|
Frisians
The Frisians are a Germanic ethnic group native to the coastal regions of the Netherlands and northwestern Germany. They inhabit an area known as Frisia and are concentrated in the Dutch provinces of Friesland and Groningen and, in Germany, East Frisia and North Frisia (which was a part of Denmark until 1864). The name is probably derived from frisselje' (to braid, thus referring to braided hair). The Frisian languages are spoken by more than 500,000 people; West Frisian is officially recognised in the Netherlands (in Friesland), and North Frisian and Saterland Frisian are recognised as regional languages in Germany. History The ancient Frisii enter recorded history in the Roman account of Drusus's 12 BC war against the Rhine Germans and the Chauci. They occasionally appear in the accounts of Roman wars against the Germanic tribes of the region, up to and including the Revolt of the Batavi around 70 AD. Frisian mercenaries were hired to assist the Roman invasion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisia
Frisia is a cross-border cultural region in Northwestern Europe. Stretching along the Wadden Sea, it encompasses the north of the Netherlands and parts of northwestern Germany. The region is traditionally inhabited by the Frisians, a West Germanic ethnic group. Etymology The contemporary name for the region stems from the Latin word Frisii; an ethnonym used for a group of tribes in modern-day Northwestern Germany, possibly being a loanword of Proto-Germanic *frisaz, meaning "curly, crisp", presumably referring to the hair of the tribesmen. In some areas, the local translation of "Frisia" is used to refer to another subregion. On the North Frisian islands, for instance, "Frisia" and "Frisians" refer to (the inhabitants of) mainland North Frisia. In Saterland Frisian, the term ''Fräislound'' specifically refers to Ostfriesland. During the French occupation of the Netherlands, the name for the Frisian department was . In English, both "Frisia" and "Friesland" may be inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch People
The Dutch (Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aruba, Suriname, Guyana, Curaçao, Argentina, Brazil, Canada,Based on Statistics Canada, Canada 2001 Censusbr>Linkto Canadian statistics. Australia, South Africa, New Zealand and the United States.According tFactfinder.census.gov The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The high degree of urbanization characteristic of Dutch society was attained at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
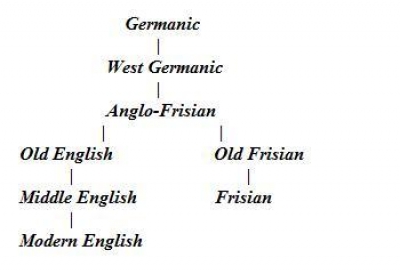
West Frisian Language
West Frisian, or simply Frisian ( fy, link=no, Frysk or ; nl, Fries , also ), is a West Germanic language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland () in the north of the Netherlands, mostly by those of Frisian ancestry. It is the most widely spoken of the Frisian languages. In the study of the evolution of English, West Frisian is notable as being the most closely related foreign tongue to the various dialects of Old English spoken across the Heptarchy, these being part of the Anglo-Frisian branch of the West Germanic family. Name The name "West Frisian" is only used outside the Netherlands, to distinguish this language from the closely related Frisian languages of Saterland Frisian and North Frisian spoken in Germany. Within the Netherlands, however, "West Frisian" refers to the West Frisian dialect of the Dutch language while the West Frisian language is almost always just called "Frisian" (in Dutch: for the Frisian language and for the Dutch dialect). The unam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saterland Frisian Language
Saterland Frisian, also known as Sater Frisian, Saterfrisian or Saterlandic (), is the last living dialect of the East Frisian language. It is closely related to the other Frisian languages: North Frisian, spoken in Germany as well, and West Frisian, spoken in the Dutch province of Friesland. Classification From a diachronical perspective, Saterland Frisian is an ''Emsfrisian'' dialect of the East Frisian language. Emsfrisian used to be spoken in the western half of the East Frisian peninsula and in the Ommelanden. The other East Frisian dialect group was the ''Weserfrisian'', formerly spoken from the eastern half of the East Frisian peninsula to beyond the Weser. Synchronically speaking, Saterland Frisian is a language. Together with West Frisian and North Frisian it belongs to Frisian branch of the Germanic languaes. The three Frisian languaes evolved from Old Frisian. Upon the living Frisian dialects, the one spoken in Heligoland (called Halunder) is the closest to Saterla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Frisian Language
North Frisian (''nordfriisk'') is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group. North Frisian is closely related to the Saterland Frisian language of Northwest Germany and West Frisian which is spoken in the Netherlands. All of these are also closely related to the English language forming the Anglo-Frisian group. The phonological system of the North Frisian dialects is strongly being influenced by Standard German and is slowly adapting to that of the German language. With a number of native speakers probably even less than 10,000 and decreasing use in mainland North Frisia, the North Frisian language is endangered. It is protected as a minority language and has become an official language in the Nordfriesland district and on Heligoland island. Classification The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interfrisian Council
The Interfrisian Council is a geopolitical organization that represents the common interests of the Frisians. The organization consists of three regional councils or "sections": North Frisia, East Frisia and West Frisia. Every three years, the presidency of the Interfrisian Council is handed over to another section. The council was established in 1956. History The chronicler wrote in the 17th century that the Frisians had a common language, and that they therefore were also one people. traveled from (Westerlauwens') Friesland to Saterland and Northern Friesland in the 19th century and recorded the dialects of Frisian on the way. In 1850 Heinrich Ehrentraut from Oldenburg produced a magazine about the Frisian language and history of the Frisian regions. In the 19th century, the Frisian Society in Leeuwarden appointed members of East and North Friesland. Also during this century contacts were particularly strong between West Frisians and North Frisians. Around 1900, the contacts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
, native_name_lang = de , region1 = , pop1 = 72,650,269 , region2 = , pop2 = 534,000 , region3 = , pop3 = 157,000 3,322,405 , region4 = , pop4 = 21,000 3,000,000 , region5 = , pop5 = 125,000 982,226 , region6 = , pop6 = 900,000 , region7 = , pop7 = 142,000 840,000 , region8 = , pop8 = 9,000 500,000 , region9 = , pop9 = 357,000 , region10 = , pop10 = 310,000 , region11 = , pop11 = 36,000 250,000 , region12 = , pop12 = 25,000 200,000 , region13 = , pop13 = 233,000 , region14 = , pop14 = 211,000 , region15 = , pop15 = 203,000 , region16 = , pop16 = 201,000 , region17 = , pop17 = 101,000 148,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frisian Languages
The Frisian (, ) languages are a closely related group of West Germanic languages, spoken by about 500,000 Frisian people, who live on the southern fringes of the North Sea in the Netherlands and Germany. The Frisian languages are the closest living language group to the Anglic languages; the two groups make up the Anglo-Frisian languages group and together with the Low German dialects these form the North Sea Germanic languages. However, modern English and Frisian are not mutually intelligible, nor are Frisian languages intelligible among themselves, owing to independent linguistic innovations and foreign influences. There are three different Frisian branches, which are usually called the Frisian languages, despite the fact that their so-called dialects are often not mutually intelligible even within these branches. These branches are: West Frisian, which is by far the most spoken of the three and is an official language in the Dutch province of Friesland, where it is spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived ''Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subject of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sønderjysk
South Jutlandic or South Jutish (South Jutish: ; da, Sønderjysk; german: Südjütisch or Plattdänisch) is a dialect of the Danish language. South Jutlandic is spoken in Southern Jutland (''Sønderjylland''; also called Schleswig or Slesvig) on both sides of the border between Denmark and Germany. Variants of the dialect include Western and Eastern South Jutlandic (including Alsisk). The former variant in Angeln (Danish: ''Angel'') and Schwansen (''Svansø'') was known as Angel Danish. The other dialects classified as belonging to the Jutlandic or Jutish (''Jysk'') group of dialects are West, East, and North Jutlandic. Usage Northern Slesvig Many older people will still speak a distinct South Jutlandic dialect, both in towns and rural areas. Younger people and children are more likely to use a dialect-tinted version of Standard Danish, but everything ranging from relatively pure dialect to Standard Danish can be found. Many are able to switch between both varieties. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friso-Saxon Dialects
Friso-Saxon ( nl, friso-saksisch) is a group of West Germanic dialects found around the North Sea coast of the Netherlands and Germany, in an area historically known as Frisia. They are dialects of Low German/Low Saxon which have experienced strong influence from a Frisian language. The term was established by the Dutch researcher Johan Winkler in his work about Dutch, Low German and Frisian dialects in the region. In the following decades the term was adopted by some of Winkler's successors.cf. Hoppenbrouwers, Cornelis Antonius Johannes / Hoppenbrouwers, Geer A. J. (2001): De indeling van de Nederlandse streektalen - dialecten van 156 steden en dorpen geklasseerd volgens de FFM. Assen, S. 50ff. Most of the Friso-Saxon dialects are spoken in areas which were historically Frisian-speaking, until Frisian was gradually replaced with Low Saxon beginning in the Late Middle Ages. However, Frisian has remained as a substratum since then in the regions concerned. The only exception to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English People
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language in England, English language, a West Germanic languages, West Germanic language, and share a common history and culture. The English identity is of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon origin, when they were known in Old English as the ('race or tribe of the Angles'). Their ethnonym is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples who migrated to Great Britain around the 5th century AD. The English largely descend from two main historical population groups the West Germanic tribes (the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians) who settled in southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Ancient Rome, Romans, and the Romano-British culture, partially Romanised Celtic Britons already living there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons. Nat Commun 7, 10326 (2016). https://doi.org/10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |