|
G-block
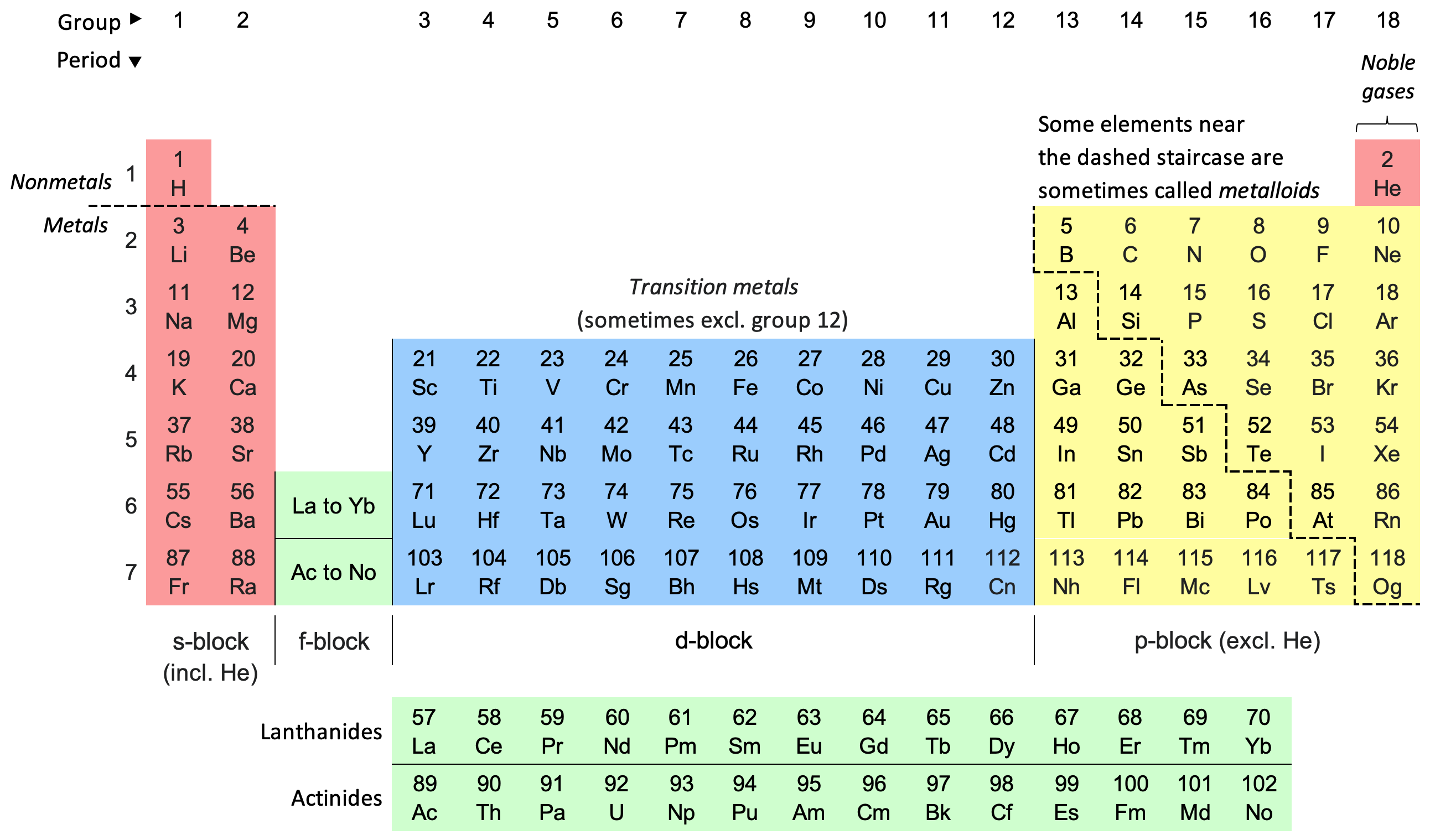
An extended periodic table theorizes about chemical elements beyond those currently known and proven. The element with the highest atomic number known is oganesson (''Z'' = 118), which completes the seventh period (row) in the periodic table. All elements in the eighth period and beyond thus remain purely hypothetical. Elements beyond 118 will be placed in additional periods when discovered, laid out (as with the existing periods) to illustrate periodically recurring trends in the properties of the elements. Any additional periods are expected to contain more elements than the seventh period, as they are calculated to have an additional so-called ''g-block'', containing at least 18 elements with partially filled g- orbitals in each period. An ''eight-period table'' containing this block was suggested by Glenn T. Seaborg in 1969. The first element of the g-block may have atomic number 121, and thus would have the systematic name unbiunium. Despite many searches, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pekka Pyykkö
Veli Pekka Pyykkö (born 12 October 1941) is a Finnish academic. He was professor of Chemistry at the University of Helsinki. From 2009–2012, he was the chairman of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science. He is known for his extension to the periodic table of elements, known as the Pyykkö model. Pyykkö has also studied the relativistic effects present in heavy atoms and their effects in NMR. Pyykkö model After the 118 elements now known, Pekka Pyykkö predicts that the orbital shells will fill up in this order: *8s, *5g, *the first two spaces of 8p, *6f, *7d, *9s, *the first two spaces of 9p, *the rest of 8p. He also suggests that period 8 be split into three parts: *8a, containing 8s, *8b, containing the first two elements of 8p, *8c, containing 7d and the rest of 8p. The compact version: Pekka Pyykkö correctly predicted the existence of chemical bonds between gold and the noble gas xenon, which is usually inert; this bond is known to occur in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Periodic Table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top right. The first periodic table to become generally accepted was that of the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869; he formulated the periodic law as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
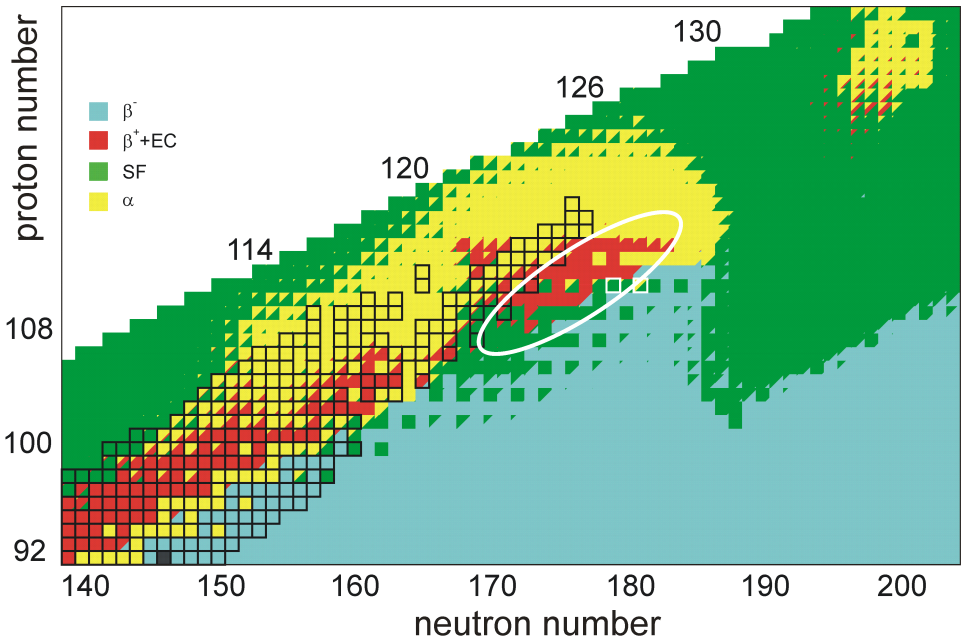
Unbihexium
Unbihexium, also known as element 126 or eka-plutonium, is a hypothetical chemical element; it has atomic number 126 and placeholder symbol Ubh. ''Unbihexium'' and ''Ubh'' are the temporary IUPAC name and symbol, respectively, until the element is discovered, confirmed, and a permanent name is decided upon. In the periodic table, unbihexium is expected to be a g-block superactinide and the eighth element in the 8th period. Unbihexium has attracted attention among nuclear physicists, especially in early predictions targeting properties of superheavy elements, for 126 may be a magic number of protons near the center of an island of stability, leading to longer half-lives, especially for 310Ubh or 354Ubh which may also have magic numbers of neutrons. Early interest in possible increased stability led to the first attempted synthesis of unbihexium in 1971 and searches for it in nature in subsequent years. Despite several reported observations, more recent studies suggest that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unbiunium
Unbiunium, also known as eka-actinium or element 121, is a hypothetical chemical element; it has symbol Ubu and atomic number 121. ''Unbiunium'' and ''Ubu'' are the temporary systematic IUPAC name and symbol respectively, which are used until the element is discovered, confirmed, and a permanent name is decided upon. In the periodic table of the elements, it is expected to be the first of the superactinides, and the third element in the eighth period. It has attracted attention because of some predictions that it may be in the island of stability. It is also likely to be the first of a new g-block of elements. Unbiunium has not yet been synthesized. It is expected to be one of the last few reachable elements with current technology; the limit could be anywhere between element 120 and 124. It will also likely be far more difficult to synthesize than the elements known so far up to 118, and still more difficult than elements 119 and 120. The teams at RIKEN in Japan and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unbibium
Unbibium, also known as element 122 or eka-thorium, is a hypothetical chemical element; it has placeholder symbol Ubb and atomic number 122. ''Unbibium'' and ''Ubb'' are the temporary Systematic element name, systematic IUPAC name and symbol respectively, which are used until the element is discovered, confirmed, and a permanent name is decided upon. In the periodic table of the elements, it is expected to follow unbiunium as the second element of the superactinides and the fourth element of the 8th Period (periodic table), period. Similarly to unbiunium, it is expected to fall within the range of the island of stability, potentially conferring additional stability on some isotopes, especially 306Ubb which is expected to have a Magic number (physics), magic number of neutrons (184). Despite several attempts, unbibium has not yet been synthesized, nor have any naturally occurring isotopes been found to exist. There are currently no plans to attempt to synthesize unbibium. In 2008, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Period (periodic Table)
A period on the periodic table is a row of chemical elements. All Chemical element, elements in a row have the same number of electron shells. Each next element in a period has one more proton and is less metallic than its predecessor. Arranged this way, elements in the same group (periodic table), group (column) have similar chemical property, chemical and physical property, physical properties, reflecting the periodic law. For example, the halogens lie in the second-to-last group (Halogen, group 17) and share similar properties, such as high reactivity and the tendency to gain one electron to arrive at a noble-gas electronic configuration. , a total of 118 elements have been discovered and confirmed. Modern quantum mechanics explains these periodic trends in properties in terms of electron shells. As atomic number increases, shells fill with electrons in approximately the order shown in the ordering rule diagram. The filling of each shell corresponds to a row in the table. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aufbau Principle
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the Aufbau principle (, from ), also called the Aufbau rule, states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons first fill Electron shell#Subshells, subshells of the lowest available energy, then fill subshells of higher energy. For example, the 1s subshell is filled before the 2s subshell is occupied. In this way, the electrons of an atom or ion form the most stable electron configuration possible. An example is the configuration for the phosphorus atom, meaning that the 1s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2s subshell has 2 electrons, the 2p subshell has 6 electrons, and so on. The configuration is often abbreviated by writing only the valence electrons explicitly, while the core electrons are replaced by the symbol for the last previous noble gas in the periodic table, placed in square brackets. For phosphorus, the last previous noble gas is neon, so the configuration is abbreviated to [Ne] 3s2 3p3, where [Ne] signifies the core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dirac Equation
In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin-1/2 massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. It is consistent with both the principles of quantum mechanics and the theory of special relativity, and was the first theory to account fully for special relativity in the context of quantum mechanics. The equation is validated by its rigorous accounting of the observed fine structure of the hydrogen spectrum and has become vital in the building of the Standard Model. The equation also implied the existence of a new form of matter, '' antimatter'', previously unsuspected and unobserved and which was experimentally confirmed several years later. It also provided a ''theoretical'' justification for the introduction of several component wave functions in Pauli' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Theory Of Relativity
The theory of relativity usually encompasses two interrelated physics theories by Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity, proposed and published in 1905 and 1915, respectively. Special relativity applies to all physical phenomena in the absence of gravity. General relativity explains the law of gravitation and its relation to the forces of nature. It applies to the cosmological and astrophysical realm, including astronomy. The theory transformed theoretical physics and astronomy during the 20th century, superseding a 200-year-old theory of mechanics created primarily by Isaac Newton. It introduced concepts including 4-dimensional spacetime as a unified entity of space and time, relativity of simultaneity, kinematic and gravitational time dilation, and length contraction. In the field of physics, relativity improved the science of elementary particles and their fundamental interactions, along with ushering in the nuclear age. With relativity, cosmolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron Cloud
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a specific region around the nucleus. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of three quantum numbers , , and , which respectively correspond to electron's energy, its orbital angular momentum, and its orbital angular momentum projected along a chosen axis ( magnetic quantum number). The orbitals with a well-defined magnetic quantum number are generally complex-valued. Real-valued orbitals can be formed as linear combinations of and orbitals, and are often labeled using associated harmonic polynomials (e.g., ''xy'', ) which describe their angular structure. An orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own projection of spin m_s. The simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spontaneous Fission
Spontaneous fission (SF) is a form of radioactive decay in which a heavy atomic nucleus splits into two or more lighter nuclei. In contrast to induced fission, there is no inciting particle to trigger the decay; it is a purely probabilistic process. Spontaneous fission is a dominant decay mode for superheavy elements, with nuclear stability generally falling as nuclear mass increases. It thus forms a practical limit to heavy element nucleon number. Heavier nuclides may be created instantaneously by physical processes, both natural (via the r-process, ''r''-process) and artificial, though rapidly decay to more stable nuclides. As such, apart from minor decay branches in primordial radionuclides, spontaneous fission is not observed in nature. Observed fission half-lives range from 60 nanoseconds () to greater than the current age of the universe (). History Following the discovery of induced fission by Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann in 1938, Soviet physicists Georgy Flyorov and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |