|
Fragment Processing
Fragment processing is a term in computer graphics referring to a collection of operations applied to fragments generated by the rasterization operation in the rendering pipeline. During the rendering of computer graphics, the rasterization step takes a primitive, described by its vertex coordinates with associated color and texture information, and converts it into a set of fragments. These fragments then undergo a series of processing steps, e.g. scissor test, alpha test, depth test, stencil test, blending, texture mapping and so on. These steps are collectively referred to as ''fragment processing''. See also * Computer representation of surfaces * Glossary of computer graphics * Graphical perception * Spatial visualization ability * Visualization (graphics) Visualization or visualisation (see spelling differences) is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or animations to communicate a message. Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, sprite graphics, rendering, ray tracing, geometry processing, computer animation, vector graphics, 3D modeling, shaders, GPU design, implicit surfaces, visualization, scientific c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture Mapping
Texture mapping is a method for mapping a texture on a computer-generated graphic. Texture here can be high frequency detail, surface texture, or color. History The original technique was pioneered by Edwin Catmull in 1974. Texture mapping originally referred to diffuse mapping, a method that simply mapped pixels from a texture to a 3D surface ("wrapping" the image around the object). In recent decades, the advent of multi-pass rendering, multitexturing, mipmaps, and more complex mappings such as height mapping, bump mapping, normal mapping, displacement mapping, reflection mapping, specular mapping, occlusion mapping, and many other variations on the technique (controlled by a materials system) have made it possible to simulate near-photorealism in real time by vastly reducing the number of polygons and lighting calculations needed to construct a realistic and functional 3D scene. Texture maps A is an image applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape or polygon. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Visualization Ability
Spatial visualization ability or visual-spatial ability is the ability to mentally manipulate 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional figures. It is typically measured with simple cognitive tests and is predictive of user performance with some kinds of user interfaces. Measurement The cognitive tests used to measure spatial visualization ability including mental rotation tasks like the Mental Rotations Test or mental cutting tasks like the Mental Cutting Test; and cognitive tests like the VZ-1 (Form Board), VZ-2 (Paper Folding), and VZ-3 (Surface Development) tests from the Kit of Factor-Reference cognitive tests produced by Educational Testing Service. Though the descriptions of spatial visualization and mental rotation sound similar, mental rotation is a particular task that can be accomplished using spatial visualization. The Minnesota Paper Form Board Test involves giving participants a shape and a set of smaller shapes which they are then instructed to determine which combina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
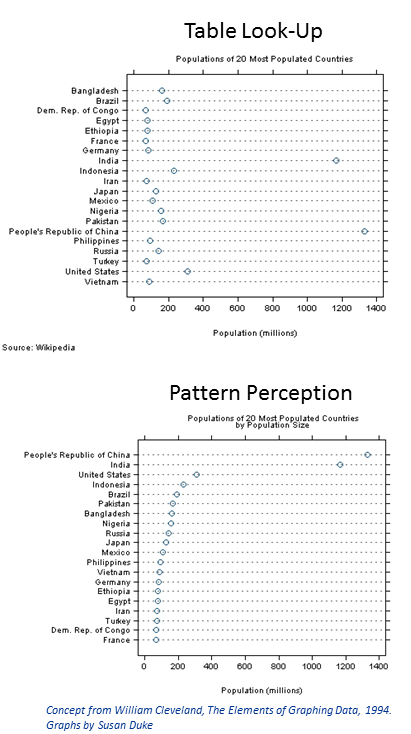
Graphical Perception
Graphical perception is the human capacity for visually interpreting information on graphs and charts. Both quantitative and qualitative information can be said to be encoded into the image, and the human capacity to interpret it is sometimes called decoding. The importance of human graphical perception, what we discern easily versus what our brains have more difficulty decoding, is fundamental to good statistical graphics design, where clarity, transparency, accuracy and precision in data display and interpretation are essential for understanding the translation of data in a graph to clarify and interpret the science. Graphical perception is achieved in dimensions or steps of discernment by: * detection : recognition of geometry which encodes physical values * assembly : grouping of detected symbol elements; discerning overall patterns in data * estimation : assessment of relative magnitudes of two physical values. Cleveland and McGill's experiments to elucidate the graphical e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Computer Graphics
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics. For more general computer hardware terms, see glossary of computer hardware terms. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I K L M N O P Q R S T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Representation Of Surfaces
In technical applications of 3D computer graphics ( CAx) such as computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing, surfaces are one way of representing objects. The other ways are wireframe (lines and curves) and solids. Point clouds are also sometimes used as temporary ways to represent an object, with the goal of using the points to create one or more of the three permanent representations. Open and closed surfaces If one considers a local parametrization of a surface: :\mathbf = \mathbf (u, v), then the curves obtained by varying ''u'' while keeping ''v'' fixed are coordinate lines, sometimes called the ''u'' ''flow lines''. The curves obtained by varying ''v'' while ''u'' is fixed are called the ''v'' flow lines. These are generalizations of the ''x'' and ''y'' Cartesian coordinate lines in the plane coordinate system and of the meridians and circles of latitude on a spherical coordinate system. Open surfaces are not closed in either direction. This means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services also include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group (known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier), a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2021 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,700 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison-Wesley
Addison-Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson PLC, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison-Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison-Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison-Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include ''The Art of Computer Programming'', ''The C++ Programming Language'', ''The Mythical Man-Month'', and ''Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison-Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison-Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first computer book was ''Progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (computer Graphics)
Texture mapping is a method for mapping a texture on a computer-generated graphic. Texture here can be high frequency detail, surface texture, or color. History The original technique was pioneered by Edwin Catmull in 1974. Texture mapping originally referred to diffuse mapping, a method that simply mapped pixels from a texture to a 3D surface ("wrapping" the image around the object). In recent decades, the advent of multi-pass rendering, multitexturing, mipmaps, and more complex mappings such as height mapping, bump mapping, normal mapping, displacement mapping, reflection mapping, specular mapping, occlusion mapping, and many other variations on the technique (controlled by a materials system) have made it possible to simulate near-photorealism in real time by vastly reducing the number of polygons and lighting calculations needed to construct a realistic and functional 3D scene. Texture maps A is an image applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape or polygon. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragment (computer Graphics)
In computer graphics, a fragment is the data necessary to generate a single pixel's worth of a drawing primitive in the frame buffer. This data may include, but is not limited to: * raster position * depth * interpolated attributes (color, texture coordinates, etc.) * stencil * alpha * window ID As a scene is drawn, drawing primitives (the basic elements of graphics output, such as points, lines, circles, text etc.) are rasterized into fragments which are textured and combined with the existing frame buffer. How a fragment is combined with the data already in the frame buffer depends on various settings. In a typical case, a fragment may be discarded if it is farther away than the pixel that is already at that location (according to the depth buffer). If it is nearer than the existing pixel, it may replace what is already there, or, if alpha blending is in use, the pixel's color may be replaced with a mixture of the fragment's color and the pixel's existing color, as in the cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates. Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance. Color science includes the perception of color by the eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The order of the coordinates is significant, and they are sometimes identified by their position in an ordered tuple and sometimes by a letter, as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the ''number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |