|
Poynting–Robertson Effect
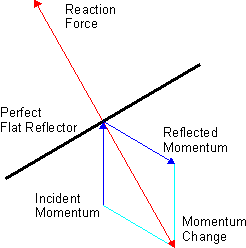
The Poynting–Robertson effect, also known as Poynting–Robertson drag, named after John Henry Poynting and Howard P. Robertson, is a process by which solar radiation causes a dust grain orbiting a star to lose angular momentum relative to its orbit around the star. This is related to radiation pressure tangential to the grain's motion. This causes dust that is small enough to be affected by this drag, but too large to be blown away from the star by radiation pressure, to spiral slowly into the star. In the case of the Solar System, this can be thought of as affecting dust grains from to in diameter. Larger dust is likely to collide with another object long before such drag can have an effect. Poynting initially gave a description of the effect in 1903 based on the luminiferous aether theory, which was superseded by the theories of relativity in 1905–1915. In 1937 Robertson described the effect in terms of general relativity. History Robertson considered dust motion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Henry Poynting
John Henry Poynting FRS (9 September 185230 March 1914) was an English physicist. He was the first professor of physics at Mason Science College from 1880 to 1900, and then the successor institution, the University of Birmingham until his death. Biography Poynting was the youngest son of Thomas Elford Poynting, a Unitarian minister. He was born at the parsonage of the Monton Unitarian Chapel in Eccles, Lancashire (his father serving as minister there from 1846 to 1878.) In his boyhood he was educated at the nearby school operated by his father. From 1867 to 1872 he attended Owens College, now the University of Manchester, where his physics teachers included Osborne Reynolds and Balfour Stewart. From 1872 to 1876 he was a student at Cambridge University, where he attained high honours in mathematics after taking grinds with Edward Routh. In the late 1870s he worked in the Cavendish Laboratory at Cambridge under James Clerk Maxwell. In 1880, he became the first professor of phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effects
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Perturbations
Orbital may refer to: Sciences Chemistry and physics * Atomic orbital * Molecular orbital * Hybrid orbital Astronomy and space flight * Orbit ** Earth orbit Medicine and physiology * Orbit (anatomy), also known as the ''orbital bone'' * Orbitofrontal cortex, a part of the brain used for decision making Business * Orbital Corporation, an Australian engine technology company * Orbital Sciences Corporation, a U.S. satellite launch and defense systems corporation * Orbital ATK, American aerospace manufacturer formed from the merger of Orbital Sciences Corporation and parts of Alliant Techsystems Transportation * Ring road (or ''orbital road'' in some regions) * Orbital (metro), a rapid transit line usually encircling a city centre * Orbital engine Other uses * Orbital (The Culture), artificial worlds from Iain M. Banks's series of science fiction novels, the Culture * Orbital (band), an English electronic dance music duo ** ''Orbital'' (1991 album) ** ''Orbital'' (1993 album) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions Of The Royal Society A
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'' is a fortnightly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Royal Society. It publishes original research and review content in a wide range of physical scientific disciplines. Articles can be accessed online a few months prior to the printed journal. All articles become freely accessible two years after their publication date. The current editor-in-chief is John Dainton. Overview ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A'' publishes themed journal issues on topics of current scientific importance and general interest within the physical, mathematical and engineering sciences, edited by leading authorities and comprising original research, reviews and opinions from prominent researchers. Past issue titles include "Supercritical fluids - green solvents for green chemistry?", "Tsunamis: Bridging science, engineering and society", "Spatial transformations: from f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
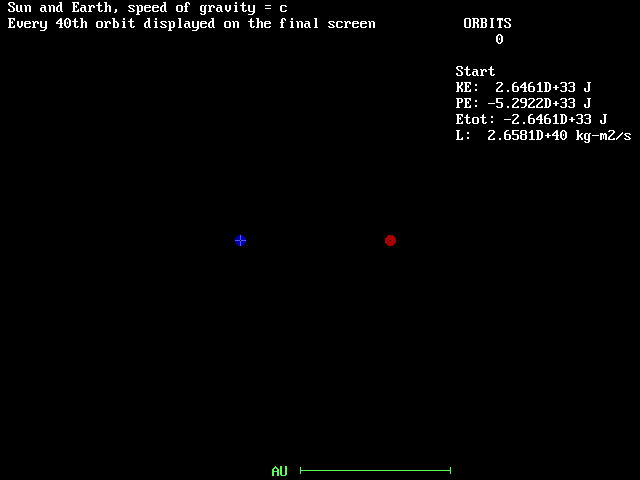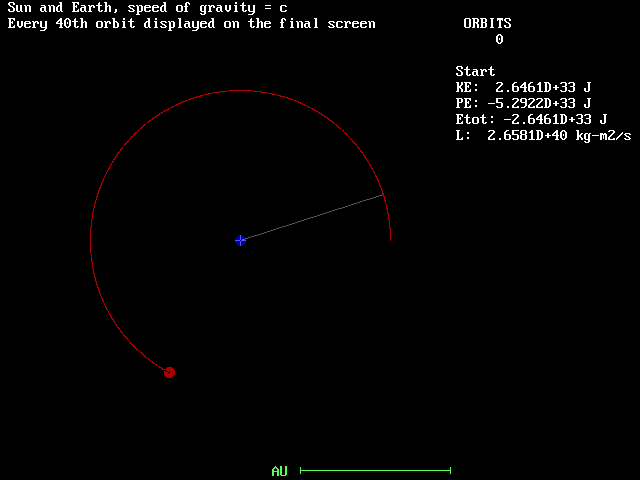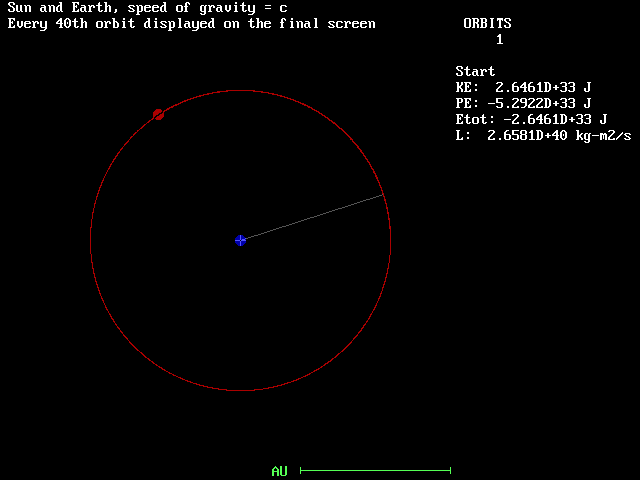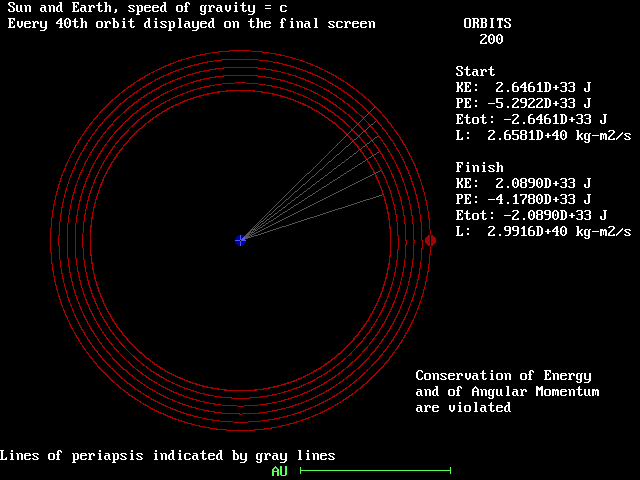
Speed Of Gravity
In classical theories of gravitation, the changes in a gravitational field propagate. A change in the distribution of energy and momentum of matter results in subsequent alteration, at a distance, of the gravitational field which it produces. In the relativistic sense, the "speed of gravity" refers to the speed of a gravitational wave, which, as predicted by general relativity and confirmed by observation of the GW170817 neutron star merger, is the same speed as the speed of light (''c''). Introduction The speed of gravitational waves in the general theory of relativity is equal to the ''speed of light'' in a vacuum, . Within the theory of special relativity, the constant is not only about light; instead it is the highest possible speed for any interaction in nature. Formally, is a conversion factor for changing the unit of time to the unit of space. This makes it the only speed which does not depend either on the motion of an observer or a source of light and / or gravity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarkovsky Effect
The Yarkovsky effect is a force acting on a rotating body in space caused by the anisotropic emission of thermal photons, which carry momentum. It is usually considered in relation to meteoroids or small asteroids (about 10 cm to 10 km in diameter), as its influence is most significant for these bodies. History of discovery The effect was discovered by the Polish-Russian civil engineer Ivan Osipovich Yarkovsky (1844–1902), who worked in Russia on scientific problems in his spare time. Writing in a pamphlet around the year 1900, Yarkovsky noted that the daily heating of a rotating object in space would cause it to experience a force that, while tiny, could lead to large long-term effects in the orbits of small bodies, especially meteoroids and small asteroids. Yarkovsky's insight would have been forgotten had it not been for the Estonian astronomer Ernst J. Öpik (1893–1985), who read Yarkovsky's pamphlet sometime around 1909. Decades later, Öpik, recalling t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differential Doppler Effect
The Differential Doppler effect occurs when light is emitted from a rotating source. In circumstellar environments it describes the difference in photons arriving at orbiting dust particles. Photons that originate from the limb that is rotating away from the particle are red-shifted, while photons emitted from the limb rotating toward the particle are blue-shifted. See also * Yarkovsky effect * Poynting–Robertson effect * Radiation pressure * Doppler effect The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who ... References Doppler effects Astrophysics {{Astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. As also confirmed by various measurement standards, which include the ''Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor and the journal ''h''-index proposed by Google Scholar, many physicists and other scientists consider ''Physical Review Letters'' to be one of the most prestigious journals in the field of physics. ''According to Google Scholar, PRL is the journal with the 9th journal h-index among all scientific journals'' ''PRL'' is published as a print journal, and is in electronic format, online and CD-ROM. Its focus is rapid dissemination of significant, or notable, results of fundamental research on all topics related to all fields of physics. This is accomplished by rapid publication of short reports, called "Letters". Papers are published and available electronically one article at a time. When published in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbits the Sun, from a maximum (aphelion) to a minimum (perihelion) and back again once each year. The astronomical unit was originally conceived as the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion; however, since 2012 it has been defined as exactly (see below for several conversions). The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |