|
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
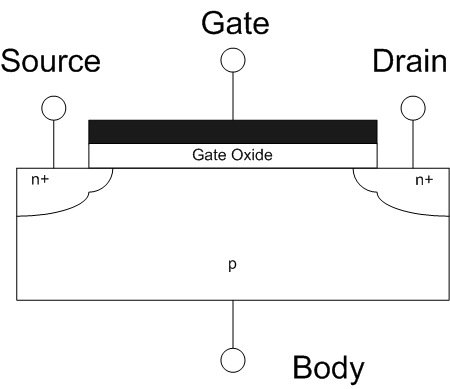
FET Cross Section
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Houser Brattain
Walter Houser Brattain (; February 10, 1902 – October 13, 1987) was an American physicist at Bell Labs who, along with fellow scientists John Bardeen and William Shockley, invented the point-contact transistor in December 1947. They shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their invention. Brattain devoted much of his life to research on surface states. Biography Walter Brattain was born in Amoy (now Xiamen), Fujian, Qing China, to American parents Ross R. Brattain and Ottilie Houser Brattain. Ross R. Brattain was a teacher at the Ting-Wen Institute, a private school for Chinese boys; Ottilie Houser Brattain was a gifted mathematician. Both were graduates of Whitman College. Ottilie and baby Walter returned to the United States in 1903, and Ross followed shortly afterward. The family lived for several years in Spokane, Washington, then settled on a cattle ranch near Tonasket, Washington in 1911. Brattain attended high school in Washington, spending one year at Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Induction Transistor
The static induction transistor (SIT) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET) capable of high-speed and high-power operation, with low distortion and low noise. It is a vertical structure device with short multichannel. The device was originally known as a VFET, with V being short for vertical. Being a vertical device, the SIT structure offers advantages in obtaining higher breakdown voltages than a conventional FET. For the SIT, the breakdown voltage is not limited by the surface breakdown between gate and drain, allowing it to operate at a very high current and voltage. The SIT has a current-voltage characteristic similar to a vacuum tube triode and it was therefore used in high-end audio products, including power amplifiers from Sony in the second half of the 1970s and Yamaha from 1973-1980. The Sony n-channel SIT had the model number 2SK82 with its p-channel complement named 2SJ28. Characteristics An SIT has: *short channel length *low gate series resistance *low gate-s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Welker
Heinrich Johann Welker (9 September 1912 in Ingolstadt – 25 December 1981 in Erlangen) was a German theoretical and applied physicist who invented the " transistron", a transistor made at Westinghouse independently of the first successful transistor made at Bell Laboratories. He did fundamental work in III-V compound semiconductors, and paved the way for microwave semiconductor elements and laser diodes. Biography and important work Starting in 1931, Welker studied at the University of Munich under Arnold Sommerfeld, and was granted a Ph.D. in 1936. The book '' Electrodynamics - Lectures on Theoretical Physics Volume III'' by Sommerfeld was based on lecture notes prepared by Welker during the winter semester of 1933/1934. Welker was granted his Habilitation under Sommerfeld in 1939.Mehra, Volume 6, Part 2, 2001, p. 868. During the war years, 1940 to 1945, Welker worked at Luftfunkforschungs Institut in Oberpfaffenhofen, but still maintained association (1942 to 1944) with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junction Field-effect Transistor
The junction-gate field-effect transistor (JFET) is one of the simplest types of field-effect transistor. JFETs are three-terminal semiconductor devices that can be used as electronically controlled switches or resistors, or to build amplifiers. Unlike bipolar junction transistors, JFETs are exclusively voltage-controlled in that they do not need a biasing current. Electric charge flows through a semiconducting channel between ''source'' and ''drain'' terminals. By applying a reverse bias voltage to a ''gate'' terminal, the channel is '' pinched'', so that the electric current is impeded or switched off completely. A JFET is usually conducting when there is zero voltage between its gate and source terminals. If a potential difference of the proper polarity is applied between its gate and source terminals, the JFET will be more resistive to current flow, which means less current would flow in the channel between the source and drain terminals. JFETs are sometimes referre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wiley & Sons
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company founded in 1807 that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East Orange, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also publishes Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar transistor allows a small current injected at one of its terminals to control a much larger current flowing between the terminals, making the device capable of amplification or switching. BJTs use two p–n junctions between two semiconductor types, n-type and p-type, which are regions in a single crystal of material. The junctions can be made in several different ways, such as changing the doping of the semiconductor material as it is grown, by depositing metal pellets to form alloy junctions, or by such methods as diffusion of n-type and p-type doping substances into the crystal. The superior predictability and performance of junction transistors quickly displaced the original point-contact transistor. Diffused transistors, alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-contact Transistor
The point-contact transistor was the first type of transistor to be successfully demonstrated. It was developed by research scientists John Bardeen and Walter Brattain at Bell Laboratories in December 1947. They worked in a group led by physicist William Shockley. The group had been working together on experiments and theories of electric field effects in solid state materials, with the aim of replacing vacuum tubes with a smaller device that consumed less power. The critical experiment, carried out on December 16, 1947, consisted of a block of germanium, a semiconductor, with two very closely spaced gold contacts held against it by a spring. Brattain attached a small strip of gold foil over the point of a plastic triangle — a configuration which is essentially a point-contact diode. He then carefully sliced through the gold at the tip of the triangle. This produced two electrically isolated gold contacts very close to each other. The piece of germanium used had a sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dangling Bond
In chemistry, a dangling bond is an unsatisfied valence on an immobilized atom. An atom with a dangling bond is also referred to as an immobilized free radical or an immobilized radical, a reference to its structural and chemical similarity to a free radical. When speaking of a dangling bond, one is generally referring to the state described above, containing one electron and thus leading to a neutrally charged atom. There are also dangling bond defects containing two or no electrons. These are negatively and positively charged respectively. Dangling bonds with two electrons have an energy close to the valence band of the material and those with none have an energy that is closer to the conduction band. Properties In order to gain enough electrons to fill their valence shells (see also octet rule), many atoms will form covalent bonds with other atoms. In the simplest case, that of a single bond, two atoms each contribute one unpaired electron, and the resulting pair of elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


