|
Fetuin
Fetuins are blood proteins that are made in the liver and secreted into the bloodstream. They belong to a large group of binding proteins mediating the transport and availability of a wide variety of cargo substances in the bloodstream. Fetuin-A is a major carrier protein of free fatty acids in the circulation. The best known representative of carrier proteins is serum albumin, the most abundant protein in the blood plasma of adult animals. Fetuin is more abundant in fetal blood, hence the name "fetuin" (from Latin, ''fetus''). Fetal bovine serum contains more fetuin than albumin, while adult serum contains more albumin than fetuin. Family members Human fetuin is synonymous with α2-HS-glycoprotein (genetic symbol AHSG), α2-HS, A2HS, AHS, HSGA, and fetuin-A. Fetuin-A exists as a single-copy gene in the human and mouse genomes. A closely related gene, fetuin-B, also exists in the human, rat, and mouse genomes. Like fetuin-A, fetuin-B is made predominantly by the liver and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein
alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein (AHSG, Alpha-2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein) also known as fetuin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AHSG'' gene. Fetuin-A belongs to the fetuin class of plasma binding proteins and is more abundant in fetal than adult blood. Function Alpha2-HS glycoprotein, a glycoprotein present in the serum, is synthesized by hepatocytes and adipocytes. The AHSG molecule consists of two polypeptide chains, which are both cleaved from a proprotein encoded from a single mRNA. It is involved in several functions, such as endocytosis, brain development and the formation of bone tissue. The protein is commonly present in the cortical plate of the immature cerebral cortex and bone marrow hemopoietic matrix, and it has therefore been postulated that it participates in the development of the tissues. However, its exact significance is still obscure. The choroid plexus is an established extrahepatic expression site. The mature circulating AHSG molecule consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α2-HS-glycoprotein
alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein (AHSG, Alpha-2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein) also known as fetuin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AHSG'' gene. Fetuin-A belongs to the fetuin class of plasma binding proteins and is more abundant in fetal than adult blood. Function Alpha2-HS glycoprotein, a glycoprotein present in the serum, is synthesized by hepatocytes and adipocytes. The AHSG molecule consists of two polypeptide chains, which are both cleaved from a proprotein encoded from a single mRNA. It is involved in several functions, such as endocytosis, brain development and the formation of bone tissue. The protein is commonly present in the cortical plate of the immature cerebral cortex and bone marrow hemopoietic matrix, and it has therefore been postulated that it participates in the development of the tissues. However, its exact significance is still obscure. The choroid plexus is an established extrahepatic expression site. The mature circulating AHSG molecule consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Α2-HS-glycoprotein
alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein (AHSG, Alpha-2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein) also known as fetuin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AHSG'' gene. Fetuin-A belongs to the fetuin class of plasma binding proteins and is more abundant in fetal than adult blood. Function Alpha2-HS glycoprotein, a glycoprotein present in the serum, is synthesized by hepatocytes and adipocytes. The AHSG molecule consists of two polypeptide chains, which are both cleaved from a proprotein encoded from a single mRNA. It is involved in several functions, such as endocytosis, brain development and the formation of bone tissue. The protein is commonly present in the cortical plate of the immature cerebral cortex and bone marrow hemopoietic matrix, and it has therefore been postulated that it participates in the development of the tissues. However, its exact significance is still obscure. The choroid plexus is an established extrahepatic expression site. The mature circulating AHSG molecule consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetuin-B
Fetuin-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FETUB'' gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fetuin family, part of the cystatin superfamily of cysteine protease inhibitors. Fetuins have been implicated in several diverse functions, including osteogenesis and bone resorption, regulation of the insulin and hepatocyte growth factor receptors, and response to systemic inflammation. This protein may be secreted by cells. See also *Fetuin-A alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein (AHSG, Alpha-2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein) also known as fetuin-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AHSG'' gene. Fetuin-A belongs to the fetuin class of plasma binding proteins and is more abundant in feta ... (alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein) References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystatin
The cystatins are a family of cysteine protease inhibitors which share a sequence homology and a common tertiary structure of an alpha helix lying on top of an anti-parallel beta sheet. The family is subdivided as described below. Cystatins show similarity to fetuins, kininogens, histidine-rich glycoproteins and cystatin-related proteins. Cystatins mainly inhibit peptidase enzymes (another term for ''proteases'') belonging to peptidase families C1 (papain family) and C13 ( legumain family). They are known to mis-fold to form amyloid deposits and are implicated in several diseases. Types The cystatin family includes: * The Type 1 cystatins, which are intracellular and are present in the cytosol of many cell types, but can also appear in body fluids at significant concentrations. They are single-chain polypeptides of about 100 residues, which have neither disulfide bonds nor carbohydrate side-chains. Type 1 cystatins are also known as Stefins (after the Stefan Institute where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
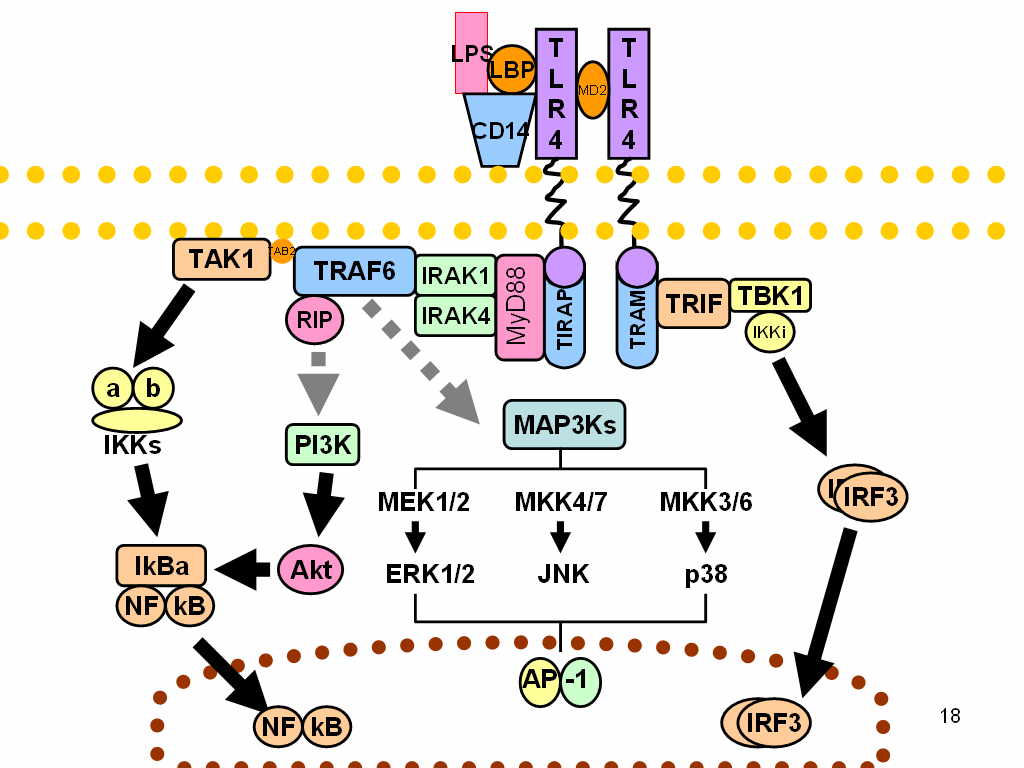
TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an intracellular signaling pathway NF-κB and inflammatory cytokine production which is responsible for activating the innate immune system. TLR4 expressing cells are myeloid (erythrocytes, granulocytes, macrophages) rather than lymphoid (T-cells, B-cells, NK cells). Most myeloid cells also express high levels of CD14, which facilitates activation of TLR4 by LPS. It is most well known for recognizing lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a component present in many Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. ''Neisseria'' spp.) and selected Gram-positive bacteria. Its ligands also include several viral proteins, polysaccharide, and a variety of endogenous proteins such as low-density lipoprotein, beta-defensins, and heat shock protein. Palmitic acid and lauric acid a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left and on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or are organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral, or may be an aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spacially segregated into distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kininogen
Kininogens are precursor proteins for kinins, biologically active polypeptides involved in blood coagulation, vasodilation, smooth muscle contraction, inflammatory regulation, and the regulation of the cardiovascular and renal systems. Types of kininogen There are two main types of kininogen (KNG), high-molecular-weight-kininogen and low-molecular-weight-kininogen, with a third type – T-kininogen – only found in rats but not humans. High molecular weight kininogen High-molecular-weight-kininogen (HK) is a non-enzymatic cofactor involved in the kinin-kallikrein system, which plays a role in blood coagulation, blood pressure regulation, and inflammation. It is synthesized in endothelial cells and is produced mostly by the liver. It is also a precursor protein for bradykinin. Low molecular weight kininogen Low-molecular-weight-kininogen (LK) is mainly a precursor protein for kallidin. LK, however, is not actively involved in blood coagulation, but its byproducts c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |