|
Ganciclovir
Ganciclovir, sold under the brand name Cytovene among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections. Ganciclovir was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1988. Medical use Ganciclovir is indicated for:Rossi S, editor. Australian Medicines Handbook 2006. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook; 2006. * Sight-threatening CMV retinitis in severely immunocompromised people * CMV pneumonitis in bone marrow transplant recipients * Prevention of CMV disease in bone marrow and solid organ transplant recipients * Confirmed CMV retinitis in people with AIDS (intravitreal implant) It is also used for acute CMV colitis in HIV/AIDS and CMV pneumonitis in immunosuppressed patients. Ganciclovir has also been used with some success in treating ''Human herpesvirus 6'' infections. Ganciclovir has also been found to be an effective treatment for herpes simplex virus epithelial keratitis. Adverse effects Ganciclovir is commonly associated with a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
Cytomegalovirus retinitis, also known as CMV retinitis, is an inflammation of the retina of the eye that can lead to blindness. Caused by human cytomegalovirus, it occurs predominantly in people whose immune system has been compromised, 15-40% of those with AIDS. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of cytomegalovirus retinitis have it usually starting in one eye (and also have the possibility of retinal detachment), presenting as: * Blurred vision * Blind spots * Specks in your vision Cause Cytomegalovirus (a type of herpes virus) is what causes cytomegalovirus retinitis. Other types of herpes viruses include herpes simplex viruses and Epstein-Barr virus. Once an individual is infected with these viruses they stay in the body for life. What triggers the virus to reactivate are the following (though CMV can also be congenital). * Leukemia * AIDS * Immunosuppressive chemotherapy Mechanism Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV or CMV) is a DNA virus in the family ''Herpesviridae'' known for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
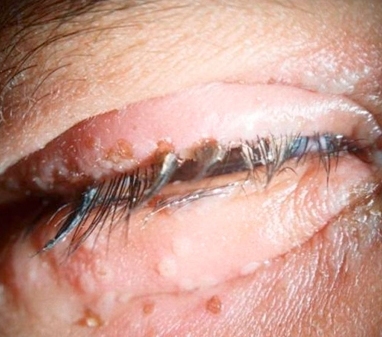
Herpes Of The Eye
Herpetic simplex keratitis is a form of keratitis caused by recurrent herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection in the cornea. It begins with infection of epithelial cells on the surface of the eye and retrograde infection of nerves serving the cornea. Primary infection typically presents as swelling of the conjunctiva and eyelids (blepharoconjunctivitis), accompanied by small white itchy lesions on the corneal surface. The effect of the lesions varies, from minor damage to the epithelium ( superficial punctate keratitis), to more serious consequences such as the formation of dendritic ulcers. Infection is unilateral, affecting one eye at a time. Additional symptoms include dull pain deep inside the eye, mild to acute dryness, and sinusitis. Most primary infections resolve spontaneously in a few weeks. Healing can be aided by the use of oral and topical antivirals. Subsequent recurrences may be more severe, with infected epithelial cells showing larger dendritic ulceration, and lesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Herpesvirus 6
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) is the common collective name for ''human betaherpesvirus 6A'' (HHV-6A) and ''human betaherpesvirus 6B'' (HHV-6B). These closely related viruses are two of the nine known herpesviruses that have humans as their primary host. HHV-6A and HHV-6B are double-stranded DNA viruses within the ''Betaherpesvirinae'' subfamily and of the genus ''Roseolovirus''. HHV-6A and HHV-6B infect almost all of the human populations that have been tested. HHV-6A has been described as more neurovirulent, and as such is more frequently found in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis. HHV-6 (and HHV-7) levels in the brain are also elevated in people with Alzheimer's disease. HHV-6B primary infection is the cause of the common childhood illness exanthema subitum (also known as roseola infantum or sixth disease). It is passed on from child to child. It is uncommon for adults to contract this disease as most people have had it by kindergarten, and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebitis
Phlebitis (or Venitis) is inflammation of a vein, usually in the legs. It most commonly occurs in superficial veins. Phlebitis often occurs in conjunction with thrombosis and is then called thrombophlebitis or superficial thrombophlebitis. Unlike deep vein thrombosis, the probability that superficial thrombophlebitis will cause a clot to break up and be transported in pieces to the lung is very low. Signs and symptoms * Localized redness and swelling * Pain or burning along the length of the vein * Vein being hard and cord-like There is usually a slow onset of a tender red area along the superficial veins on the skin. A long, thin red area may be seen as the inflammation follows a superficial vein. This area may feel hard, warm, and tender. The skin around the vein may be itchy and swollen. The area may begin to throb or burn. Symptoms may be worse when the leg is lowered, especially when first getting out of bed in the morning. A low-grade fever may occur. Sometimes phlebitis m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass). Biological relevance Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an important indicator of kidney health, because it is an easily measured byproduct of muscle metabolism that is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Creatinine itself is produced via a biological system involving creatine, phosphocreatine (also known as creatine phosphate), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP, the body's immediate energy supply). Creatine is synthesized primarily in the liver from the methylation of glycocyamine (guanidino acetate, synthesized in the kidney from the amino acids arginine and glycine) by S-Adenosyl methionine. It is then transported through blood to the other organs, muscle, and brain, where, through phosphorylation, it becomes the high-energy compound phosphocreatine. Creatine conversion to phosphocreatine is catalyzed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes nucleic acid, genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in animals, such mutagens can therefore be carcinogens, although not all necessarily are. All mutagens have characteristic mutational signatures with some chemicals becoming mutagenic through cellular processes. The process of DNA becoming modified is called mutagenesis. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called "spontaneous mutations" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, DNA error, errors in DNA replication, repair and Genetic recombination, recombination. Discovery The first mutagens to be identified were carcinogens, substances that were shown to be linked to cancer. Tumors were described more than 2,000 years before the discovery of chromosomes and DNA; in 500 B.C., the Greece, Greek physician Hippocrates named tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μl) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μl. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood - thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine complete blood count. Some individuals with thrombocytopenia may experience external bleeding, such as nosebleeds or bleeding gums. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells. Spermatozoa are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |