|
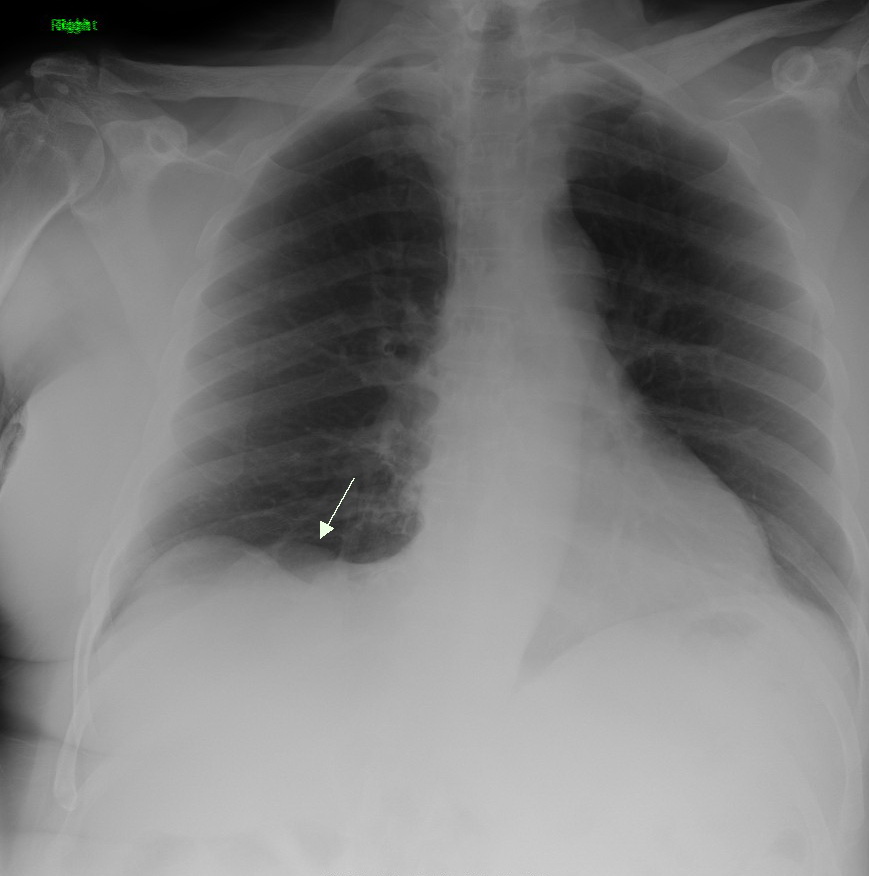
Foreign Body Aspiration
Foreign body aspiration occurs when a foreign body enters the airway which can cause difficulty breathing or choking. Objects may reach the respiratory tract and the digestive tract from the mouth and nose, but when an object enters the respiratory tract it is termed aspiration. The foreign body can then become lodged in the trachea or further down the respiratory tract such as in a bronchus. Regardless of the type of object, any aspiration can be a life-threatening situation and requires timely recognition and action to minimize risk of complications. While advances have been made in management of this condition leading to significantly improved clinical outcomes, there were still 2,700 deaths resulting from foreign body aspiration in 2018. Approximately one child dies every five days due to choking on food in the United States, highlighting the need for improvements in education and prevention. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of foreign body aspiration vary based on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respirology
Pulmonology (, , from Latin ''pulmō, -ōnis'' "lung" and the Greek suffix "study of"), pneumology (, built on Greek πνεύμων "lung") or pneumonology () is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty . Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30. It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas. Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to |
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol (drug), alcohol that results in significant Mental health, mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognized diagnostic entity. Predominant diagnostic classifications are alcohol use disorder (DSM-5) or alcohol dependence (ICD-11); these are defined in their respective sources. Excessive alcohol use can damage all organ systems, but it particularly affects the brain, heart, liver, pancreas and immune system. Alcoholism can result in mental illness, delirium tremens, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, Heart arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, an impaired immune response, liver cirrhosis and alcohol and cancer, increased cancer risk. Drinking during pregnancy can result in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Women are generally more sensitive than men to the harmful effects of alcohol, primarily due to their smaller body weight, lower capacity to metaboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epileptic Seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness ( tonic-clonic seizure), to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness (focal seizure), to a subtle momentary loss of awareness (absence seizure). Most of the time these episodes last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur. Seizures may be provoked and unprovoked. Provoked seizures are due to a temporary event such as low blood sugar, alcohol withdrawal, abusing alcohol together with prescription medication, low blood sodium, fever, brain infection, or concussion. Unprovoked seizures occur without a known or fixable cause such that ongoing seizures are likely. Unprovoked seizures may be exacerbated by stress or slee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanide Poisoning
Cyanide poisoning is poisoning that results from exposure to any of a number of forms of cyanide. Early symptoms include headache, dizziness, fast heart rate, shortness of breath, and vomiting. This phase may then be followed by seizures, slow heart rate, low blood pressure, loss of consciousness, and cardiac arrest. Onset of symptoms usually occurs within a few minutes. Some survivors have long-term neurological problems. Toxic cyanide-containing compounds include hydrogen cyanide gas and a number of cyanide salts. Poisoning is relatively common following breathing in smoke from a house fire. Other potential routes of exposure include workplaces involved in metal polishing, certain insecticides, the medication sodium nitroprusside, and certain seeds such as those of apples and apricots. Liquid forms of cyanide can be absorbed through the skin. Cyanide ions interfere with cellular respiration, resulting in the body's tissues being unable to use oxygen. Diagnosis is often diffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.Definitions Retrieved on 20 September 2014."Stairway to Recovery: Glossary of Terms" . Retrieved on 19 March 2021 Typically it is used for cases when a risk to health will potentially result. An overdose may result in a toxic state or . Classification [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisoning
A poison can be any substance that is harmful to the body. It can be swallowed, inhaled, injected or absorbed through the skin. Poisoning is the harmful effect that occurs when too much of that substance has been taken. Poisoning is not to be confused with envenomation. Acute poisoning is exposure to a poison on one occasion or during a short period of time. Symptoms develop in close relation to the degree of exposure. Absorption of a poison is necessary for systemic poisoning (that is, in the blood throughout the body). In contrast, substances that destroy tissue but do not absorb, such as lye, are classified as corrosives rather than poisons. Furthermore, many common household medications are not labeled with skull and crossbones, although they can cause severe illness or even death. In the medical sense, toxicity and poisoning can be caused by less dangerous substances than those legally classified as a poison. Toxicology is the study and practice of the symptoms, mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common conditions of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and they have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. Emphysema is defined as enlarged airspaces ( alveoli) whose walls have broken down resulting in permanent damage to the lung tissue. Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Both of these conditions can exist without airflow limitation when they are not classed as COPD. Emphysema is just one of the structural abnormalities that can limit airflow and can exist without ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diagnosis is usually based on the pattern of symptoms, response to therapy over time, and spirometry lung function testing. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegeneration, neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in short-term memory, remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include primary progressive aphasia, problems with language, Orientation (mental), disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and challenging behaviour, behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years. The cause of Alzheimer's disease is poorly understood. There are many environmental and genetic risk factors associated with its development. The strongest genetic risk factor is from an alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Trauma
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Depending on the severity of injury, quickness of management, and transportation to an appropriate medical facility (called a trauma center) may be necessary to prevent loss of life or limb. The initial assessment is critical, and involves a physical evaluation and also may include the use of imaging tools to determine the types of injuries accurately and to formulate a course of treatment. In 2002, unintentional and intentional injuries were the fifth and seventh leading causes of deaths worldwide, accounting for 6.23% and 2.84% of all deaths. For research purposes the definition often is based on an injury severity score (ISS) of greater than 15. Classification Injuries generally are classified by either severity, the location of damage, or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trauma (medicine)
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries. Treatment of a major injury is typically carried out by a health professional and varies greatly depending on the nature of the injury. Traffic collisions are the most common cause of accidental injury and injury-related death among humans. Injuries are distinct from chronic conditions, psychological trauma, infections, or medical procedures, though injury can be a contributing factor to any of these. Several major health organizations have established systems for the classification and description of human injuries. Occurrence Injuries may be intentional or unintentional. Intentional injuries may be acts of vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |