|
Five-planet Nice Model
The five-planet Nice model is a numerical model of the early Solar System that is a revised variation of the Nice model. It begins with five giant planets, the four that exist today plus an additional ice giant between Saturn and Uranus in a chain of mean-motion resonances. After the resonance chain is broken, the five giant planets undergo a period of planetesimal-driven migration, followed by a period of orbital instability with gravitational encounters between planets similar to that in the original Nice model. During the instability the additional giant planet is scattered inward onto a Jupiter-crossing orbit and is ejected from the Solar System following an encounter with Jupiter. The model was first formally proposed in 2011 after simulations indicated that it was more likely to reproduce the current Solar System than a four-planet Nice model. A five-planet Nice model The following is a version of the five-planet Nice model that results in an early instability and repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation And Evolution Of The Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a protoplanetary disk out of which the planets, moons, asteroids, and other small Solar System bodies formed. This model, known as the nebular hypothesis, was first developed in the 18th century by Emanuel Swedenborg, Immanuel Kant, and Pierre-Simon Laplace. Its subsequent development has interwoven a variety of scientific disciplines including astronomy, chemistry, geology, physics, and planetary science. Since the dawn of the space age in the 1950s and the discovery of extrasolar planets in the 1990s, the model has been both challenged and refined to account for new observations. The Solar System has evolved considerably since its initial formation. Many moons have formed from circling discs of gas and dust around their parent planets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetesimal
Planetesimals are solid objects thought to exist in protoplanetary disks and debris disks. Per the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis, they are believed to form out of cosmic dust grains. Believed to have formed in the Solar System about 4.6 billion years ago, they aid study of its formation. Formation A widely accepted theory of planet formation, the so-called planetesimal hypotheses, the Chamberlin–Moulton planetesimal hypothesis and that of Viktor Safronov, states that planets form from cosmic dust grains that collide and stick to form ever-larger bodies. Once a body reaches around a kilometer in size, its constituent grains can attract each other directly through mutual gravity, enormously aiding further growth into moon-sized protoplanets. Smaller bodies must instead rely on Brownian motion or turbulence to cause the collisions leading to sticking. The mechanics of collisions and mechanisms of sticking are intricate. Alternatively, planetesimals may form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogue Planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a host planetary system. Such objects have been ejected from the planetary system in which they formed or have never been gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf. The Milky Way alone may have billions to trillions of rogue planets, a range the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will likely be able to narrow down. Some planetary-mass objects may have formed in a similar way to stars, and the International Astronomical Union has proposed that such objects be called sub-brown dwarfs. A possible example is Cha 110913−773444, which may have been ejected and become a rogue planet, or formed on its own to become a sub-brown dwarf. Astronomers have used the Herschel Space Observatory and the Very Large Telescope to observe a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid Belt
The asteroid belt is a torus-shaped region in the Solar System, located roughly between the orbits of the planets Jupiter and Mars. It contains a great many solid, irregularly shaped bodies, of many sizes, but much smaller than planets, called asteroids or minor planets. This asteroid belt is also called the main asteroid belt or main belt to distinguish it from other asteroid populations in the Solar System such as near-Earth asteroids and trojan asteroids. The asteroid belt is the smallest and innermost known circumstellar disc in the Solar System. About 60% of its mass is contained in the four largest asteroids: Ceres, Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea. The total mass of the asteroid belt is calculated to be 3% that of the Moon. Ceres, the only object in the asteroid belt large enough to be a dwarf planet, is about 950 km in diameter, whereas Vesta, Pallas, and Hygiea have mean diameters less than 600 km. The remaining bodies range down to the size of a dust particle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. For celestial objects in general, the sidereal period ( sidereal year) is referred to by the orbital period, determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, e.g. Earth around the Sun, relative to the fixed stars projected in the sky. Orbital periods can be defined in several ways. The tropical period is more particularly about the position of the parent star. It is the basis for the solar year, and respectively the calendar year. The synodic period incorporates not only the orbital relation to the parent star, but also to other celestial objects, making it not a mere different approach to the orbit of an object around its parent, but a period of orbital relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
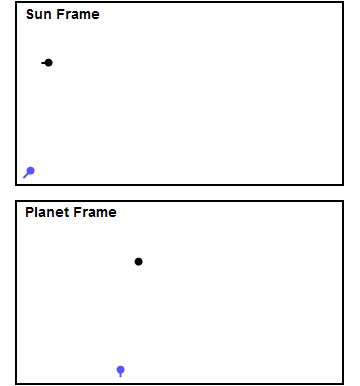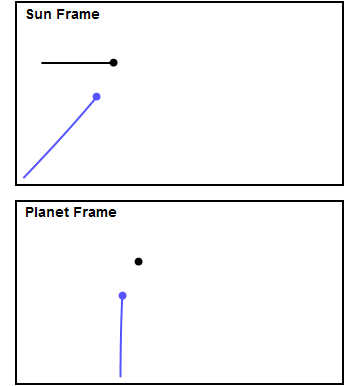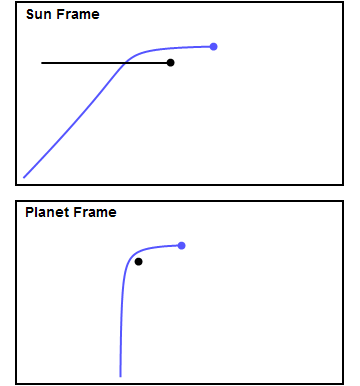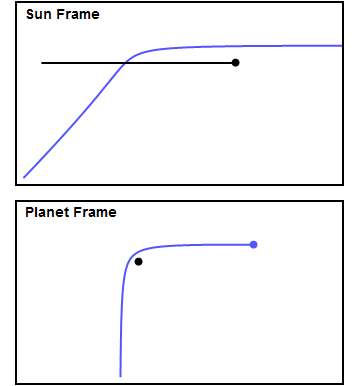
Gravity Assist
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and velocity by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon and it was used by interplanetary probes from Mariner 10 onward, including the two Voyager probes' notable flybys of Jupiter and Saturn. Explanation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system remains constant. Angular momentum has both a direction and a magnitude, and both are conserved. Bicycles and motorcycles, frisbees, rifled bullets, and gyroscopes owe their useful properties to conservation of angular momentum. Conservation of angular momentum is also why hurricanes form spirals and neutron stars have high rotational rates. In general, conservation limits the possible motion of a system, but it does not uniquely determine it. The three-dimensional angular momentum for a point particle is classically represented as a pseudovector , the cross product of the particle's position vector (relative to some origin) and its momentum vector; the latter is in Newtonian mechanics. Unlike linear momentum, angular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
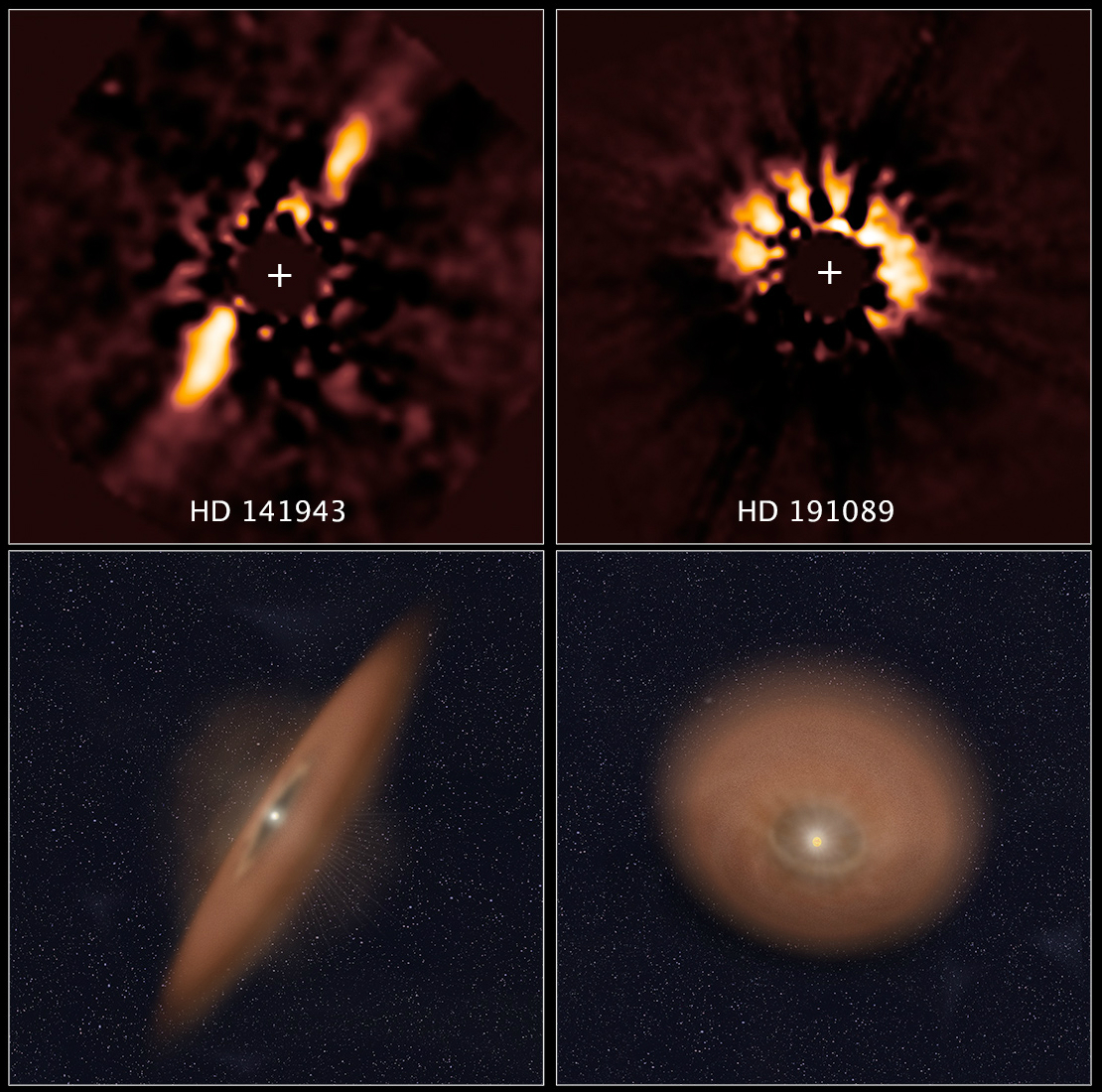
Circumstellar Disc
A circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the reservoirs of material out of which planets may form. Around mature stars, they indicate that planetesimal formation has taken place, and around white dwarfs, they indicate that planetary material survived the whole of stellar evolution. Such a disc can manifest itself in various ways. Young star According to the widely accepted model of star formation, sometimes referred to as the nebular hypothesis, a young star (protostar) is formed by the gravitational collapse of a pocket of matter within a giant molecular cloud. The infalling material possesses some amount of angular momentum, which results in the formation of a gaseous protoplanetary disc around the young, rotating star. The former is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an average distance of . It is named after the Neptune (mythology), Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poynting–Robertson Effect
The Poynting–Robertson effect, also known as Poynting–Robertson drag, named after John Henry Poynting and Howard P. Robertson, is a process by which solar radiation causes a dust grain orbiting a star to lose angular momentum relative to its orbit around the star. This is related to radiation pressure tangential to the grain's motion. This causes dust that is small enough to be affected by this drag, but too large to be blown away from the star by radiation pressure, to spiral slowly into the star. In the case of the Solar System, this can be thought of as affecting dust grains from to in diameter. Larger dust is likely to collide with another object long before such drag can have an effect. Poynting initially gave a description of the effect in 1903 based on the luminiferous aether theory, which was superseded by the theories of relativity in 1905–1915. In 1937 Robertson described the effect in terms of general relativity. History Robertson considered dust motion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and Impact structure, structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped History of the Earth, Earth's history, and have been implicated in the giant impact theory, formation of the Earth� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |