.Green, ''Alexander to Actium: The Historical Evolution of the Hellenistic Age'', 255. Around 242 BC, Leonidas was exiled from Sparta and forced to seek refuge in the temple of Athena after opposing the reforms of the Eurypontid King, Agis IV. Cleomenes' brother-in-law, Cleombrotus, who was a suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Sparta
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Lives
Plutarch's ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'', commonly called ''Parallel Lives'' or ''Plutarch's Lives'', is a series of 48 biographies of famous men, arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, probably written at the beginning of the second century AD. The surviving ''Parallel Lives'' (Greek: Βίοι Παράλληλοι, ''Bíoi Parállēloi'') comprises 23 pairs of biographies, each pair consisting of one Greek and one Roman of similar destiny, such as Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar, or Demosthenes and Cicero. It is a work of considerable importance, not only as a source of information about the individuals described, but also about the times in which they lived. Motivation ''Parallel Lives'' was Plutarch's second set of biographical works, following the Lives of the Roman Emperors from Augustus to Vitellius. Of these, only the Lives of Galba and Otho survive. As he explains in the first paragraph of his ''Life of Alexander'', Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Senate
The Greek Senate ( el, Γερουσία, ''Gerousia'') was the upper chamber of the parliament in Greece, extant several times in the country's history. Local senates during the War of Independence During the early stages of the Greek War of Independence, prior to the establishment of a centralized administration, a number of regional councils were established, most of which were termed "senate", but which were unicameral bodies: the Senate of Western Continental Greece, the Areopagus of Eastern Continental Greece (sometimes referred to as "senate"), and the Peloponnesian Senate. 1829–1833 A unicameral body with purely advisory functions, the Senate was established in 1829 by the Fourth National Assembly at Argos in replacement of the ''Panellinion'', established the previous year. It had 27 members, 21 of whom were chosen by the Governor (Ioannis Kapodistrias) from 63 candidates nominated by the Assembly, and further six who were appointed directly by the Governor. Georgio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenic Parliament
The Hellenic Parliament ( el, Ελληνικό Κοινοβούλιο, Elliniko Kinovoulio; formally titled el, Βουλή των Ελλήνων, Voulí ton Ellínon, Boule (ancient Greece), Boule of the Greeks, Hellenes, label=none), also known as the Parliament of the Hellenes, the Hellenic Bouleterion or Greek Parliament, is the Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of Greece, located in the Old Royal Palace, overlooking Syntagma Square in Athens. The parliament is the supreme democratic institution that represents the citizens through an elected body of Members of Parliament (MPs). It is a Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of 300 members, elected for a four-year term. In 1844–1863 and 1927–1935, the parliament was Bicameralism, bicameral with an upper house (the Greek Senate, senate) and a lower house (the chamber of deputies), which retained the name . Several important Greek statesmen have served as the speaker of the Hellenic Parliament. History Constitutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Thebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleombrotus I
Cleombrotus I ( el, Κλεόμβροτος ; died 6 July 371 BC) was a Spartan king of the Agiad line, reigning from 380 BC until 371 BC. Little is known of Cleombrotus' early life. Son of Pausanias, he became king of Sparta after the death of his brother Agesipolis I in 380 BC, and led the allied Spartan-Peloponnesian army against the Thebans under Epaminondas in the Battle of Leuctra. His death and the utter defeat of his army led to the end of Spartan dominance in ancient Greece. Cleombrotus was succeeded by his son Agesipolis II. His other son was Cleomenes II. Many historians cite Cleombrotus as having pro-Theban tendencies, unlike his fellow king, Agesilaus II. He was blamed for the humiliating defeat at Leuctra by his contemporaries for being biased towards the enemy, though some modern historians do not believe that he was actually pro-Theban.Xenophon, ''Hell.'' He was the first Spartan king to die in battle since Leonidas at the Battle of Thermopylae. References Furthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agis II
Agis II ( grc-gre, Ἄγις; died c. 399 BC) was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.Agis II fro Livius.Org Life Agis succeeded his father in 427 BC, and reigned a little more than 26 years. In the summer of 426 BC, he led an army of Peloponnesians and their allies as far as the |
.jpg)